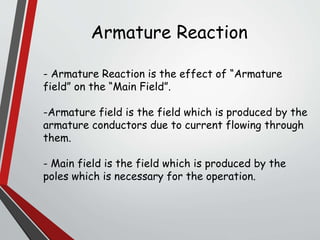
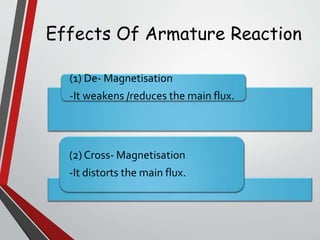
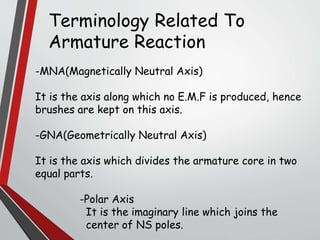
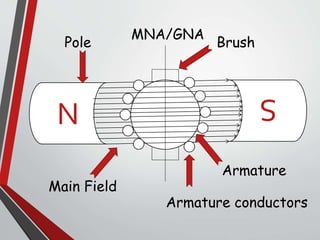
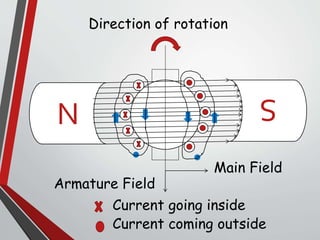
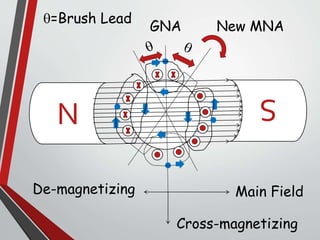
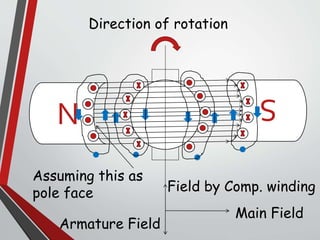
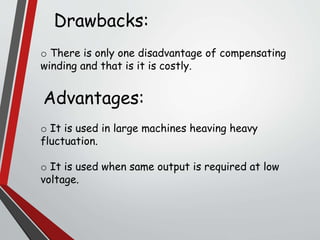
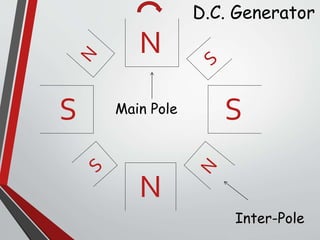
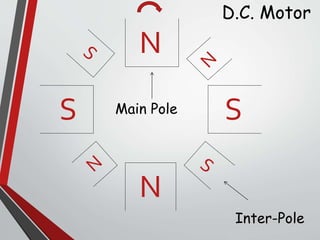
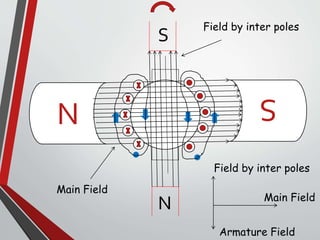
This document discusses armature reaction in DC generators and motors. It explains that armature reaction is caused by the magnetic field produced by current flowing through the armature windings, which distorts the main magnetic field produced by the poles. This shifts the magnetically neutral axis and causes brush shift. Compensating windings and interpoles are used to counteract the cross-magnetizing effect of armature reaction and make commutation sparkless. Compensating windings carry current in the opposite direction of the armature below the poles, while interpoles have the same polarity as the leading pole and induce a reversing e.m.f. to help current reversal during commutation.