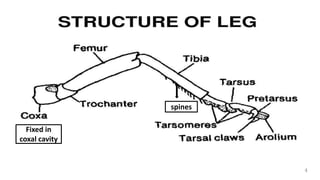
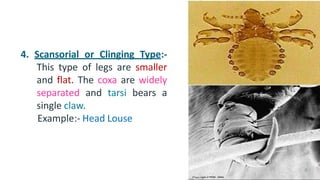
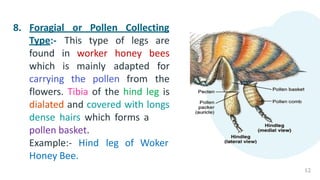
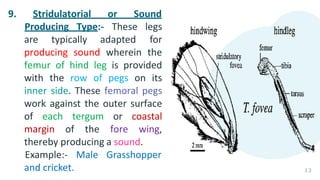
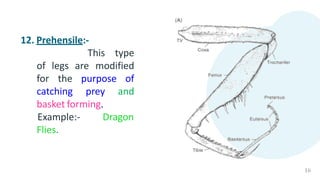
The document summarizes the different types of modifications that insect legs undergo according to the insect's habits and habitats. There are 12 main types of leg modifications described: 1) walking, 2) running, 3) jumping, 4) clinging, 5) digging, 6) grasping, 7) swimming, 8) pollen collecting, 9) sound producing, 10) sticking, 11) antennae cleaning, and 12) prehensile legs. Each modification type is accompanied by an example insect to illustrate the structure and function of the specialized leg.