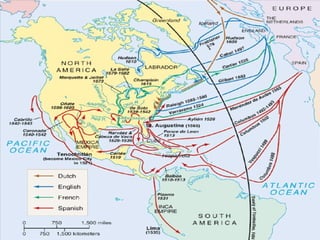
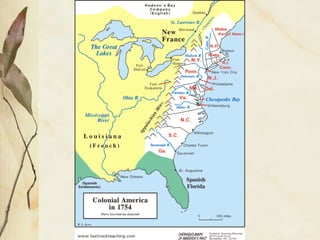
The document provides a detailed overview of colonial America, covering politics, economics, and society from the early 1600s to the 1700s. It discusses the founding and evolution of the 13 colonies, from their origins as proprietary or royal colonies established for economic or religious reasons, to the development of self-government and distinct regional identities. The economies shifted from reliance on industries like shipbuilding and subsistence farming to the rise of cash crops and slavery. Society was largely shaped by religion, with literacy and family structure varying significantly between New England and the South.