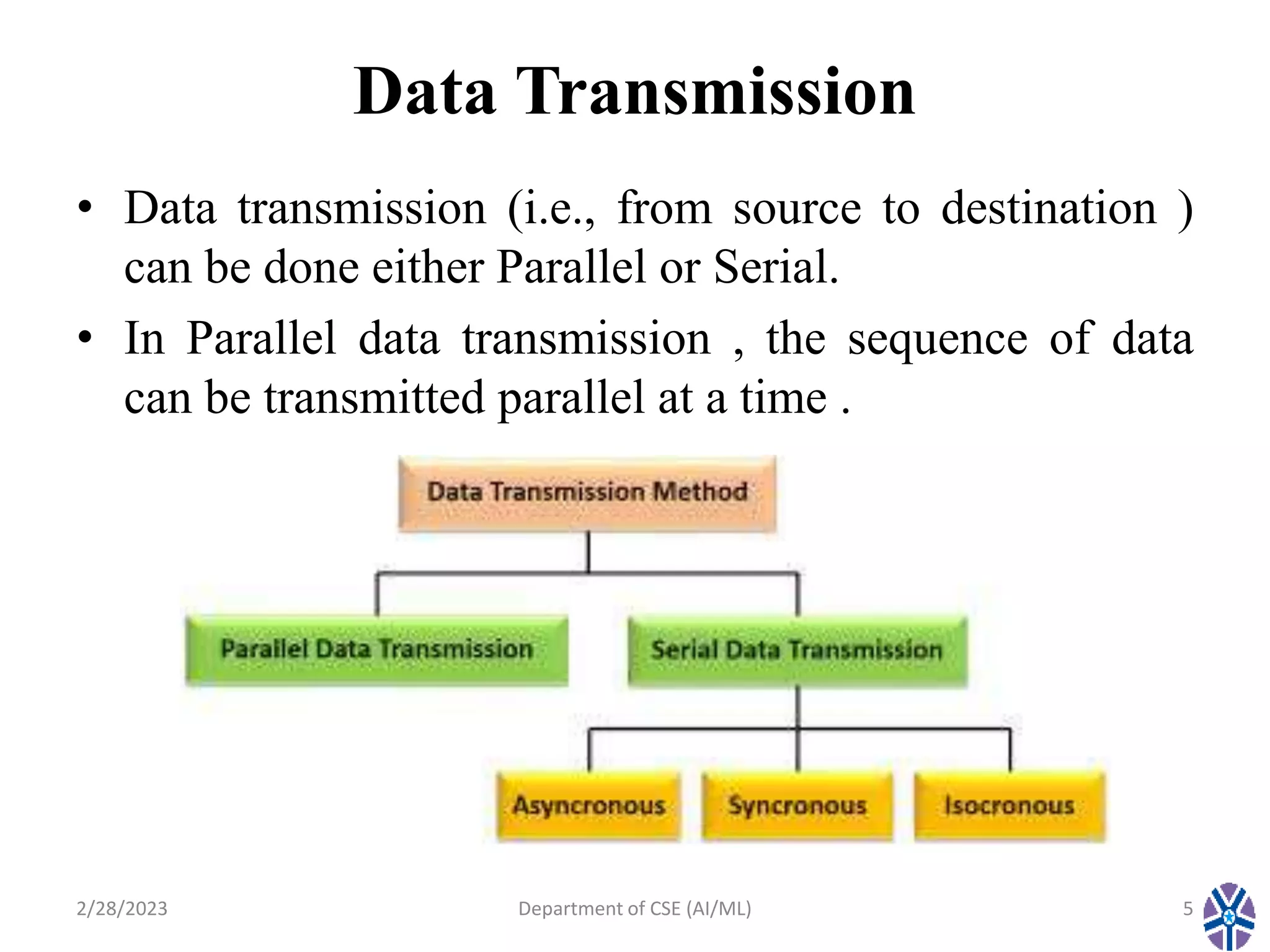
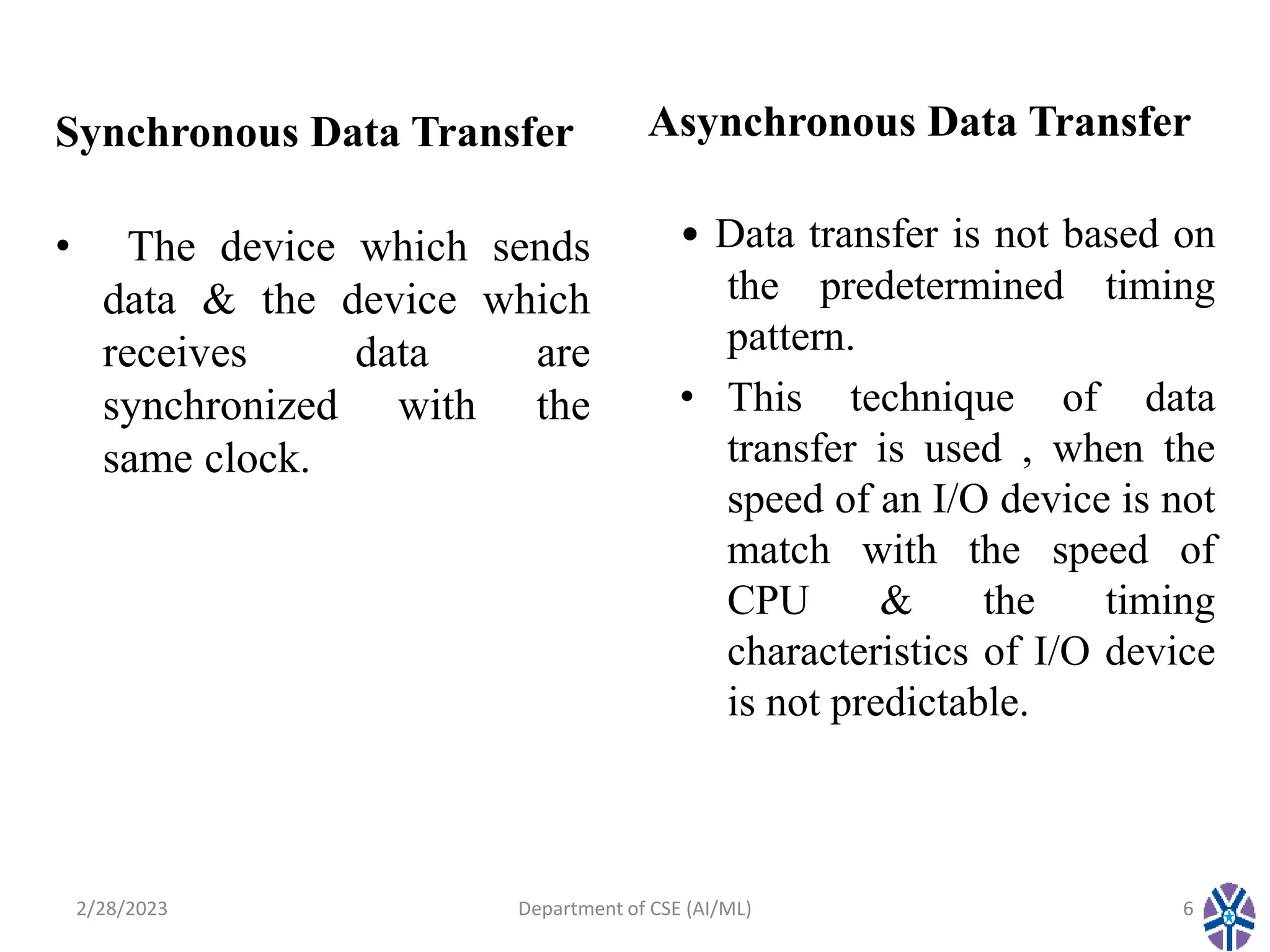
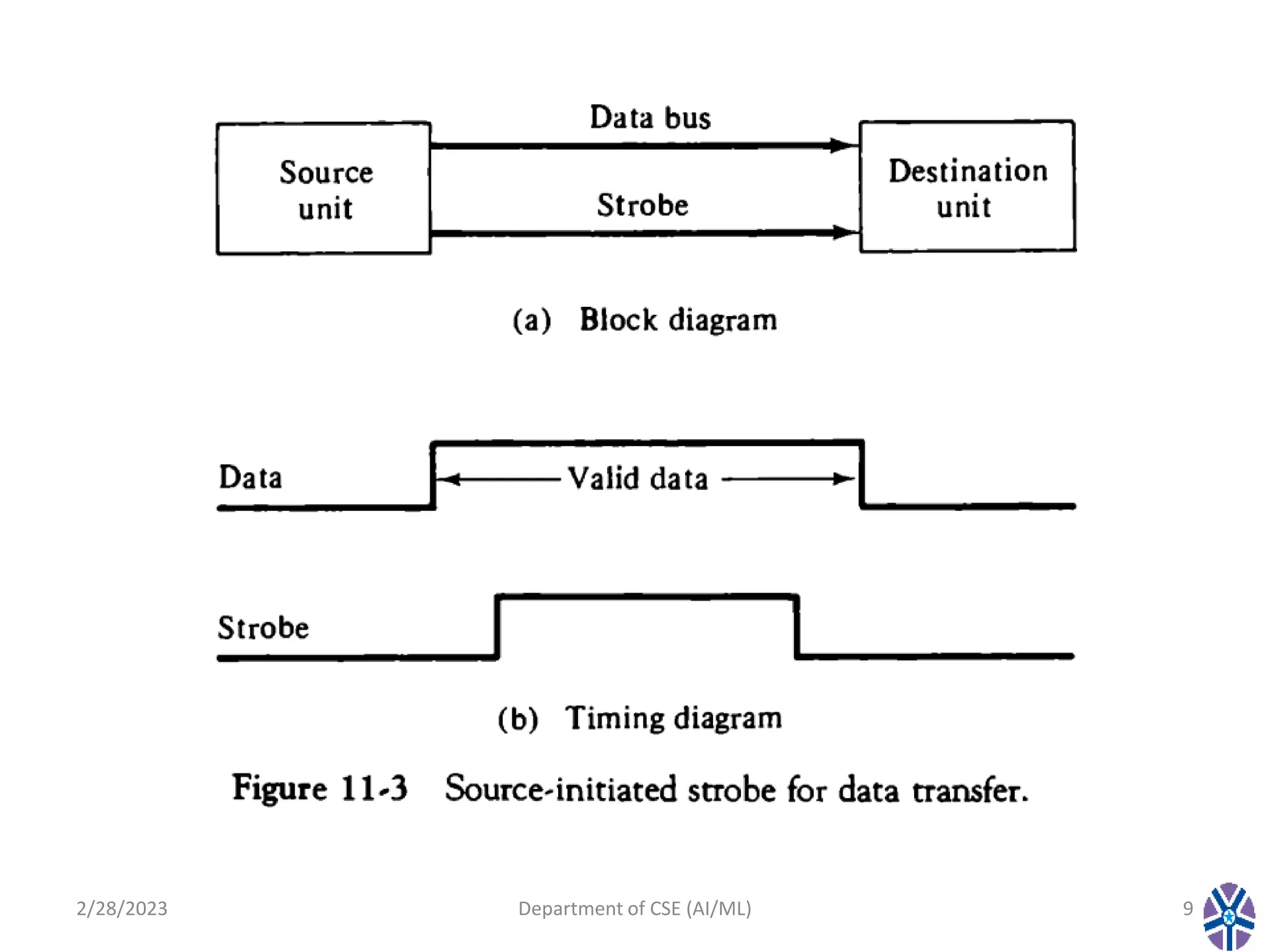
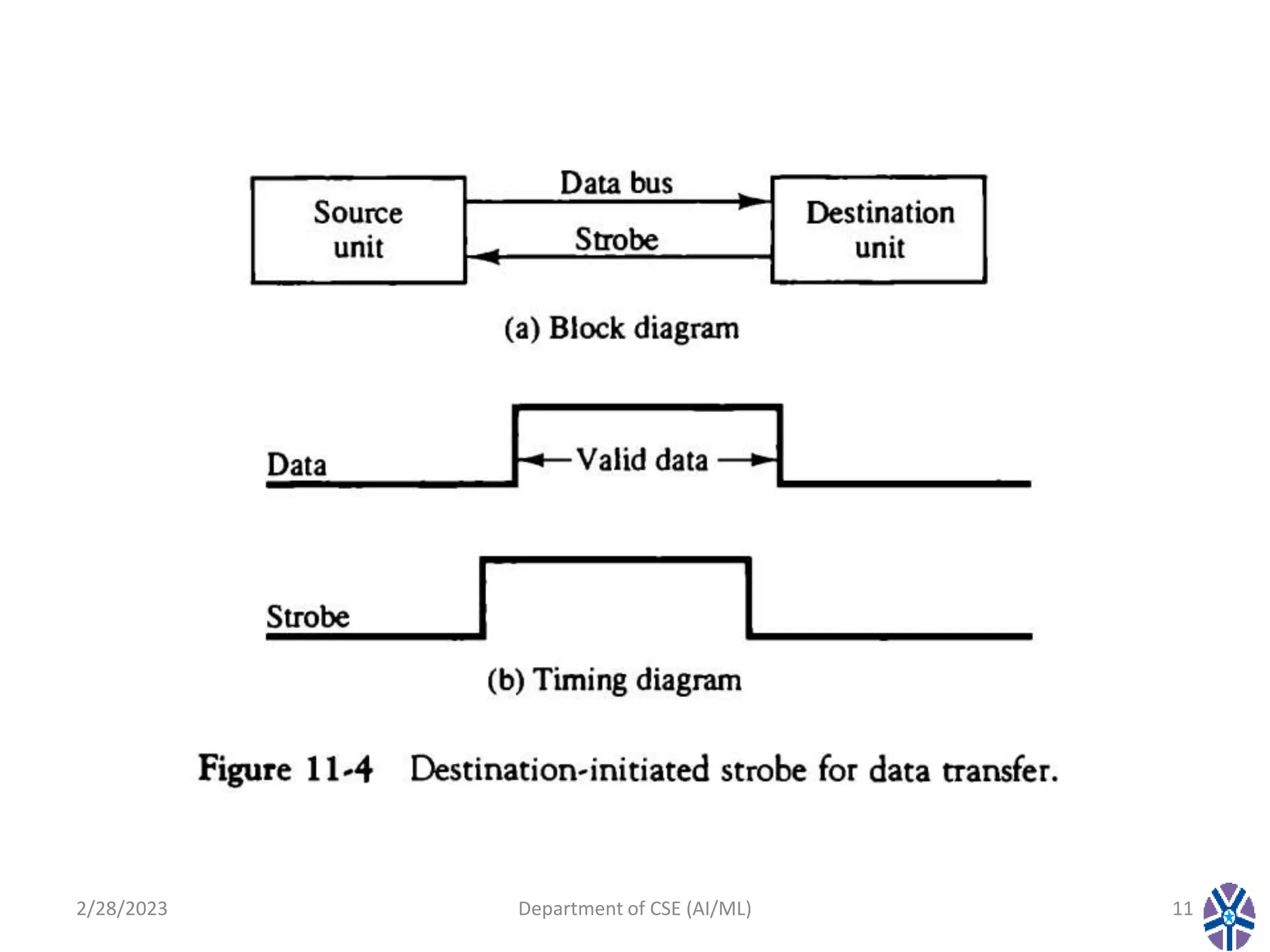
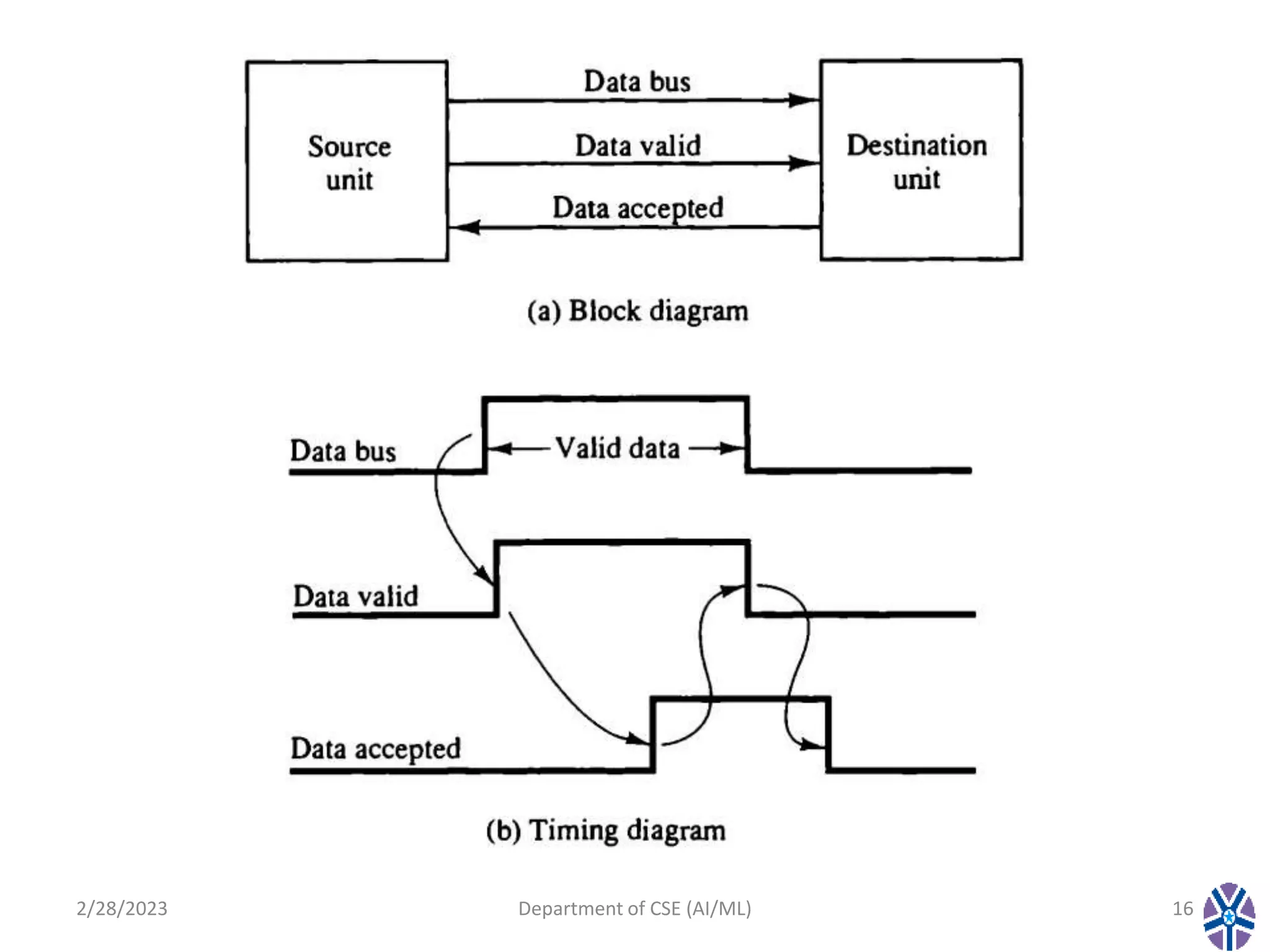
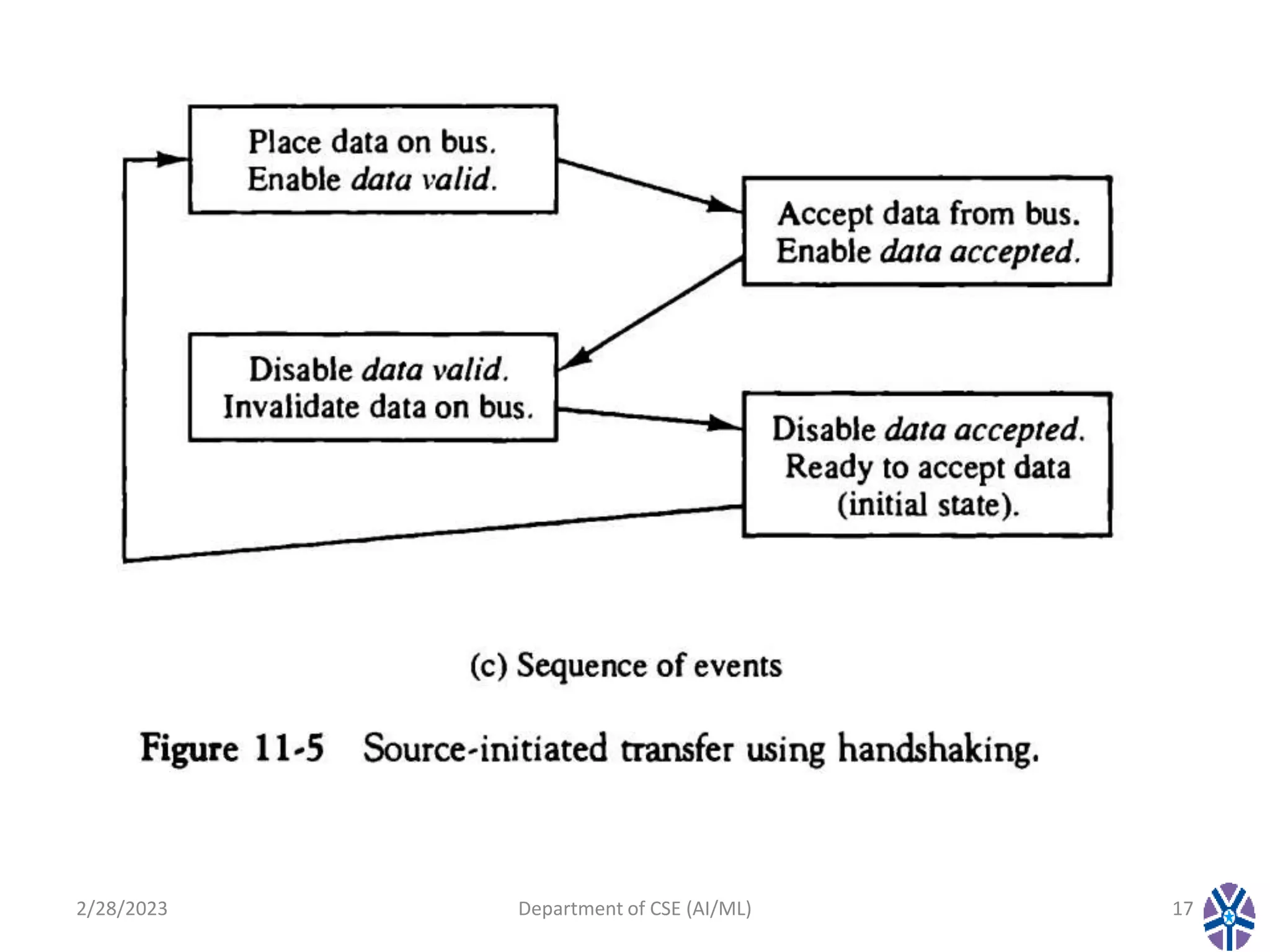
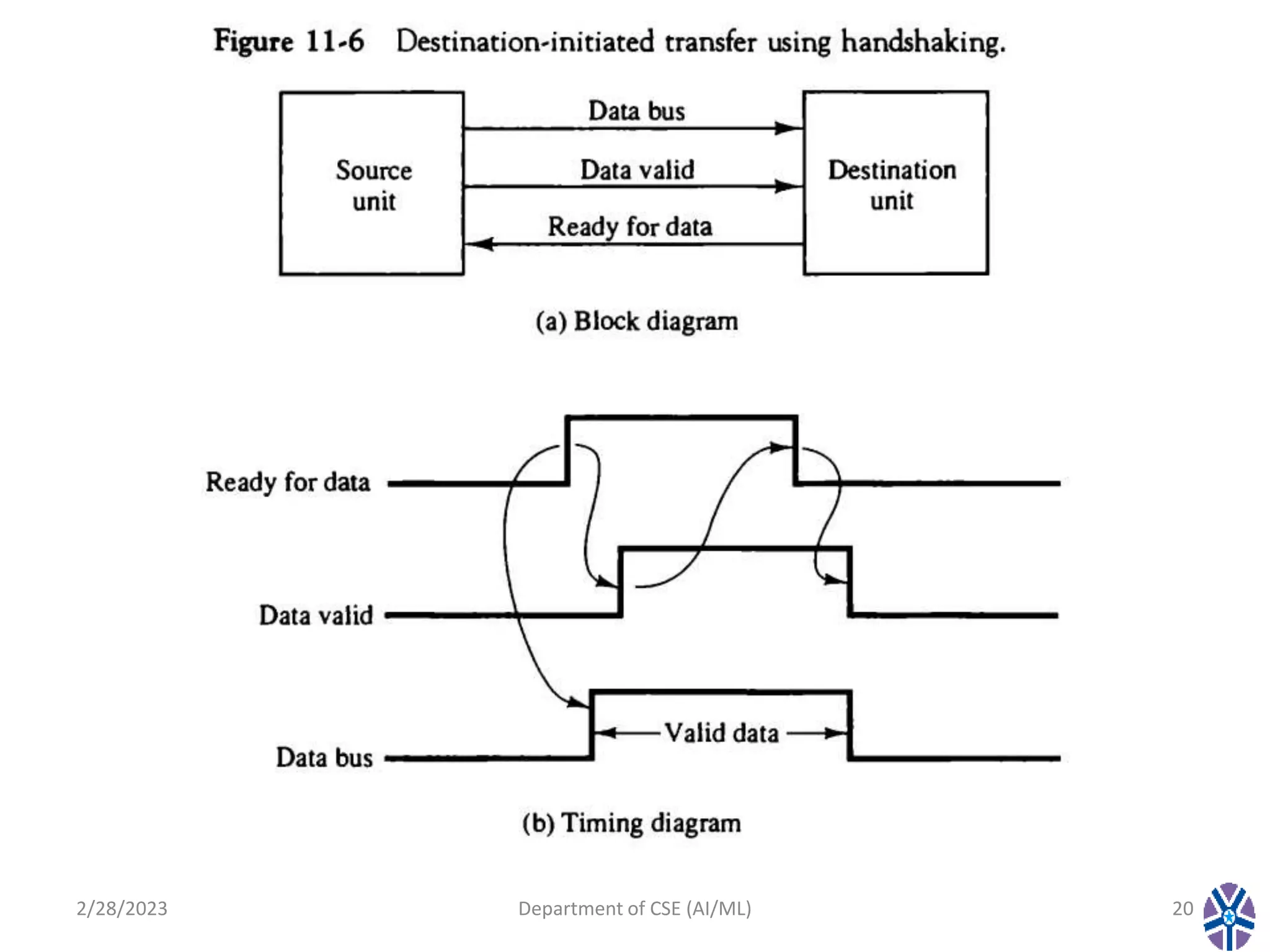
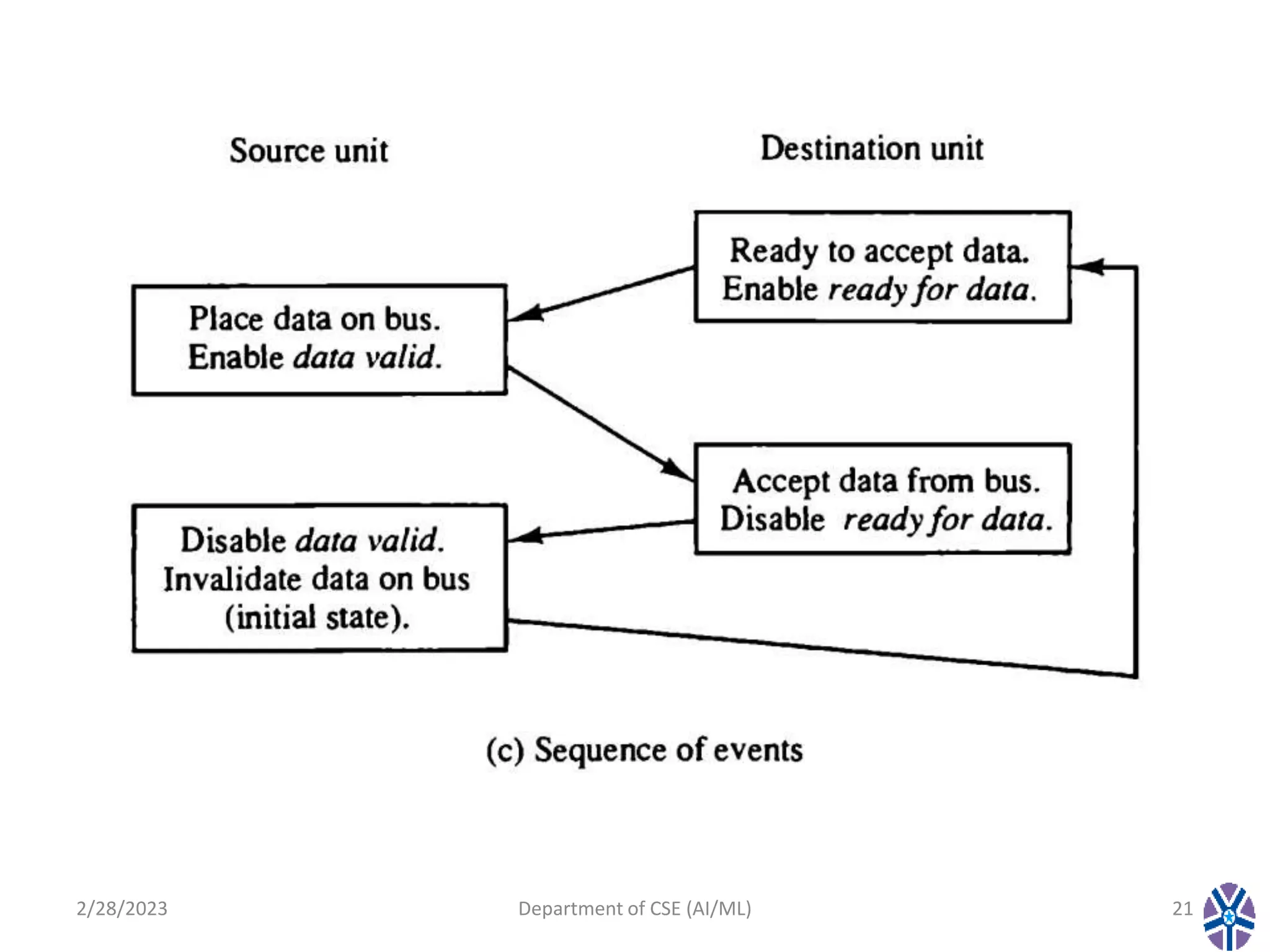
This document contains the summary of a session on computer organization and architecture. It discusses asynchronous data transfer methods like strobe control and handshaking. Strobe control uses a single strobe line to time data transfers, while handshaking uses two control signals - one from the source to indicate valid data and another from the destination to acknowledge receipt. It explains source initiated and destination initiated handshaking transfers through state diagrams. The next session will cover modes of transfer.