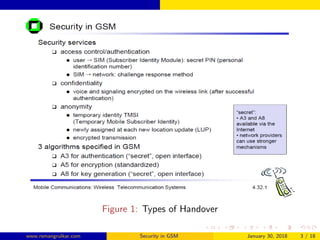
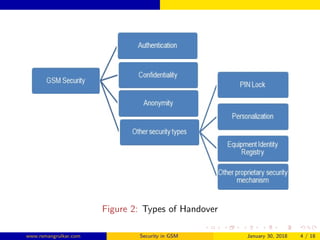
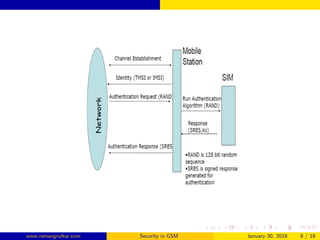
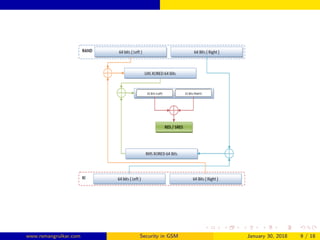
GSM security aims to authenticate SIM cards connecting to the network and encrypt wireless communications between mobile phones and the core network. The authentication center authenticates each SIM using authentication triplets to generate an encryption key for encrypting voice and SMS data. While the A5 algorithm encrypts communications, the A3 and A8 algorithms perform authentication and generate session keys, with COMP128 implementing these functions through table lookups and compression. Currently, only the COMP128v1 SIM cards can be cloned, as that version has been cracked, and it accounts for 70% of SIM cards in use.