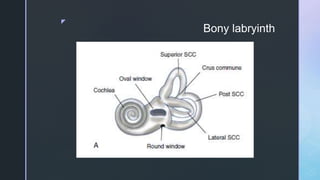
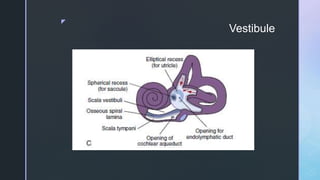
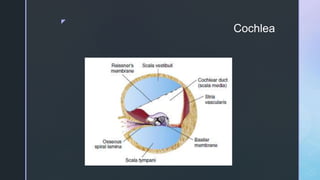
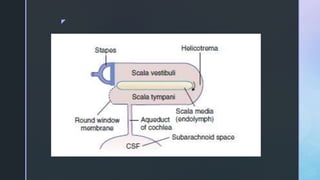
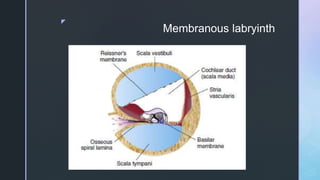
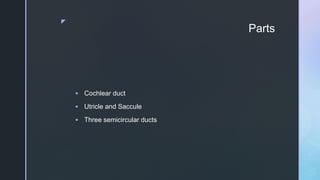
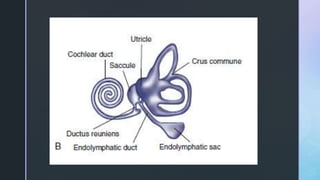
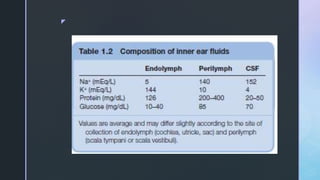
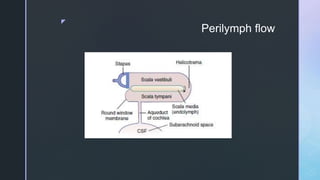
The document summarizes the surgical anatomy of the inner ear. It describes the components of the inner ear as the bony labyrinth containing the vestibule, semicircular canals, and cochlea, and the membranous labyrinth containing the cochlear duct, utricle, saccule, and semicircular canals. It provides details on each of these structures, including their composition and functions. It also discusses the inner ear fluids of endolymph and perilymph, their ion concentrations, and theories about their formation and flow within the inner ear.