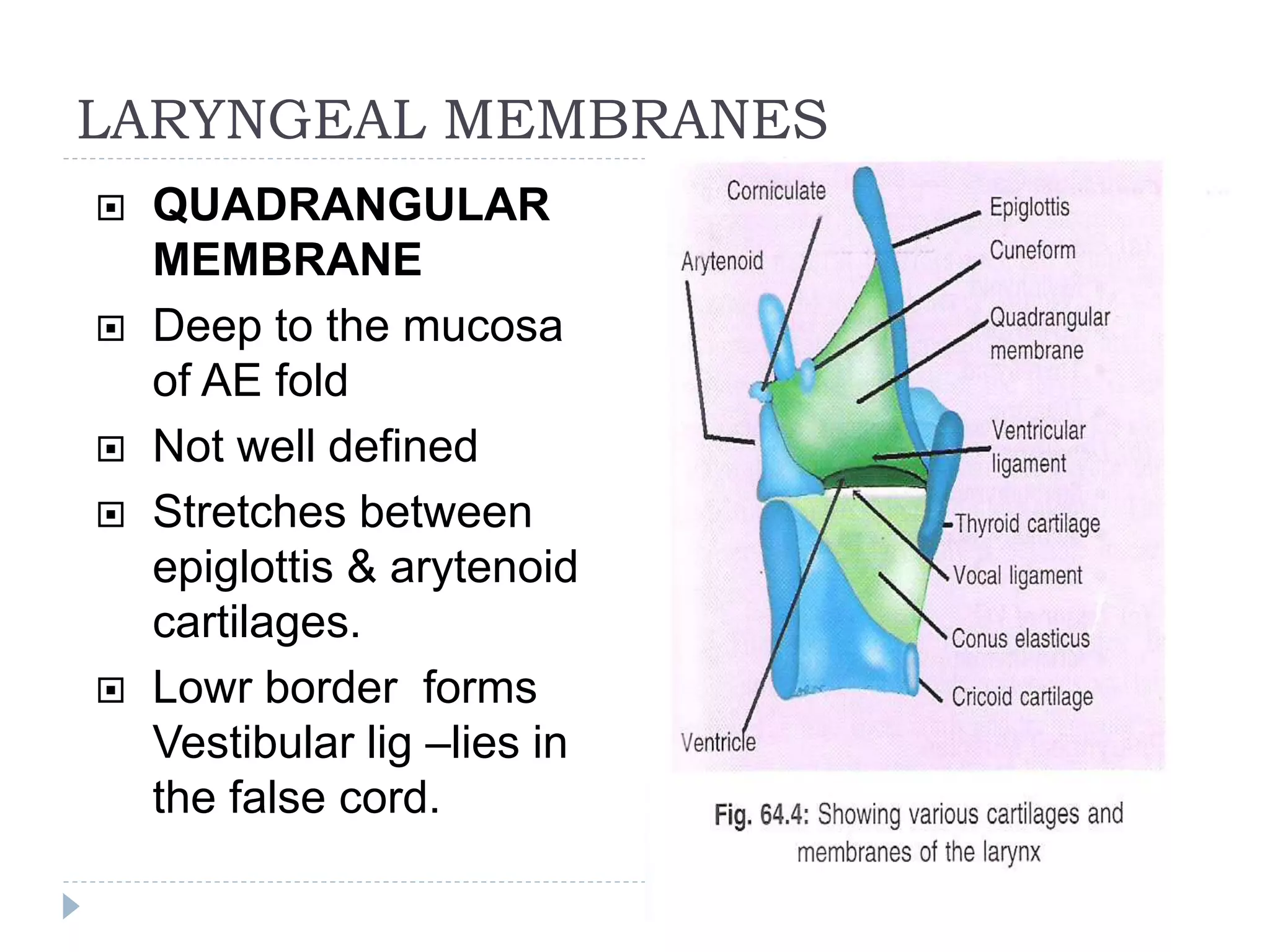
The larynx develops from two primordia - the supraglottis develops from the third and fourth branchial arches, while the glottis and subglottis develop from the sixth branchial arch. This gives the larynx a dual blood supply. The supraglottis includes the epiglottis, aryepiglottic folds, and arytenoids. The glottis is made up of the vocal cords. The subsite below the glottis is also called the subglottis. The larynx contains membranes like the cricovocal membrane and quadrangular membrane. It also contains spaces like the ventricle and pre-epiglottic space








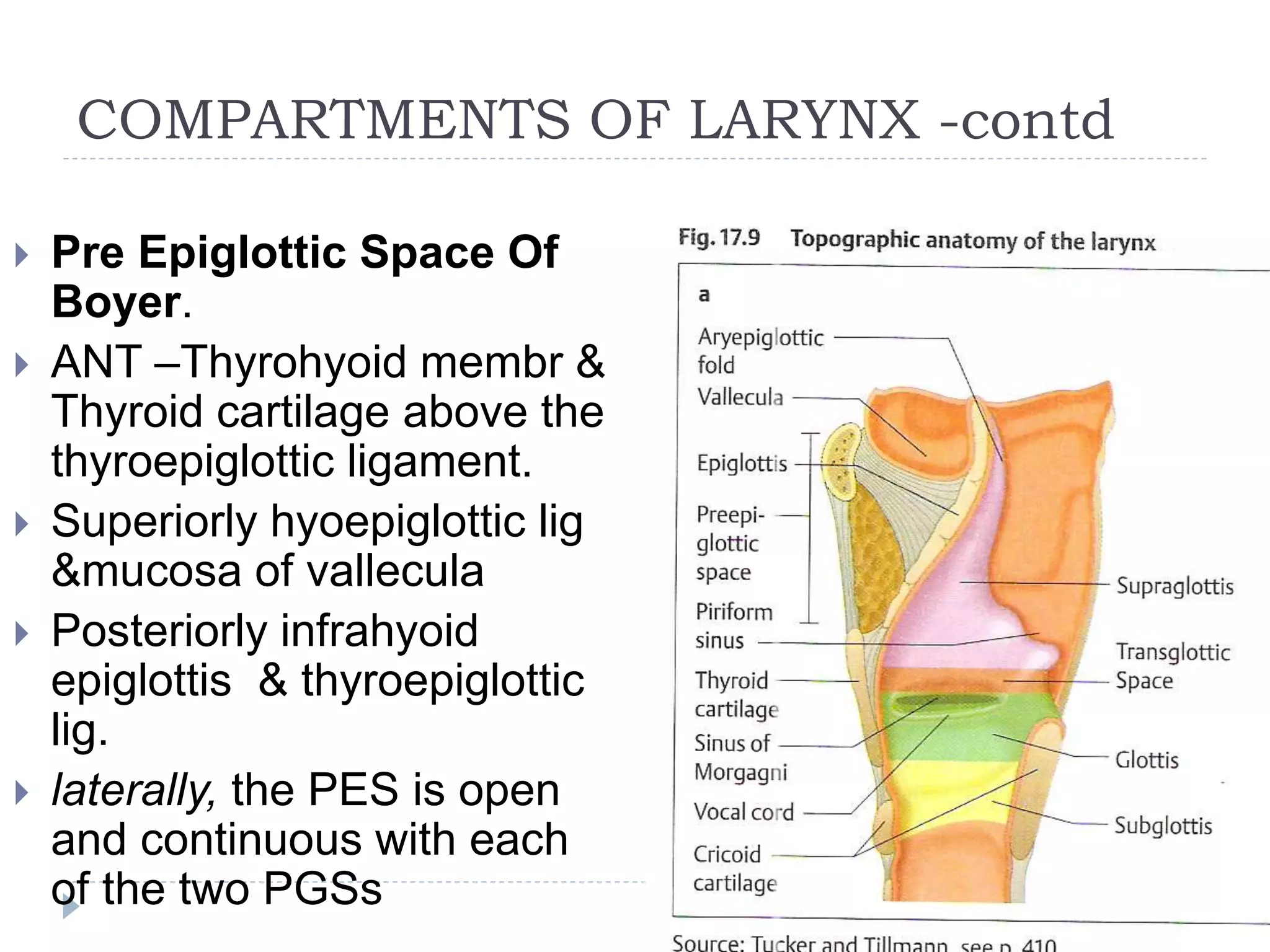
![The PES contains fat and areolar
tissue[7] and is frequently invaded
by tumors because the cartilage of
the epiglottis has multiple small
fenestrations through which
cancers arising from the infrahyoid
epiglottis may pass. Superiorly, the
hyoepiglottic ligament provides a
barrier to spread of tumor to the
tongue base (Fig. 107-3). The
lymphatics of the PES drain
through the thyrohyoid membrane,
spreading to lymph nodes on both
sides of the neck, primarily in
zones II and III (Fig. 107-4).[5]
Supraglottic tumors with PES
involvement are staged as T3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/larynx-200511070310/75/Larynx-11-2048.jpg)



