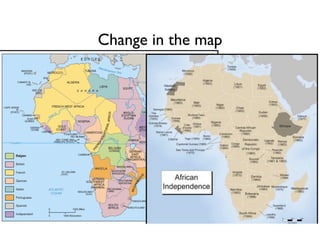
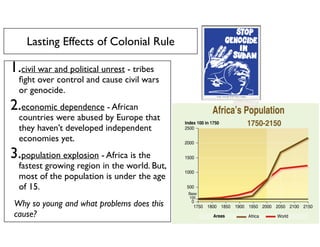
The document summarizes key aspects of African nationalism and decolonization. It discusses how Europeans practiced paternalism over African citizens. It also describes how Pan-Africanism emerged as a belief in uniting Africa in response to European colonialism. Important figures like Marcus Garvey and Leopold Sedar Senghor promoted Pan-Africanism and negritude. After World War 2 weakened European powers, independence movements gained strength and new African nations emerged, though colonial legacies had lasting effects.