This document discusses the key assumptions of the cognitive approach to mental health. It states that:
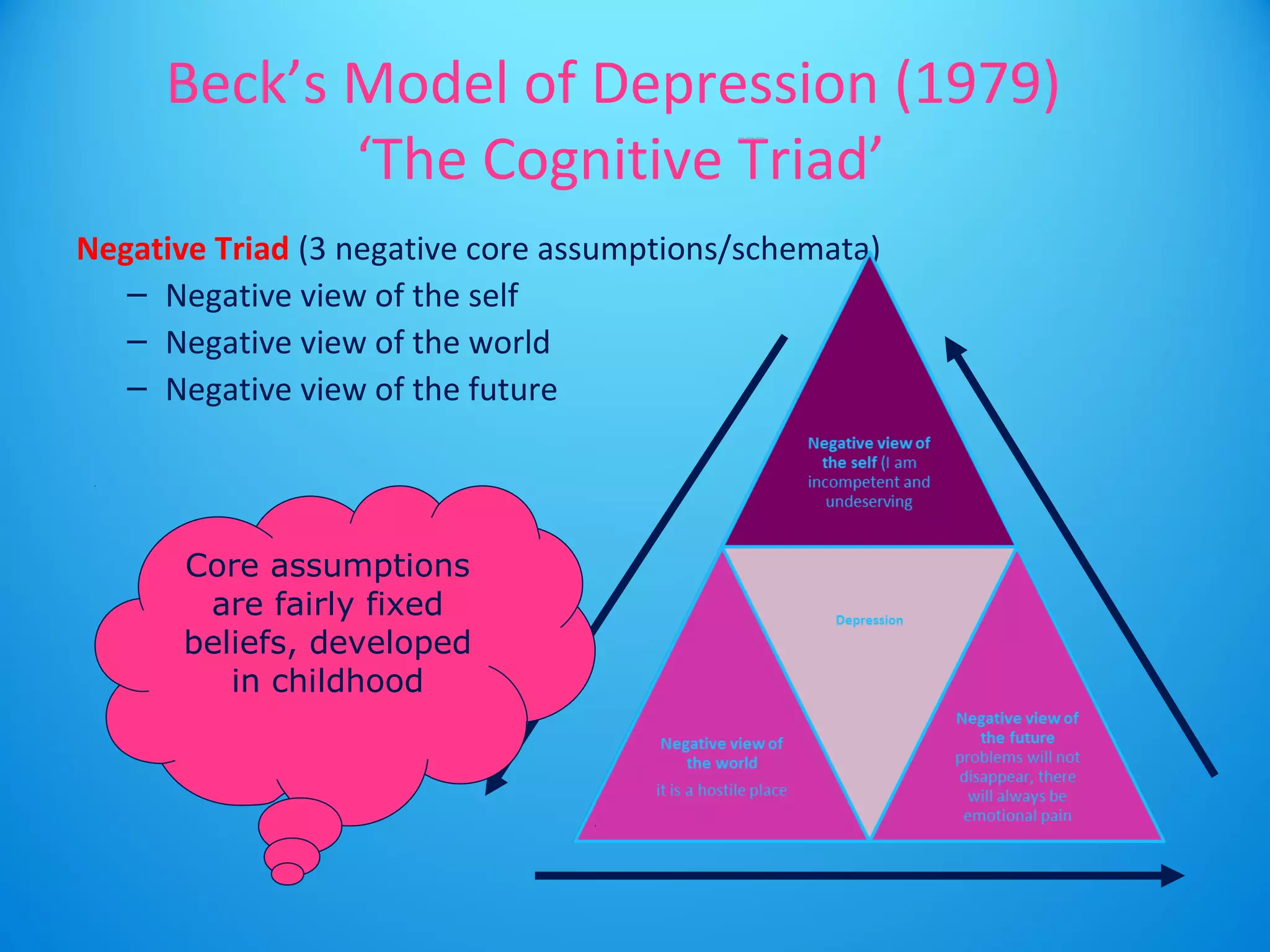
- Individuals with mental disorders have distorted and irrational thinking which can cause maladaptive behavior.
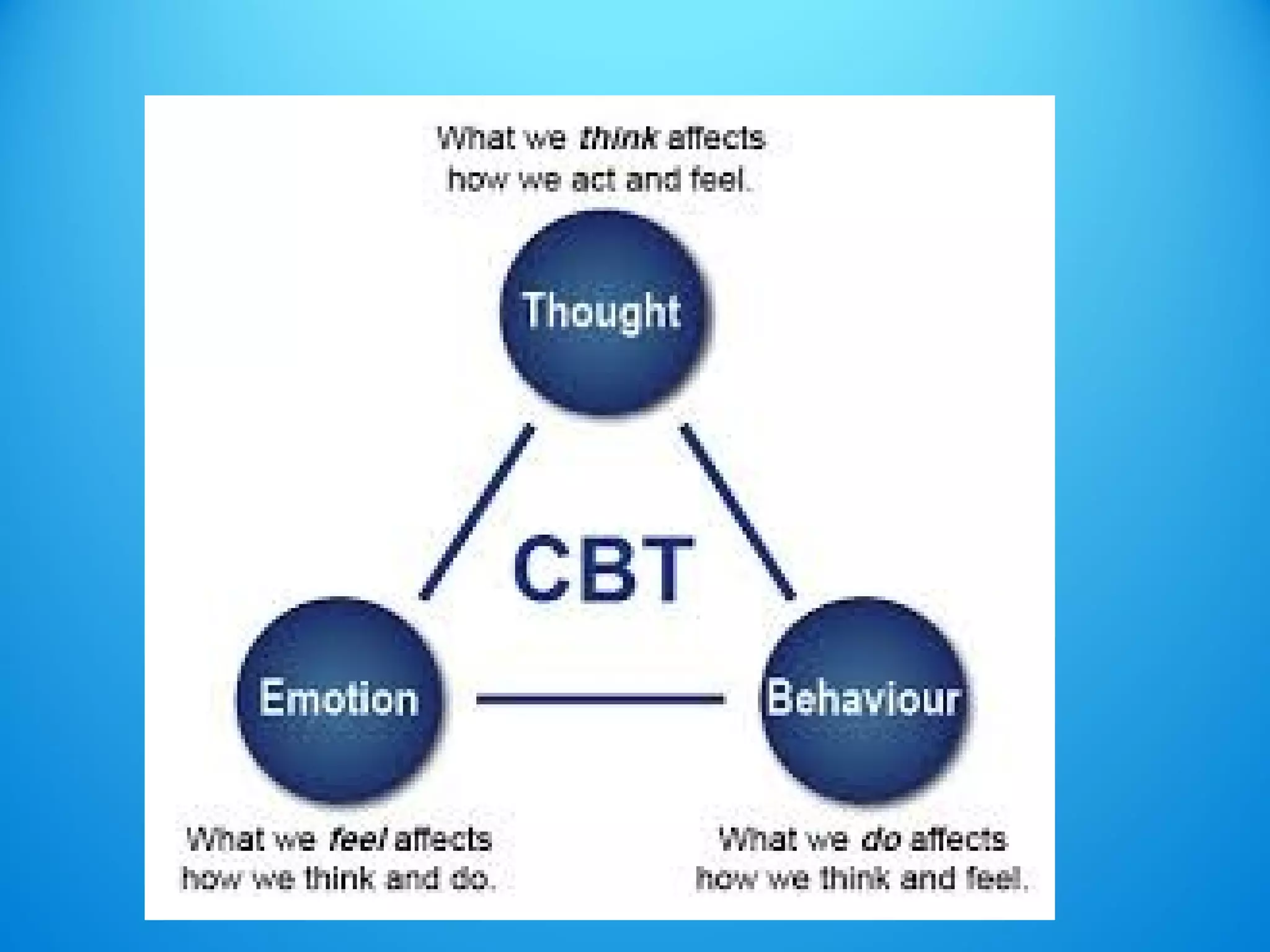
- It is usually how one thinks about a problem, rather than the problem itself, that causes psychological issues.
- People can overcome disorders by learning more adaptive thinking patterns. If one's thoughts are more positive, their mental state can improve.