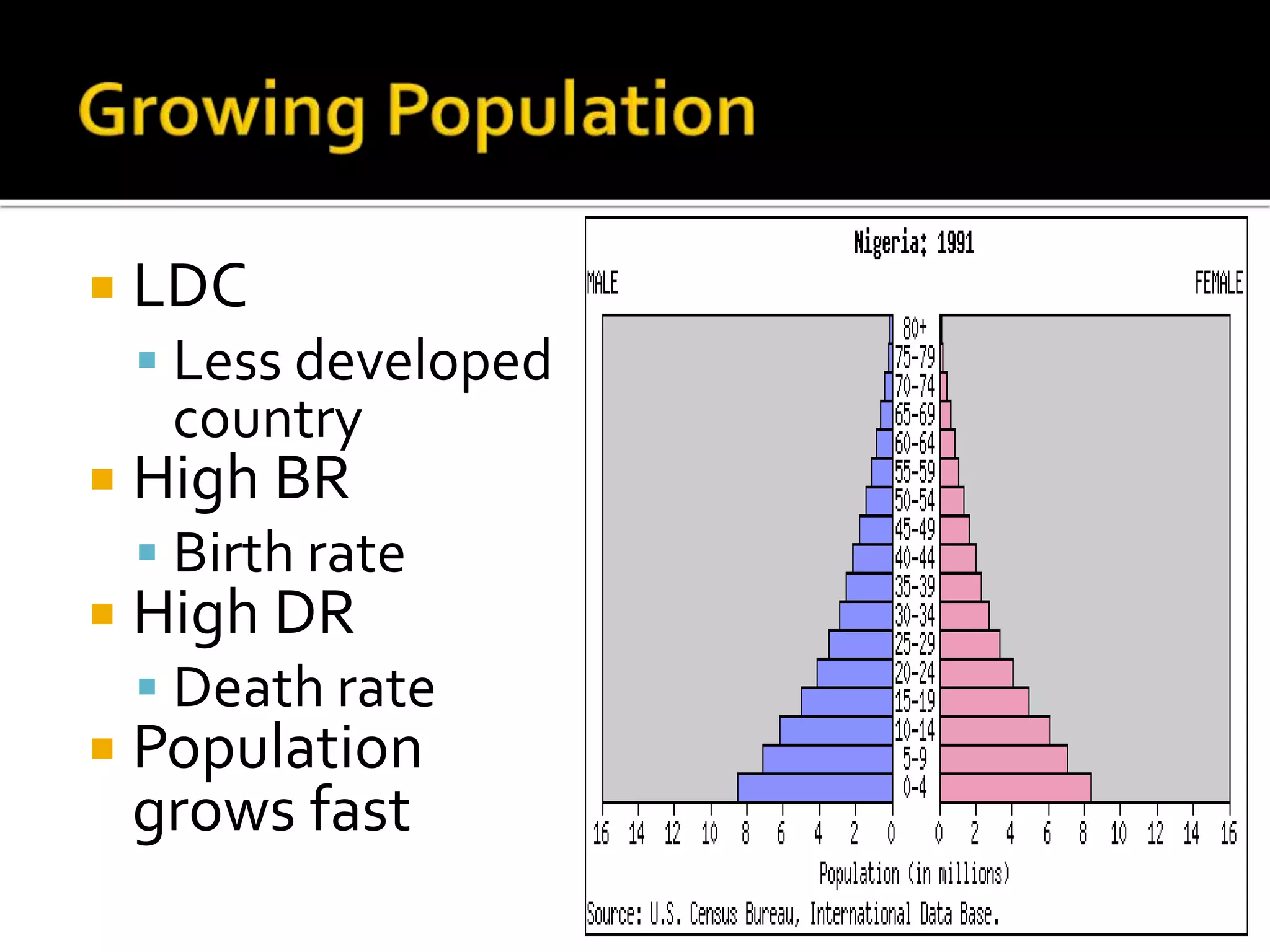
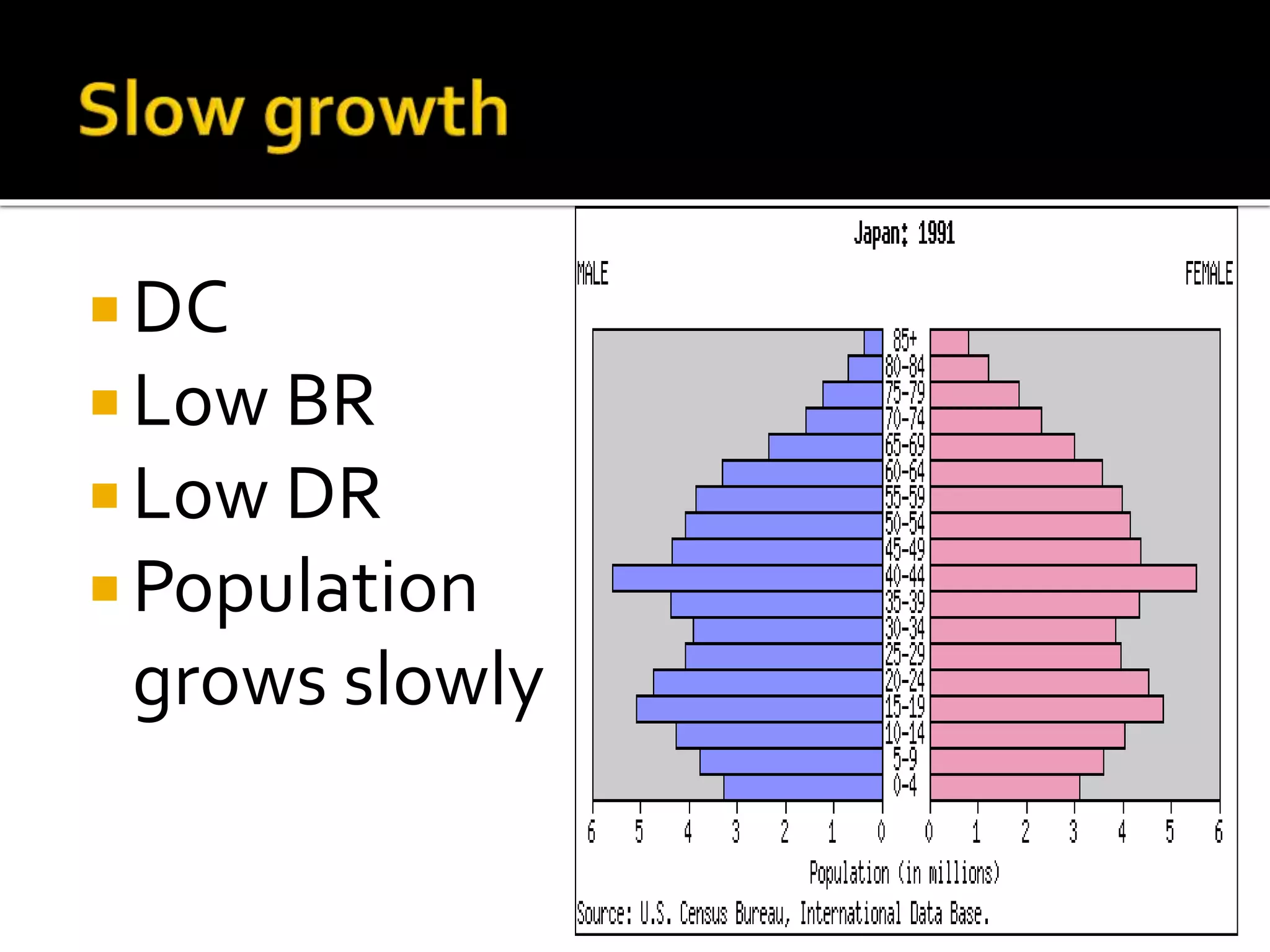
This document provides information about population growth rates in less developed countries (LDCs) and developed countries (DCs). It discusses the high population growth rates in LDCs due to factors like early marriage, high child mortality rates, lack of family planning education, and religious beliefs. This leads to issues like overcrowding, food shortages, and pressure on social services. Ways to reduce high growth include economic development, birth control programs, and increasing literacy. DCs have slower or declining growth due to lower birth rates from family planning, education, higher costs of living, and preferences for smaller families.