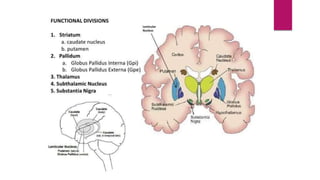
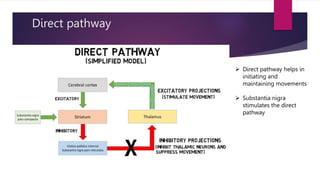
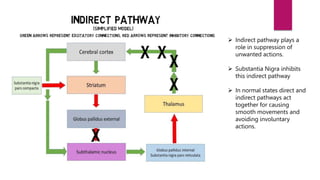
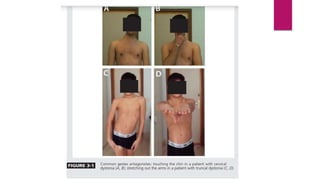
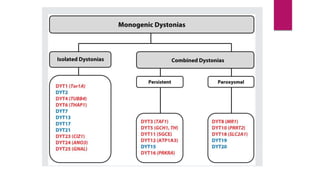
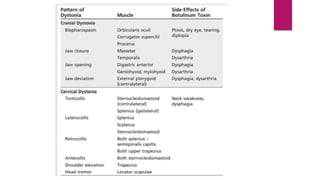
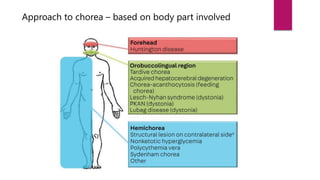
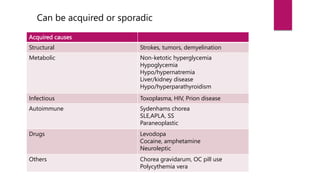
This document discusses various movement disorders including chorea, athetosis, and dystonia. It describes the basal ganglia pathways and how they relate to movement. It defines different types of dystonia such as focal, segmental, and generalized dystonia. It also describes specific forms of dystonia like blepharospasm, cervical dystonia, and oromandibular dystonia. Treatment options for dystonia and chorea are discussed including physical therapy, medications, botulinum toxin injections, and deep brain stimulation. The causes of chorea are outlined including genetic disorders like Huntington's disease.