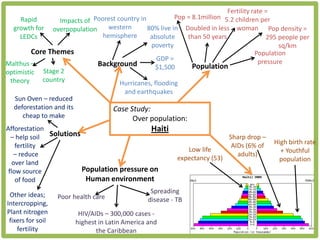
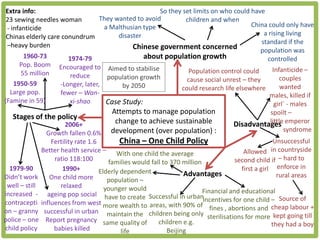
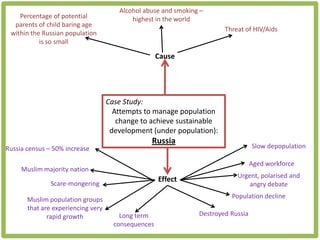
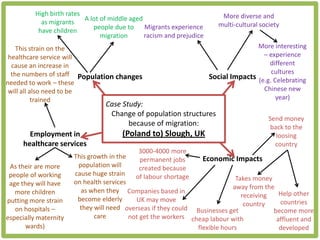
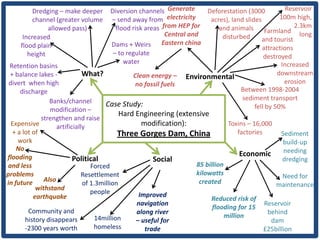
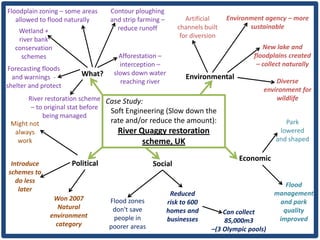
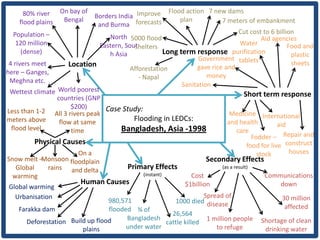
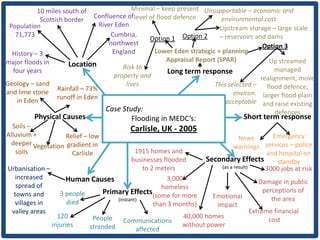
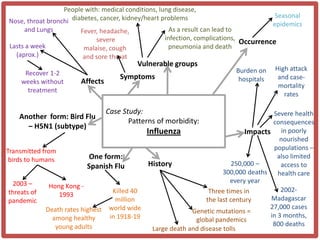
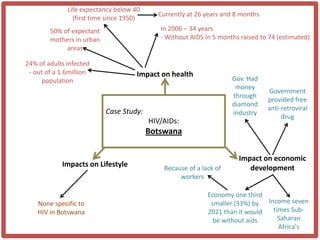
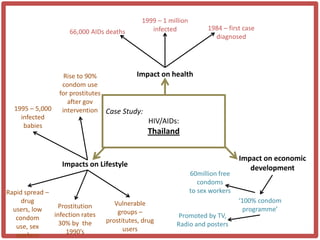
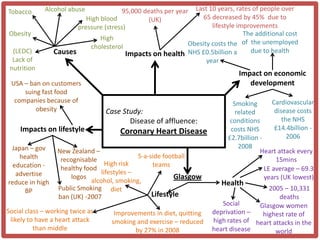
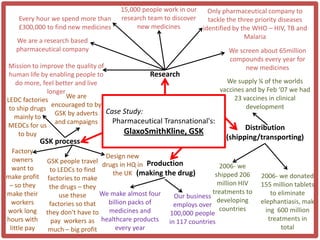
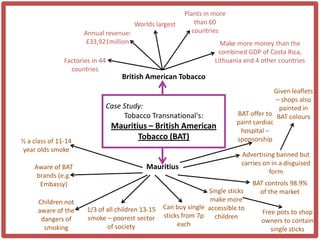
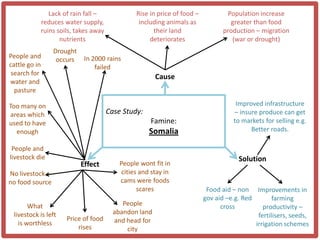
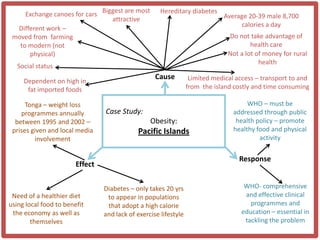
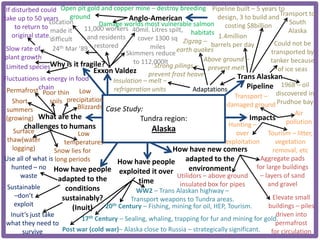
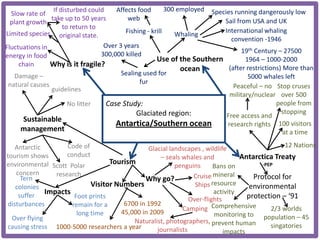
Haiti is the poorest country in the Western Hemisphere with 80% of the population living in absolute poverty. It has experienced rapid population growth, doubling in size in less than 50 years to over 8 million people. This has resulted in high population density of 295 people per square kilometer and significant population pressure on the limited resources and fragile environment. Solutions that have been tried include family planning programs, education initiatives, and efforts to increase economic opportunities.