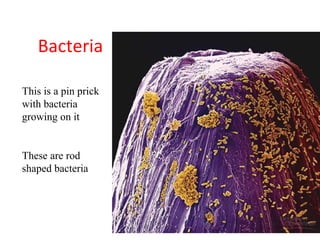
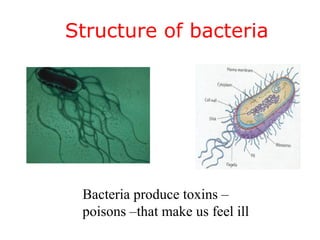
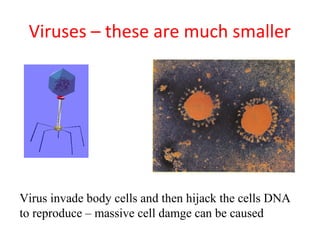
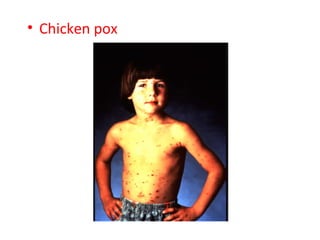
Diseases can be acquired through genetic, microbial, or parasitic means, with pathogens such as bacteria and viruses being the most common causes. Bacteria can thrive outside host organisms and produce toxins, while viruses require host cells to reproduce, often causing significant cell damage. The document lists various viral and bacterial infectious diseases, highlighting examples like AIDS, chicken pox, and tuberculosis.





![A few diseases – wikipedia linked
• Viral infectious diseases
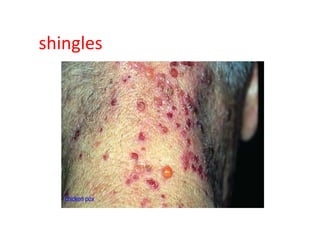
• AIDS – AIDS Related Complex – Chickenpox (Varicella) – Common cold –
Cytomegalovirus Infection – Colorado tick fever – Dengue fever –
Ebola haemorrhagic fever – Epidemic parotitis –
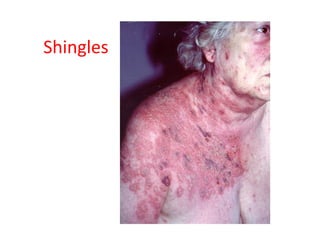
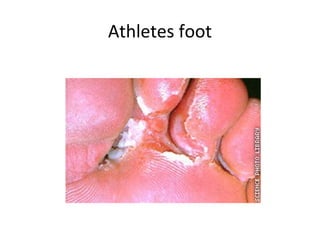
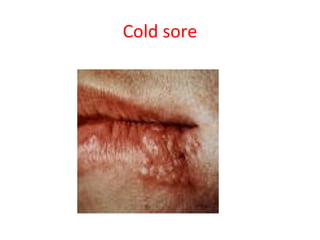
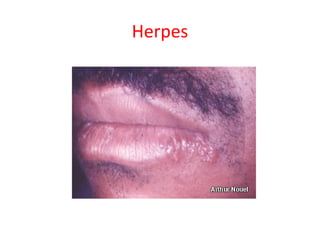
Hand, foot and mouth disease – Hepatitis – Herpes simplex – Herpes zoster –
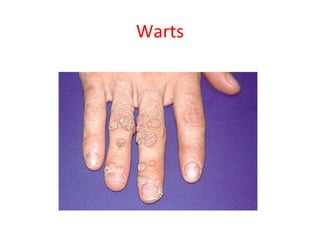
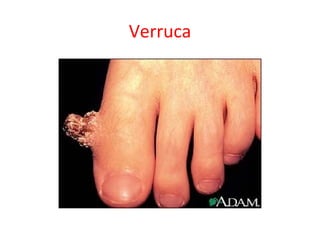
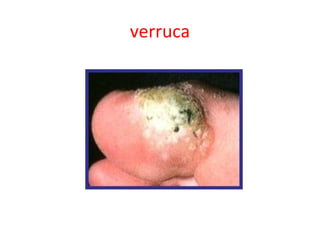
HPV – Influenza (Flu) – Lassa fever – Measles – Marburg haemorrhagic fever –
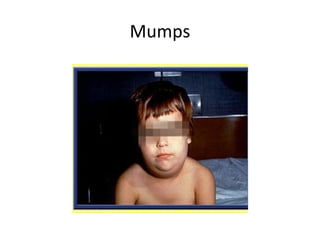
Infectious mononucleosis – Mumps – Poliomyelitis –
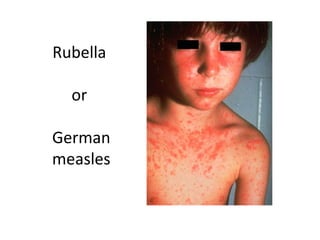
Progressive multifocal leukencephalopathy – Rabies – Rubella – SARS –
Smallpox (Variola) – Viral encephalitis – Viral gastroenteritis – Viral meningitis
– Viral pneumonia – West Nile disease – Yellow fever
• [edit]
• Bacterial infectious diseases
• Anthrax – Bacterial Meningitis – Brucellosis – Campylobacteriosis –
Cat Scratch Disease – Cholera – Diphtheria – Epidemic Typhus – Gonorrhea –
Impetigo– Legionellosis – Leprosy (Hansen's Disease) – Leptospirosis –
Listeriosis – Lyme Disease – Melioidosis – MRSA infection – Nocardiosis –
Pertussis (Whooping Cough) – Plague – Pneumococcal pneumonia –
Psittacosis – Q fever – Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF) – Salmonellosis
– Scarlet Fever – Shigellosis – Syphilis – Tetanus – Trachoma – Tuberculosis –
Tularemia – Typhoid Fever – Typhus; Urinary Tract Infections](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aqab1a11-4diseasepicsrg1-120921082016-phpapp01/85/Aqa-b1a-11-4_disease_pics_rg-1-22-320.jpg)