Asexual reproduction in plants
•
32 likes•28,968 views
Asexual reproduction is a process in which new organism is produced from a single parent without the involvement of gametes or cells. Many unicellular and multi cellular organisms reproduce asexually.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Sexual and Asexual Reproduction in Plants

Provides every relevant knowledge about the topic for the students of Grade- 7 and 8
Recommended
Sexual and Asexual Reproduction in Plants

Provides every relevant knowledge about the topic for the students of Grade- 7 and 8
Parts of the flower

Parts of a Flower
Sepals
Petals
Receptacle
Pistil
Stamen
Stamen
The stamen (plural stamina or stamens) is the pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
Filament- Supports the Anther
Anther- Produces Pollen Grains
Pistil
The ovule producing part of a flower.
The ovary often supports a long style, topped by a stigma. The mature ovary is a fruit, and the mature ovule is a seed. Stigma: The part of the pistil where pollen germinates.
Peduncle
The stalk of a flower.
Types of Flowers
Complete Flowers- have both male and female parts
Incomplete Flowers- have either male or female parts but not both.
Pollination
is the act of transferring pollen grains from the male anther of a flower to the female stigma. The goal of every living organism, including plants, is to create offspring for the next generation. One of the ways that plants can produce offspring is by making seeds.
How Are Plants Pollinated?
Bees
Birds
Wind
Humans
Animals
How Are Flowers Useful to Us?
Flowers are not just beautiful to look at,
but they also serve a vital role in our ecosystem.
Flowers help our ecosystem flourish and attract a plethora of life to the area and facilitate the expansion of our environment. If flowers are cut down or destroyed before pollination can occur, that particular species has a high chance of dying off in that area. In addition, local wildlife will also vanish in that area since they would have no food. Flowers help keep the ecosystem growing and provide new plant life, as well as help sustain local insects and birds.
References
https://www.google.com/search?q=the+warmth+of+the+sun&biw=1366&bih=624&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwijzIvum-vNAhVGE5QKHVPECrQQ_AUICCgD#tbm=isch&q=flower&imgdii=FzbkxijP3tcE6M%3A%3BFzbkxijP3tcE6M%3A%3B9HeLL-NVdsjrxM%3A&imgrc=FzbkxijP3tcE6M%3A
https://www.google.com/search?q=plants+need+to+grow&biw=1366&bih=624&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&sqi=2&ved=0ahUKEwiJtPjrnOvNAhXCj5QKHcPEAP0Q_AUIBigB#tbm=isch&q=parts+of+flower+for+kindergarten&imgrc=e6V8oQskJakoiM%3A
https://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.biotik.org%2Flaos%2Fdefs%2FStamen_en.gif&imgrefurl=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.biotik.org%2Flaos%2Fdefs%2F354_en.html&docid=Ds4mwro4x7NUhM&tbnid=QKkshukLyPxM2M%3A&w=455&h=283&noj=1&ved=0ahUKEwiDpou4pOvNAhWGKJQKHR2ZD3kQMwg6KAcwBw&iact=mrc&uact=8&biw=1366&bih=624#h=283&imgdii=QKkshukLyPxM2M%3A%3BQKkshukLyPxM2M%3A%3Bsk-2e39y3k6kCM%3A&w=455
https://www.google.com/search?q=stamen&biw=1366&bih=624&noj=1&source=lnms&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiDpou4pOvNAhWGKJQKHR2ZD3kQ_AUIBygA&dpr=1
Parts of the plants and their functions

Power point sobre les plantes i les funcions de les seves parts. Utilitzat a Cicle Mitjà PILE
Interactions within ecosystems

I can't claim credit for this presentation's original format; which a colleague downloaded. I've just added and tweaked a little so that it fits within my class's syllabus.
Parts of a plant/plant life cycle (teach)

Basic presentation of the parts of a plant and of the life cycle of plants. Pitched at about the 2nd, 3rd or 4th grade level. Lots of descriptive pictures and diagrams.
Vegetative Propagation artificial and natural

Reproduction chapter class 10 Vegetative propagation Natural and artificial
More Related Content
What's hot
Parts of the flower

Parts of a Flower
Sepals
Petals
Receptacle
Pistil
Stamen
Stamen
The stamen (plural stamina or stamens) is the pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
Filament- Supports the Anther
Anther- Produces Pollen Grains
Pistil
The ovule producing part of a flower.
The ovary often supports a long style, topped by a stigma. The mature ovary is a fruit, and the mature ovule is a seed. Stigma: The part of the pistil where pollen germinates.
Peduncle
The stalk of a flower.
Types of Flowers
Complete Flowers- have both male and female parts
Incomplete Flowers- have either male or female parts but not both.
Pollination
is the act of transferring pollen grains from the male anther of a flower to the female stigma. The goal of every living organism, including plants, is to create offspring for the next generation. One of the ways that plants can produce offspring is by making seeds.
How Are Plants Pollinated?
Bees
Birds
Wind
Humans
Animals
How Are Flowers Useful to Us?
Flowers are not just beautiful to look at,
but they also serve a vital role in our ecosystem.
Flowers help our ecosystem flourish and attract a plethora of life to the area and facilitate the expansion of our environment. If flowers are cut down or destroyed before pollination can occur, that particular species has a high chance of dying off in that area. In addition, local wildlife will also vanish in that area since they would have no food. Flowers help keep the ecosystem growing and provide new plant life, as well as help sustain local insects and birds.
References
https://www.google.com/search?q=the+warmth+of+the+sun&biw=1366&bih=624&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwijzIvum-vNAhVGE5QKHVPECrQQ_AUICCgD#tbm=isch&q=flower&imgdii=FzbkxijP3tcE6M%3A%3BFzbkxijP3tcE6M%3A%3B9HeLL-NVdsjrxM%3A&imgrc=FzbkxijP3tcE6M%3A
https://www.google.com/search?q=plants+need+to+grow&biw=1366&bih=624&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&sqi=2&ved=0ahUKEwiJtPjrnOvNAhXCj5QKHcPEAP0Q_AUIBigB#tbm=isch&q=parts+of+flower+for+kindergarten&imgrc=e6V8oQskJakoiM%3A
https://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.biotik.org%2Flaos%2Fdefs%2FStamen_en.gif&imgrefurl=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.biotik.org%2Flaos%2Fdefs%2F354_en.html&docid=Ds4mwro4x7NUhM&tbnid=QKkshukLyPxM2M%3A&w=455&h=283&noj=1&ved=0ahUKEwiDpou4pOvNAhWGKJQKHR2ZD3kQMwg6KAcwBw&iact=mrc&uact=8&biw=1366&bih=624#h=283&imgdii=QKkshukLyPxM2M%3A%3BQKkshukLyPxM2M%3A%3Bsk-2e39y3k6kCM%3A&w=455
https://www.google.com/search?q=stamen&biw=1366&bih=624&noj=1&source=lnms&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiDpou4pOvNAhWGKJQKHR2ZD3kQ_AUIBygA&dpr=1
Parts of the plants and their functions

Power point sobre les plantes i les funcions de les seves parts. Utilitzat a Cicle Mitjà PILE
Interactions within ecosystems

I can't claim credit for this presentation's original format; which a colleague downloaded. I've just added and tweaked a little so that it fits within my class's syllabus.
Parts of a plant/plant life cycle (teach)

Basic presentation of the parts of a plant and of the life cycle of plants. Pitched at about the 2nd, 3rd or 4th grade level. Lots of descriptive pictures and diagrams.
Vegetative Propagation artificial and natural

Reproduction chapter class 10 Vegetative propagation Natural and artificial
What's hot (20)
Similar to Asexual reproduction in plants
Asexual reproduction

All the basic concepts you need to know is presented in a very simple way for you to understand.
How do organisms reproduce part 1 (Asexual Reproduction)

This PPt contains chapter 8:- Asexual reproduction for Class 10 CBSE
Reproduction in organisms, Class XII

A Detail Description of Chapter Reproduction in Organisms of NCERT Class XII. The matter can be used by the Students of class X also.
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS

PPT ON ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION. MADE BY SARA YADAV. PLS LIKE IF IT HELPS YOU AND FOLLOW ME FOR MORE SUCH PPTs
Reproduction In Living Beings Class - 10th

PowerPoint Presentation on the topic - 'Reproduction In Living Beings'. For Class:- 10th
Created By - 'Neha Rohtagi'.
I hope that you will found this presentation useful and it will help you out for your concept understanding.
Thank You!
Please give feedbacks and suggestions to get presentations on more interesting topics.
Similar to Asexual reproduction in plants (20)
How do organisms reproduce part 1 (Asexual Reproduction)

How do organisms reproduce part 1 (Asexual Reproduction)
asexualreproduction-240204040209-8abe19b0d.pptx.pptx

asexualreproduction-240204040209-8abe19b0d.pptx.pptx
More from BIOLOGY TEACHER
MARCH MONTH || LIST OF IMPORTANT DAYS ||

The Gregorian calendar consists of the following 12 months:The National Day is a designated date on which celebrations mark the nationhood of a nation or non-sovereign country. This nationhood can be symbolized by the date of independence, of becoming a republic or a significant date for a patron saint or a ruler (birthday, accession, removal, etc).
FEBRAURY MONTH || LIST OF MORTANT DAYS |

The Gregorian calendar consists of the following 12 months:The National Day is a designated date on which celebrations mark the nationhood of a nation or non-sovereign country. This nationhood can be symbolized by the date of independence, of becoming a republic or a significant date for a patron saint or a ruler (birthday, accession, removal, etc).
LIST OF IMPORTANT DAYS- JANUARY MONTH ||

The National Day is a designated date on which celebrations mark the nationhood of a nation or non-sovereign country. This nationhood can be symbolized by the date of independence, of becoming a republic or a significant date for a patron saint or a ruler (birthday, accession, removal, etc).
Amazing Facts about Animals -3 | Interesting facts 

Learn incredible facts about some of our planet's most amazing animals.
Amazing Facts about Animals -2 | Interesting facts 

Learn incredible facts about some of our planet's most amazing animals.
https://youtu.be/bsDlRG0LLW8
Amazing Facts about Animals -1 | Interesting facts 

Learn incredible facts about some of our planet's most amazing animals.
DIVERSITY IN LIVING WORLD - (CLASS XI, CBSE BIOLOGY)

Biology is the science of life forms and living processes. The living world comprises an amazing diversity of living organisms. Early man could easily perceive the difference between inanimate matter and living organisms. Early man deified some of the inanimate matter (wind, sea, fire etc.) and some among the animals and plants. A common feature of all such forms of inanimate and animate objects was the sense of awe or fear that they evoked. The description of living organisms including human beings began much later in human history.
THE LIVING ORGANISMS -CHARACTERISTICS AND HABITATS-3 CBSE-V CHAPTER-9

Organisms
An organism is simply defined as any living thing, ranging from microscopic bacteria to large elephants and everything in between.
Different types of plants and animals are found in different areas.
E.g. deserts have camel and cacti as plants. Beaches show coconut trees and crabs. Fishes and other marine animals inhabit the sea
HUMAN CIRCULATORY SYSTEM CHAPTER 8 - CBSE BIOLOGY CLASS-VII

* Circulatory System: This system is concerned with the circulation of body fluids to distribute various substances to various body parts. The circulatory system is also known as the cardiovascular system.
TRANSPORTATION IN PLANTS - CBSE (CHAPTER-9)NBIOLOGY

Transport of substance in plants
To circulate water, essential nutrients, excretory products, and gases within the plants for various purposes, transportation in plants is necessary. In vascular tissues, this transportation in the plant takes place. By a suction force, water and minerals are transported to various parts of the plant.
ON THE MOVE AGAIN - ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES CBSE-V

Dhanu’s village
Today all the relatives have come to Dhanu’s house to celebrate Dushera. They have come with their luggage in their bullockcarts. Dhanu’s father is the eldest in the family. So all the festivals are celebrated at their house. Dhanu’s mother (aai ), mother’s brother’s wife (mami ) and father’s brother’s wife (kaki ) are busy making puranpoli (sweet rotis made from jaggery and gram).
Along with this a spicy kadi dish is also made. The day passes in laughing and chatting. But by evening everyone’s mood changes. The women and children begin to pack their luggage. The men sit down with the mukadam (agent who lends money) for the meeting. The mukadam gives the details of the loan taken by each family.
LIKE FATHER, LIKE DAUGHTER - ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES CBSE-V

Tell
Does your face or anything else look similar to that of someone else in your family? What is it? Did someone tell you this or did you find it out yourself? How do you feel when people compare you with someone else in your family? Why do you feel so? Who laughs the loudest in your family? Laugh like that person.
WHOSE FORESTS ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES CBSE-V

They enjoy the wild fruits. They look for birds, whose calls they imitate. Joining them in all this fun is their favourite didi – Suryamani. Every Sunday Suryamani takes the children to the forest.
As they move around, she shows them how to recognize the trees, the plants, and animals. Children enjoy this special class in a forest! Suryamani always says, “To learn to read the forest is as important as reading books.”
A SEED TELLS A FARMER’S STORY - ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES CBSE-V

I am a small seed!
I am a small bajra seed. I have stayed in this beautiful wooden box since 1940. I want to tell you my story. This is a long story but not mine alone. It is also the story of my farmer Damjibhai and his family. If I do not tell my story now, it might be too late!
I was born in Vangaam in Gujarat. That year there was a good bajra (millet) crop. There was a festive mood in the village. Our area was famous for its grain and vegetables. Each year Damjibhai kept aside some seeds from a good crop. This way our bajra family went on from one generation to another. Good seeds were stored in dried gourd (lauki ) which was coated with mud.
NO PLACE FOR US? - ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES CBSE-V

He would help some memsahib (lady) to carry her bags, or go to the railway station to pick up empty bottles and newspapers to sell to the kabadiwalla (junk seller). Somehow they were managing their life in the city. It was night, but Sidya had not come home. Jhimli was watching a dance on TV, through the neighbour’s window. Jatrya did not like watching TV. Here, everything was so different. The day would pass running around for work, but the evening brought back old memories.
ACROSS THE WALL - ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES CBSE-V

Stars in her eyes (Indian Express, 2007)
Just 13 years old, Afsana Mansuri has already jumped over the wall. The wall between her jhuggi and the local basketball court. The wall made by society, for a girl who washes utensils for a living. The gender wall her mother had put up for her. Today, Afsana herself has become a strong wall of NBA, the Nagpada Basketball Association of Mumbai.
WHO WILL DO THIS WORK - ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES CBSE-V

Yes, Class-IV (or, Group-D) service means the lowest level posts in Government. This includes Peon, Chaprasi, Daftri, Dispatch Rider, etc. However, nowadays all these employees are called Multi-Tasking Skilled (MTS) workers. Fourth class services are the lowest class services in any organisation.
BLOW HOT, BLOW COLD - ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES CBSE-V

The woodcutter replied, “It is too cold. My hands are frozen, so I blow on them to warm them up a little. Then, when they get cold again I warm them again by blowing.” You can warm your hands by blowing on them because your breath is hotter than your skin (particularly on a cold day). By blowing, you transfer energy from inside your body to your hands by convection. Moist air, like your breath, carries a lot of energy so it warms things more quickly than dry air.
A SHELTER SO HIGH! - ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES CBSE-V

I am Gaurav Jani and this is ‘Loner ’ – my partner – my motorcycle.
But, Loner is never lonely. We are together all the time. I and my motorcycle wait for a chance to get away from the busy, crowded and noisy city of Mumbai. We like to travel to different parts of this wonderful country. Let me tell you about our amazing journey on the highest roads in India.
WHEN THE EARTH SHOOK!-ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES CBSE-V

Earthquakes are usually caused when rock underground suddenly breaks along a fault. This sudden release of energy causes the seismic waves that make the ground shake. ... The rocks are still pushing against each other, but not moving. After a while, the rocks break because of all the pressure that's built up.
More from BIOLOGY TEACHER (20)
Amazing Facts about Animals -3 | Interesting facts 

Amazing Facts about Animals -3 | Interesting facts
Amazing Facts about Animals -2 | Interesting facts 

Amazing Facts about Animals -2 | Interesting facts
Amazing Facts about Animals -1 | Interesting facts 

Amazing Facts about Animals -1 | Interesting facts
DIVERSITY IN LIVING WORLD - (CLASS XI, CBSE BIOLOGY)

DIVERSITY IN LIVING WORLD - (CLASS XI, CBSE BIOLOGY)
THE LIVING ORGANISMS -CHARACTERISTICS AND HABITATS-3 CBSE-V CHAPTER-9

THE LIVING ORGANISMS -CHARACTERISTICS AND HABITATS-3 CBSE-V CHAPTER-9
HUMAN CIRCULATORY SYSTEM CHAPTER 8 - CBSE BIOLOGY CLASS-VII

HUMAN CIRCULATORY SYSTEM CHAPTER 8 - CBSE BIOLOGY CLASS-VII
TRANSPORTATION IN PLANTS - CBSE (CHAPTER-9)NBIOLOGY

TRANSPORTATION IN PLANTS - CBSE (CHAPTER-9)NBIOLOGY
LIKE FATHER, LIKE DAUGHTER - ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES CBSE-V

LIKE FATHER, LIKE DAUGHTER - ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES CBSE-V
A SEED TELLS A FARMER’S STORY - ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES CBSE-V

A SEED TELLS A FARMER’S STORY - ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES CBSE-V
WHO WILL DO THIS WORK - ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES CBSE-V

WHO WILL DO THIS WORK - ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES CBSE-V
BLOW HOT, BLOW COLD - ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES CBSE-V

BLOW HOT, BLOW COLD - ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES CBSE-V
WHEN THE EARTH SHOOK!-ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES CBSE-V

WHEN THE EARTH SHOOK!-ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES CBSE-V
Recently uploaded
Unit 2- Research Aptitude (UGC NET Paper I).pdf

This slide describes the research aptitude of unit 2 in the UGC NET paper I.
TESDA TM1 REVIEWER FOR NATIONAL ASSESSMENT WRITTEN AND ORAL QUESTIONS WITH A...

TESDA TM1 REVIEWER FOR NATIONAL ASSESSMENT WRITTEN AND ORAL QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS.
Sectors of the Indian Economy - Class 10 Study Notes pdf

The Indian economy is classified into different sectors to simplify the analysis and understanding of economic activities. For Class 10, it's essential to grasp the sectors of the Indian economy, understand their characteristics, and recognize their importance. This guide will provide detailed notes on the Sectors of the Indian Economy Class 10, using specific long-tail keywords to enhance comprehension.
For more information, visit-www.vavaclasses.com
Welcome to TechSoup New Member Orientation and Q&A (May 2024).pdf

In this webinar you will learn how your organization can access TechSoup's wide variety of product discount and donation programs. From hardware to software, we'll give you a tour of the tools available to help your nonprofit with productivity, collaboration, financial management, donor tracking, security, and more.
Model Attribute Check Company Auto Property

In Odoo, the multi-company feature allows you to manage multiple companies within a single Odoo database instance. Each company can have its own configurations while still sharing common resources such as products, customers, and suppliers.
Polish students' mobility in the Czech Republic

Polish students mobility to the Czech Republic within eTwinning project "Medieval adventures with Marco Polo"
Supporting (UKRI) OA monographs at Salford.pptx

How libraries can support authors with open access requirements for UKRI funded books
Wednesday 22 May 2024, 14:00-15:00.
Introduction to Quality Improvement Essentials

This is a presentation by Dada Robert in a Your Skill Boost masterclass organised by the Excellence Foundation for South Sudan (EFSS) on Saturday, the 25th and Sunday, the 26th of May 2024.
He discussed the concept of quality improvement, emphasizing its applicability to various aspects of life, including personal, project, and program improvements. He defined quality as doing the right thing at the right time in the right way to achieve the best possible results and discussed the concept of the "gap" between what we know and what we do, and how this gap represents the areas we need to improve. He explained the scientific approach to quality improvement, which involves systematic performance analysis, testing and learning, and implementing change ideas. He also highlighted the importance of client focus and a team approach to quality improvement.
Palestine last event orientationfvgnh .pptx

An EFL lesson about the current events in Palestine. It is intended to be for intermediate students who wish to increase their listening skills through a short lesson in power point.
Instructions for Submissions thorugh G- Classroom.pptx

This presentation provides a briefing on how to upload submissions and documents in Google Classroom. It was prepared as part of an orientation for new Sainik School in-service teacher trainees. As a training officer, my goal is to ensure that you are comfortable and proficient with this essential tool for managing assignments and fostering student engagement.
MARUTI SUZUKI- A Successful Joint Venture in India.pptx

Let us know about Maruti Suzuki, a successful Joint venture in India.
Overview on Edible Vaccine: Pros & Cons with Mechanism

This ppt include the description of the edible vaccine i.e. a new concept over the traditional vaccine administered by injection.
GIÁO ÁN DẠY THÊM (KẾ HOẠCH BÀI BUỔI 2) - TIẾNG ANH 8 GLOBAL SUCCESS (2 CỘT) N...

GIÁO ÁN DẠY THÊM (KẾ HOẠCH BÀI BUỔI 2) - TIẾNG ANH 8 GLOBAL SUCCESS (2 CỘT) N...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
https://app.box.com/s/4hfk1xwgxnova7f4dm37birdzflj806wStudents, digital devices and success - Andreas Schleicher - 27 May 2024..pptx

Andreas Schleicher presents at the OECD webinar ‘Digital devices in schools: detrimental distraction or secret to success?’ on 27 May 2024. The presentation was based on findings from PISA 2022 results and the webinar helped launch the PISA in Focus ‘Managing screen time: How to protect and equip students against distraction’ https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/education/managing-screen-time_7c225af4-en and the OECD Education Policy Perspective ‘Students, digital devices and success’ can be found here - https://oe.cd/il/5yV
Cambridge International AS A Level Biology Coursebook - EBook (MaryFosbery J...

for studentd in cabridge board
The Roman Empire A Historical Colossus.pdf

The Roman Empire, a vast and enduring power, stands as one of history's most remarkable civilizations, leaving an indelible imprint on the world. It emerged from the Roman Republic, transitioning into an imperial powerhouse under the leadership of Augustus Caesar in 27 BCE. This transformation marked the beginning of an era defined by unprecedented territorial expansion, architectural marvels, and profound cultural influence.
The empire's roots lie in the city of Rome, founded, according to legend, by Romulus in 753 BCE. Over centuries, Rome evolved from a small settlement to a formidable republic, characterized by a complex political system with elected officials and checks on power. However, internal strife, class conflicts, and military ambitions paved the way for the end of the Republic. Julius Caesar’s dictatorship and subsequent assassination in 44 BCE created a power vacuum, leading to a civil war. Octavian, later Augustus, emerged victorious, heralding the Roman Empire’s birth.
Under Augustus, the empire experienced the Pax Romana, a 200-year period of relative peace and stability. Augustus reformed the military, established efficient administrative systems, and initiated grand construction projects. The empire's borders expanded, encompassing territories from Britain to Egypt and from Spain to the Euphrates. Roman legions, renowned for their discipline and engineering prowess, secured and maintained these vast territories, building roads, fortifications, and cities that facilitated control and integration.
The Roman Empire’s society was hierarchical, with a rigid class system. At the top were the patricians, wealthy elites who held significant political power. Below them were the plebeians, free citizens with limited political influence, and the vast numbers of slaves who formed the backbone of the economy. The family unit was central, governed by the paterfamilias, the male head who held absolute authority.
Culturally, the Romans were eclectic, absorbing and adapting elements from the civilizations they encountered, particularly the Greeks. Roman art, literature, and philosophy reflected this synthesis, creating a rich cultural tapestry. Latin, the Roman language, became the lingua franca of the Western world, influencing numerous modern languages.
Roman architecture and engineering achievements were monumental. They perfected the arch, vault, and dome, constructing enduring structures like the Colosseum, Pantheon, and aqueducts. These engineering marvels not only showcased Roman ingenuity but also served practical purposes, from public entertainment to water supply.
Recently uploaded (20)
Basic phrases for greeting and assisting costumers

Basic phrases for greeting and assisting costumers
TESDA TM1 REVIEWER FOR NATIONAL ASSESSMENT WRITTEN AND ORAL QUESTIONS WITH A...

TESDA TM1 REVIEWER FOR NATIONAL ASSESSMENT WRITTEN AND ORAL QUESTIONS WITH A...
Sectors of the Indian Economy - Class 10 Study Notes pdf

Sectors of the Indian Economy - Class 10 Study Notes pdf
Welcome to TechSoup New Member Orientation and Q&A (May 2024).pdf

Welcome to TechSoup New Member Orientation and Q&A (May 2024).pdf
aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa

aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
Instructions for Submissions thorugh G- Classroom.pptx

Instructions for Submissions thorugh G- Classroom.pptx
MARUTI SUZUKI- A Successful Joint Venture in India.pptx

MARUTI SUZUKI- A Successful Joint Venture in India.pptx
Overview on Edible Vaccine: Pros & Cons with Mechanism

Overview on Edible Vaccine: Pros & Cons with Mechanism
GIÁO ÁN DẠY THÊM (KẾ HOẠCH BÀI BUỔI 2) - TIẾNG ANH 8 GLOBAL SUCCESS (2 CỘT) N...

GIÁO ÁN DẠY THÊM (KẾ HOẠCH BÀI BUỔI 2) - TIẾNG ANH 8 GLOBAL SUCCESS (2 CỘT) N...
Students, digital devices and success - Andreas Schleicher - 27 May 2024..pptx

Students, digital devices and success - Andreas Schleicher - 27 May 2024..pptx
Cambridge International AS A Level Biology Coursebook - EBook (MaryFosbery J...

Cambridge International AS A Level Biology Coursebook - EBook (MaryFosbery J...
Asexual reproduction in plants
- 1. Asexual Reproduction in Plants
- 2. Asexual Reproduction in Plants 1. Involves only one parent, 2. Does not involve seeds or the fusion of gametes 3. Instead part of a plant’s stem, leaves or roots can become new plants, 4. Produces offspring / clones genetically identical to the parent, 5. Allows plants to be produced much faster then sexual reproduction. There are six types of a sexual reproduction. They are: 1) fission 2) budding 3) spore formation 4) regeneration 5) fragmentation 6) vegetative propagation
- 3. ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS Fission Budding Spore formation Regeneration Fragmenta tion Vegetative propagation Multiple Fission Binary Fission BudLeafRootStem BulbRhizomeTuberRunner
- 4. There are two types Fission : In fission, unicellular organism splits to form new organisms. It is a process of reproduction in organisms such as protozoa and many bacteria. Binary Fission: In binary fission, the parent cell divides into two after reaching a point where it has fully grown. In this process, after splitting parent cell do not exist and two new organisms are formed. Examples of unicellular organisms that undergo binary fission are amoeba, paramecium, Leishmania etc.
- 5. Multiple Fission: Multiple fission is also a process of asexual reproduction in which parent cell splits to form many new organisms. This happens when cyst is formed around a unicellular organism. Inside this cyst the nucleus of an organism breaks in many smaller nuclei. When the favorable conditions come, the cyst breaks and the many daughter cells inside it are released. Plasmodium
- 6. Budding: The word bud means small outgrowth. In the process of budding, a small bud grows on the body of parent organism and when the time comes it detaches itself to form a new organism. Hydra and yeast undergoes the process of budding. Hydra reproducing by the method of budding. Yeast reproducing by the method of budding.
- 7. •Spore formation The method of spore formation occurs in both unicellular and multi-cellular organisms. This process takes place in plants. In spore formation, the parent plant produces hundreds of reproductive units called spores in its spore case. When this spore case of the plant bursts, these spores travel in air and land on food or soil. Here they germinate and produce new plants. EX: Fungi like Rhizopus, Mucor, etc., are examples of spore formation.
- 8. Regeneration Regeneration is an asexual method of reproduction. In this process, if the body of a parent organism gets cut, then each cut part can regenerate and form a whole new organism from its body parts. This happens because when the body of an organism that can undergo regeneration gets cut then the cells of cut body part divide rapidly and form a ball of cells. These cells then move to their proper places to form organs and body parts. Regeneration occurs in both plants and animals. EX: Hydra and planaria undergo regeneration. Regeneration in Planeria.
- 9. •Fragmentation Fragmentation occurs in multicellular organisms, be it plants or animals. In this process the multicellular organism breaks into two or more pieces on maturation. Each piece than grows into a new organism. Spirogyra which is a plant and sea anemones which is a sea animal undergoes the process of fragmentation.
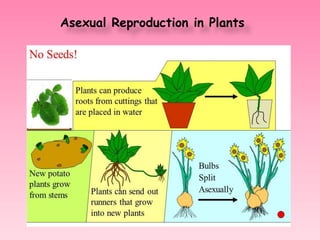
- 10. Vegetative Propagation: Vegetative propagation is a type of sexual reproduction in which the 1. Stems (Runner, tuber, rhizome and &bulb) 2. Roots, 3.Leaves 4.Buds give rises in to new plant. These are also called vegetative parts of the plants.
- 11. 1. Modified Stems (a) Runners • Horizontal stem which grows or runs over the soil surface. • The terminal bud sends up new shoots & down new roots from it. Ex: Strawberries
- 12. B. Rhizomes- Modified stems that grow under the soil, produce new roots from stem. Ex- Grasses
- 13. C. Tubers-: shorter, thicker stems that produce an “eye” which is capable of producing a new plant. Ex-Potato
- 14. D. Bulbs: Stem covered with modified leaves which can produce a new plant. Ex: Onion E. Food Storing Roots Roots which are capable of producing a new plant Ex: carrots & beets
- 15. 3. Modified Leaves • Some plants produce Plantlets along the edges of the leaves. • When they reach a certain size, they fall off and grow into new plants. Ex: Cacti
- 16. 4. Modified Buds Bulbs : A bulb (an underground bud) has a reduced stem, roots, fleshy leaves swollen with stored food and a main bud in the centre which grows into a new plant Ex: Onion, Daffodil, Tulip
- 17. Vegetative Propagation Artificial Method of Asexual reproduction most used in agriculture 1. Cuttings- pieces of stem cut from parent kept in water, moist soil or sand Will put out new roots. Ex:-Many garden plants like
- 18. Grafting- Buds or sections are cut from one plant is attached to another that is already rooted in the soil. Ex- Roses, Fruit Trees
- 19. 3. Layering : A branch of a plant is bent over and pinned down into the soil at a node. It is covered over with soil & eventually new roots & shoots develop useful for the propagation of woody plants. Ex: blackberry, gooseberry.
- 20. 4.Tissue culture- pieces of the center of stem are removed placed in flasks with growth medium a whole new plant will develop
- 21. Advantages of artificial vegetative propagation •The new plant will have exact features as that of parent plant. •Fruit trees grown by grafting bear fruit much earlier. •Plants need less attention in their early years. •Many plants can be grown from just one parent. •Can get seedless plants. Thank you, Nanditha Akunuri B.Sc, B.Ed, M.sc, M.A, M.Ed, (P.hD)
Editor's Notes
- 2. Rhizomes- modified stems that grow under the soil, produce new roots from stem. Ex- Grasses 3. Tubers- shorter, thicker stems that produce an “eye” which is capable of producing a new plant. Ex-Potato
