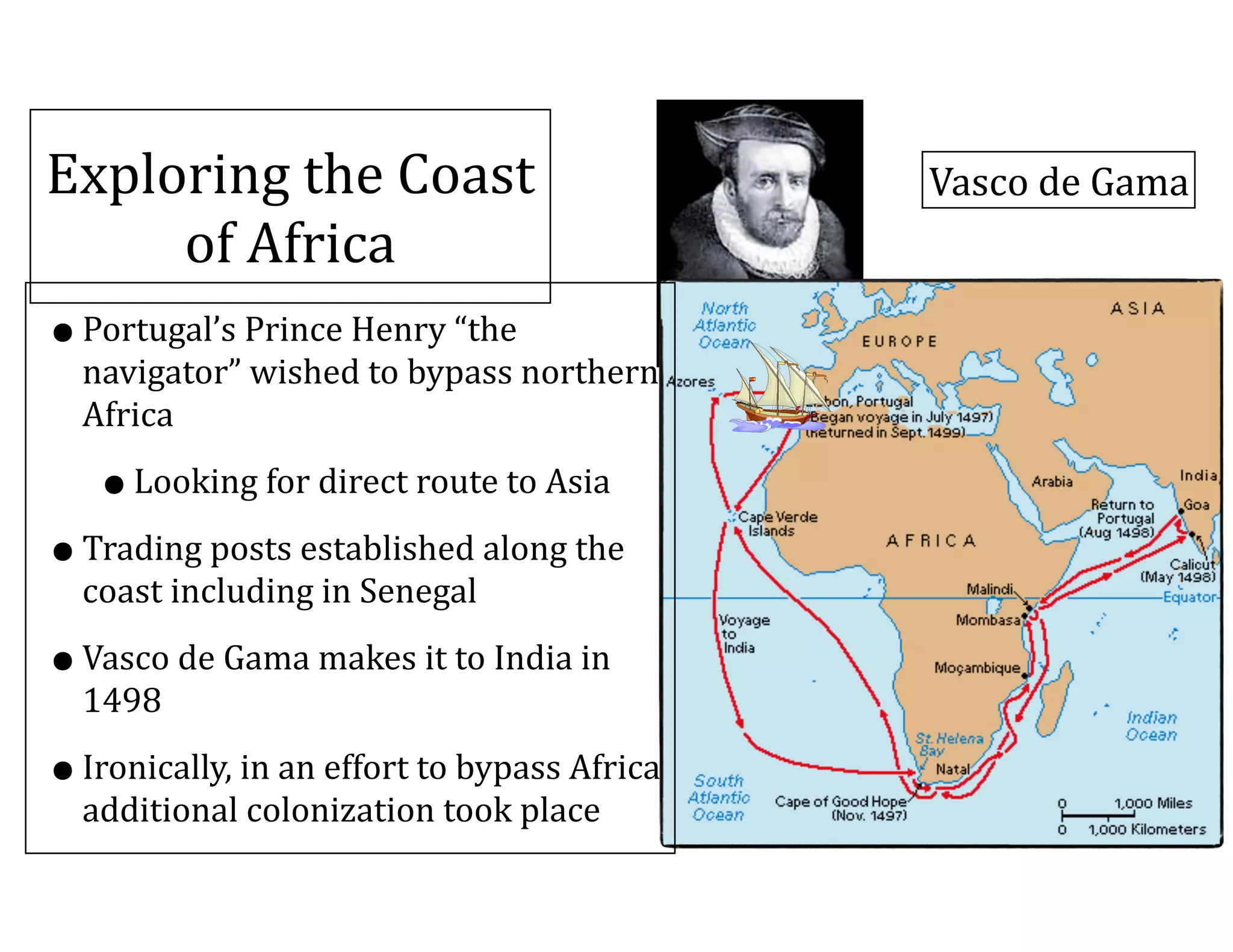
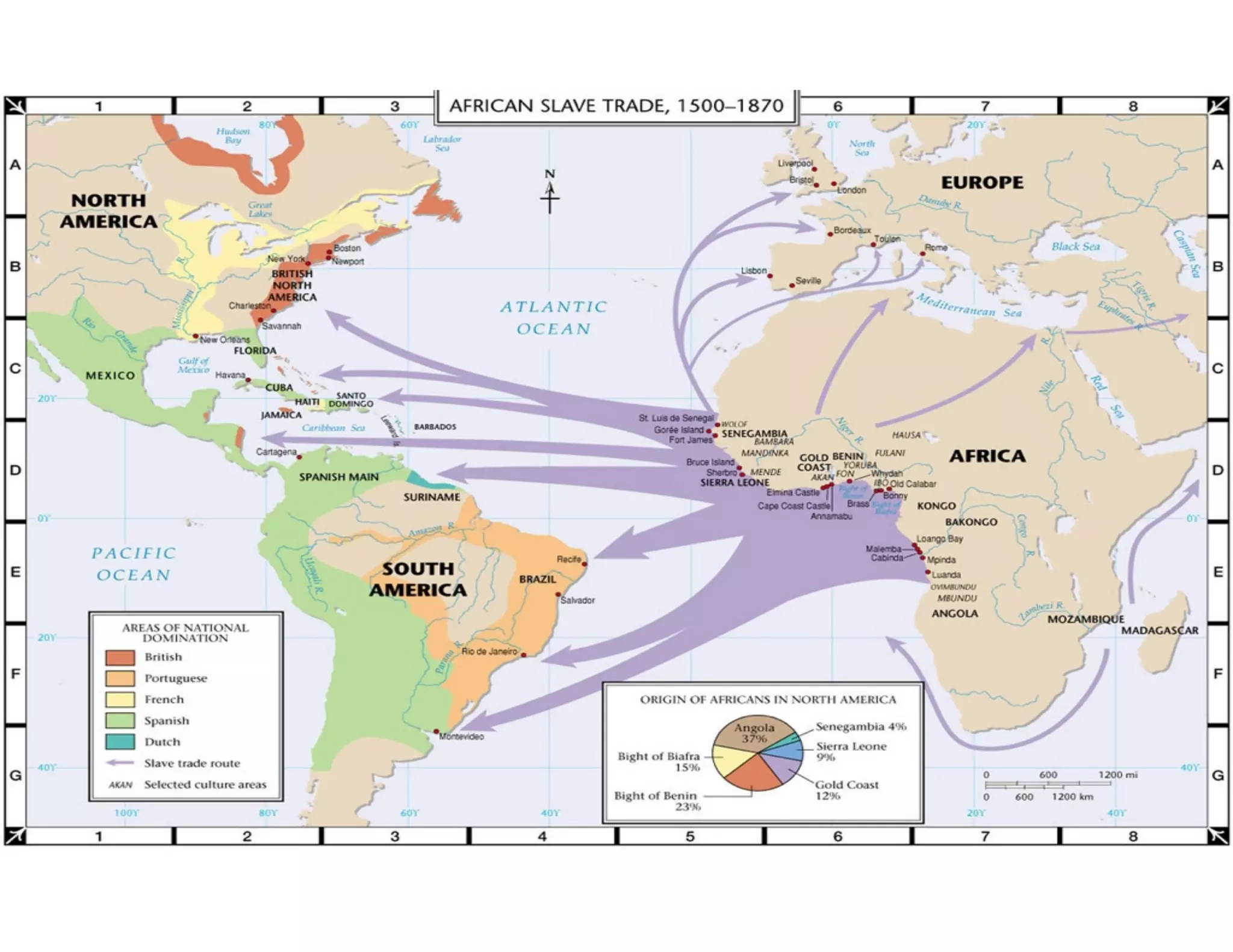
This document outlines the agenda and key topics for a lecture on West African trading empires between 790-1600 CE. It discusses the rise and fall of several major empires, including Ghana, Mali, Songhai, and Benin, and how the trans-Saharan gold-salt trade led to the growth of cities and spread of Islam. It also examines how increased demand for slaves in the 1500s due to European colonization of the Americas led to the devastation of the African slave trade.