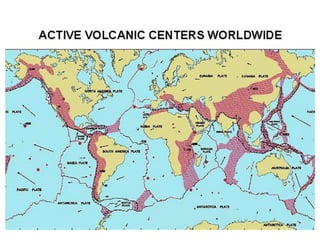
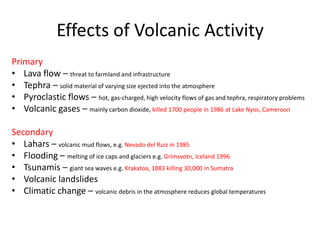
The document discusses plate tectonics and associated hazards. It describes the structure of the Earth's interior with an inner core, outer core, mantle and crust. The crust is divided into plates that move via convection currents in the asthenosphere. Plates interact at boundaries that are either constructive, destructive, or conservative. Destructive boundaries result in volcanoes, earthquakes and fold mountains through processes like subduction. Plate movement is evidenced by magnetic striping in ocean crust. Hazards vary depending on the type of boundary and are managed differently in LEDCs and MEDCs.