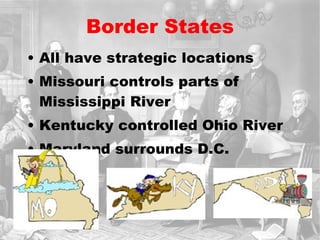
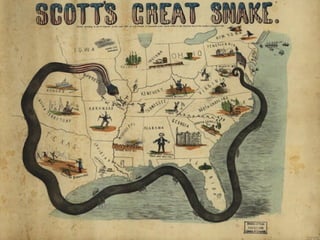
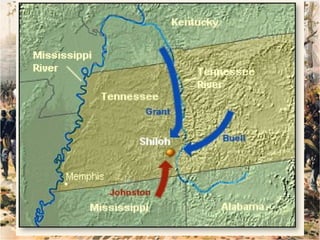
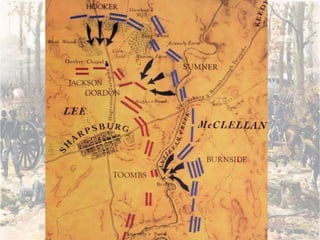
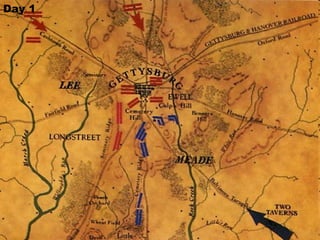
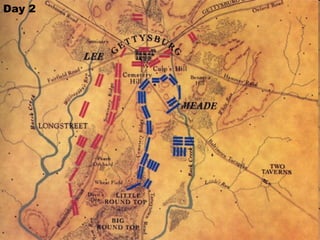
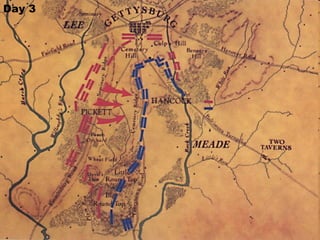
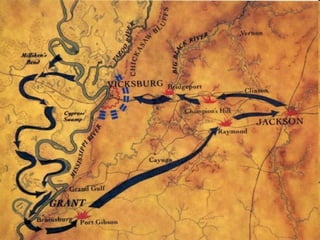
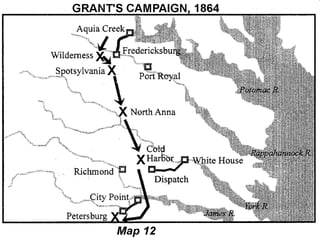
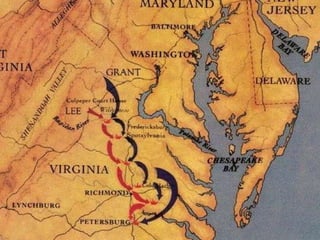
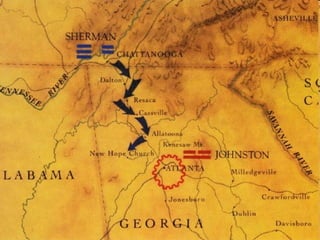
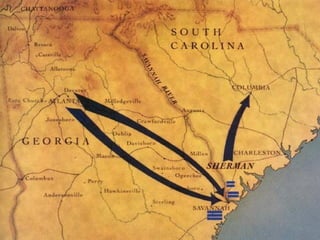
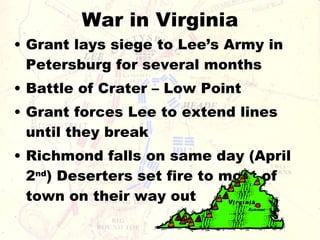
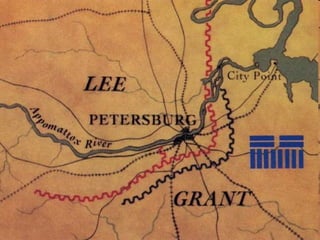
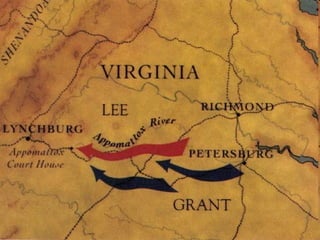
The Civil War was fought between the Union (North) and the Confederacy (South) from 1861 to 1865. It resulted in around 600,000 casualties and determined that the United States would remain unified rather than split into multiple countries. Key events and battles included the First Battle of Bull Run, which showed the war would not be short; Gettysburg, a major turning point; Sherman's March to the Sea, which helped turn sentiment against the Confederacy; and Lee's surrender to Grant at Appomattox, effectively ending the war. The Union's victory abolished slavery and strengthened the federal government.