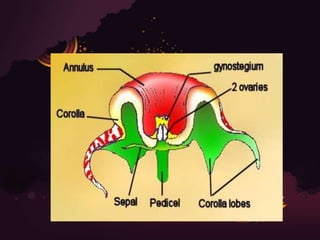
This document provides information on the Asclepiadaceae plant family. It discusses the classification, distribution, habitat, morphology, and examples of some members of the family. The family has 280 genera and 1800 species that are mainly found in tropical regions. Plants in the family are mostly herbs, shrubs, or woody climbers that produce milky latex. Flowers are bisexual and have a fused corolla with corolline corona. Some economically important members include Asclepias curassavica which is used ornamentally and medicinally, Cryptostegia grandiflora which produces latex for rubber, and Hemidesmus indicus which has medicinal roots.