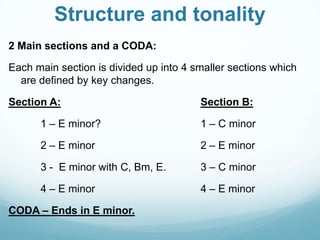
Steve Reich's "Electric Counterpoint" is a minimalist work composed in 1987 for an electric guitarist. It uses layering and phase shifting techniques where short melodic motifs are played across multiple tracks of electric guitars and bass. The piece has three movements and is composed of short repeating ostinato patterns that build up in complexity through the layering of guitar and bass parts.