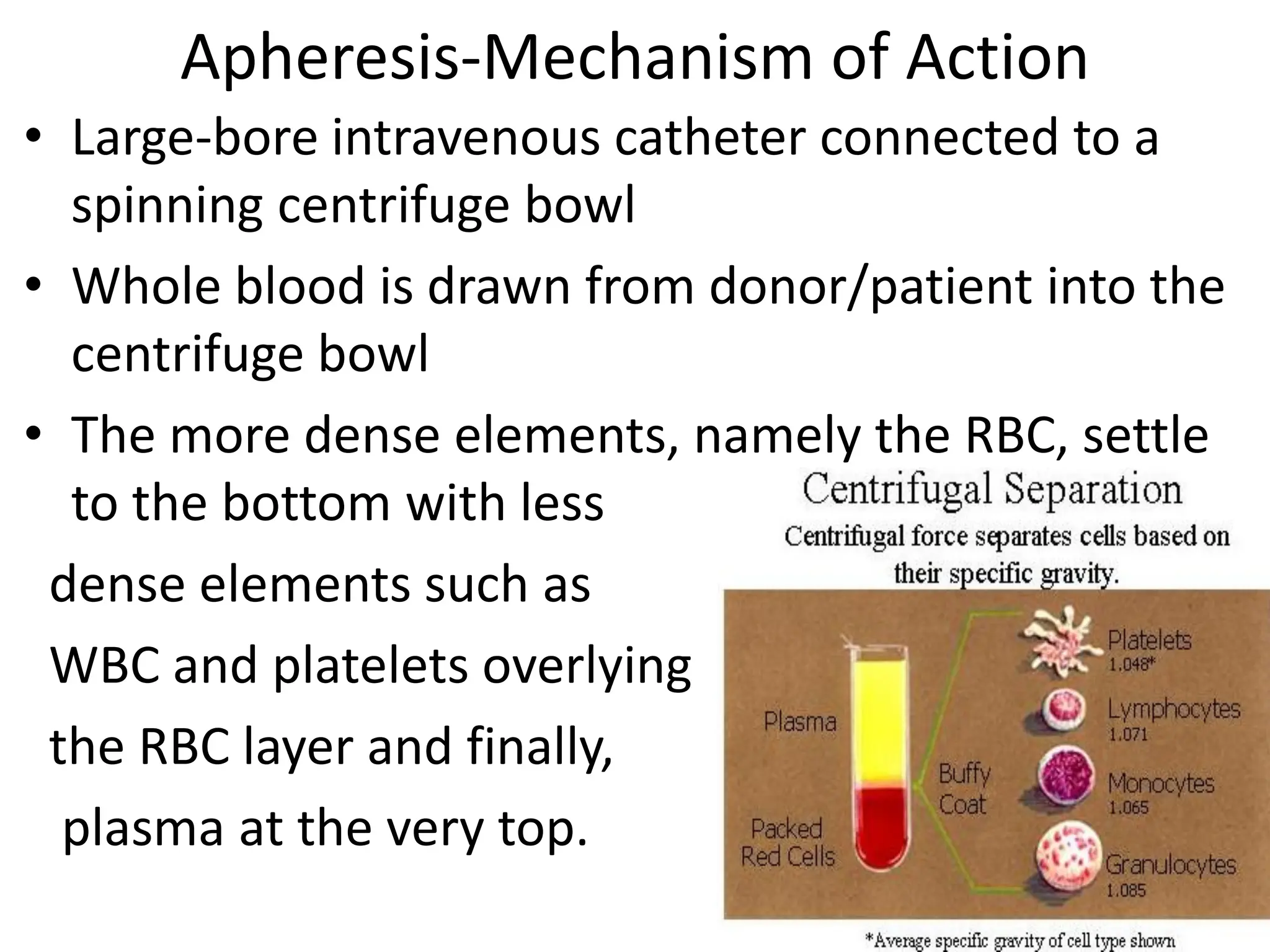
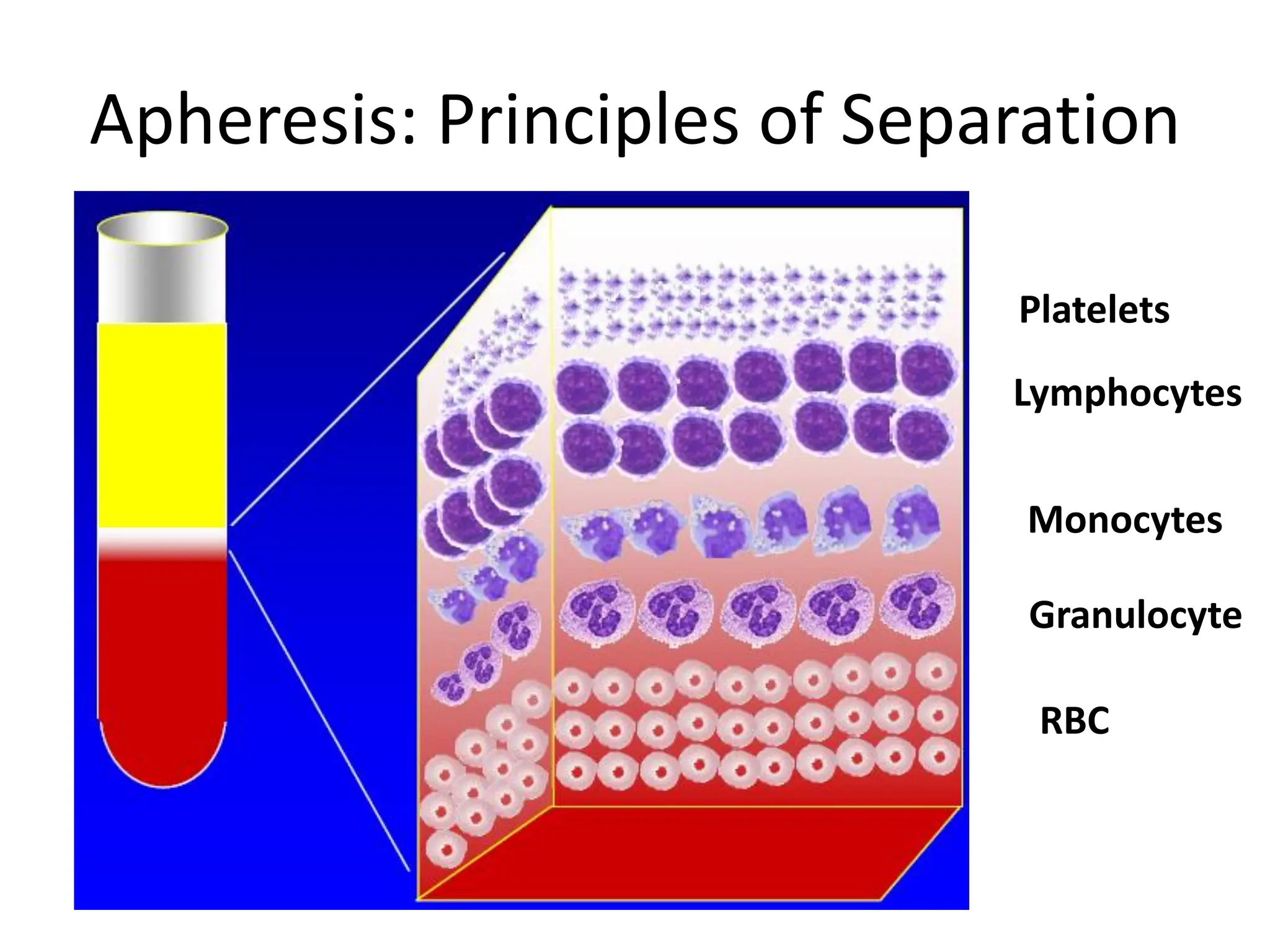
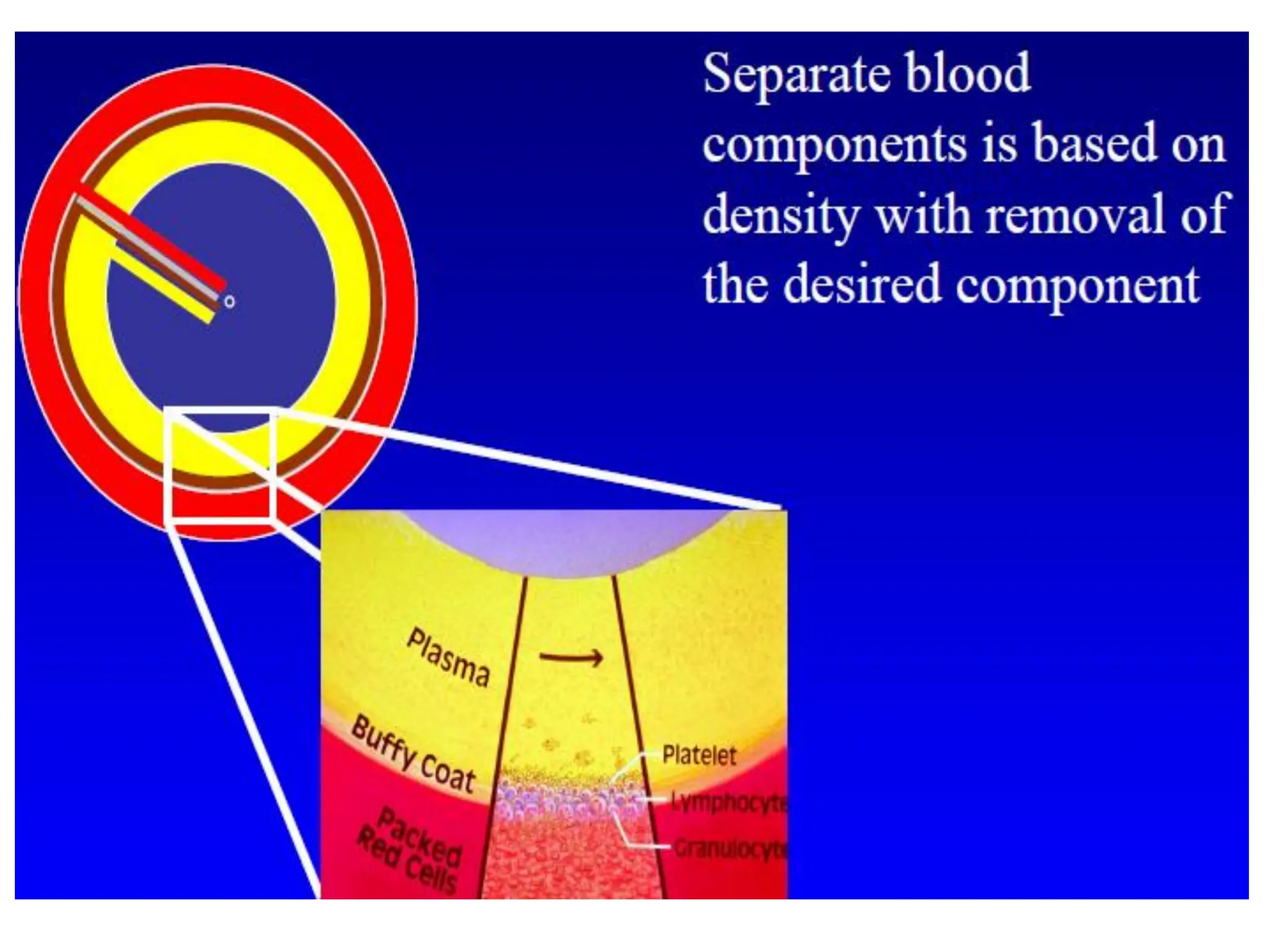
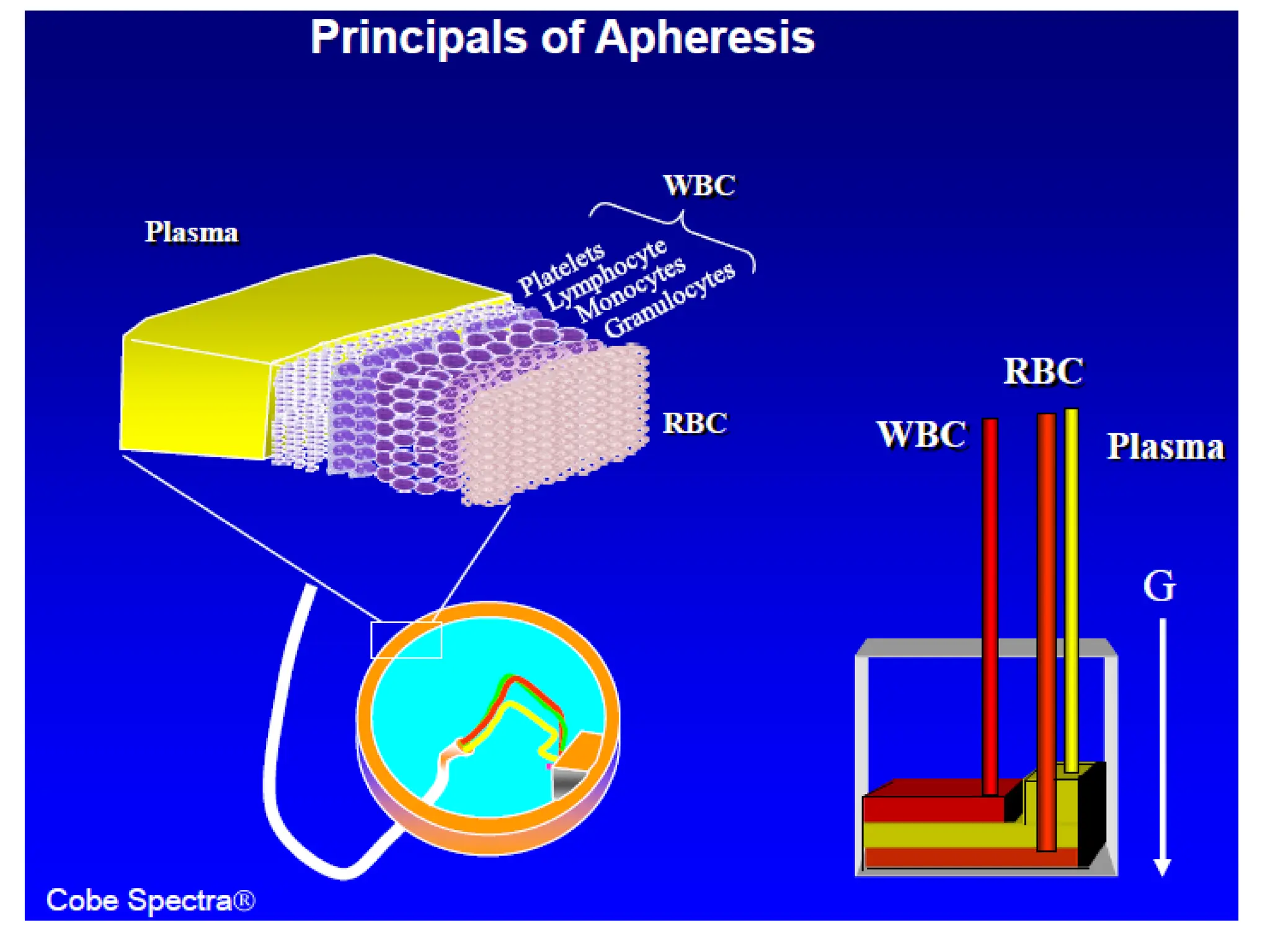
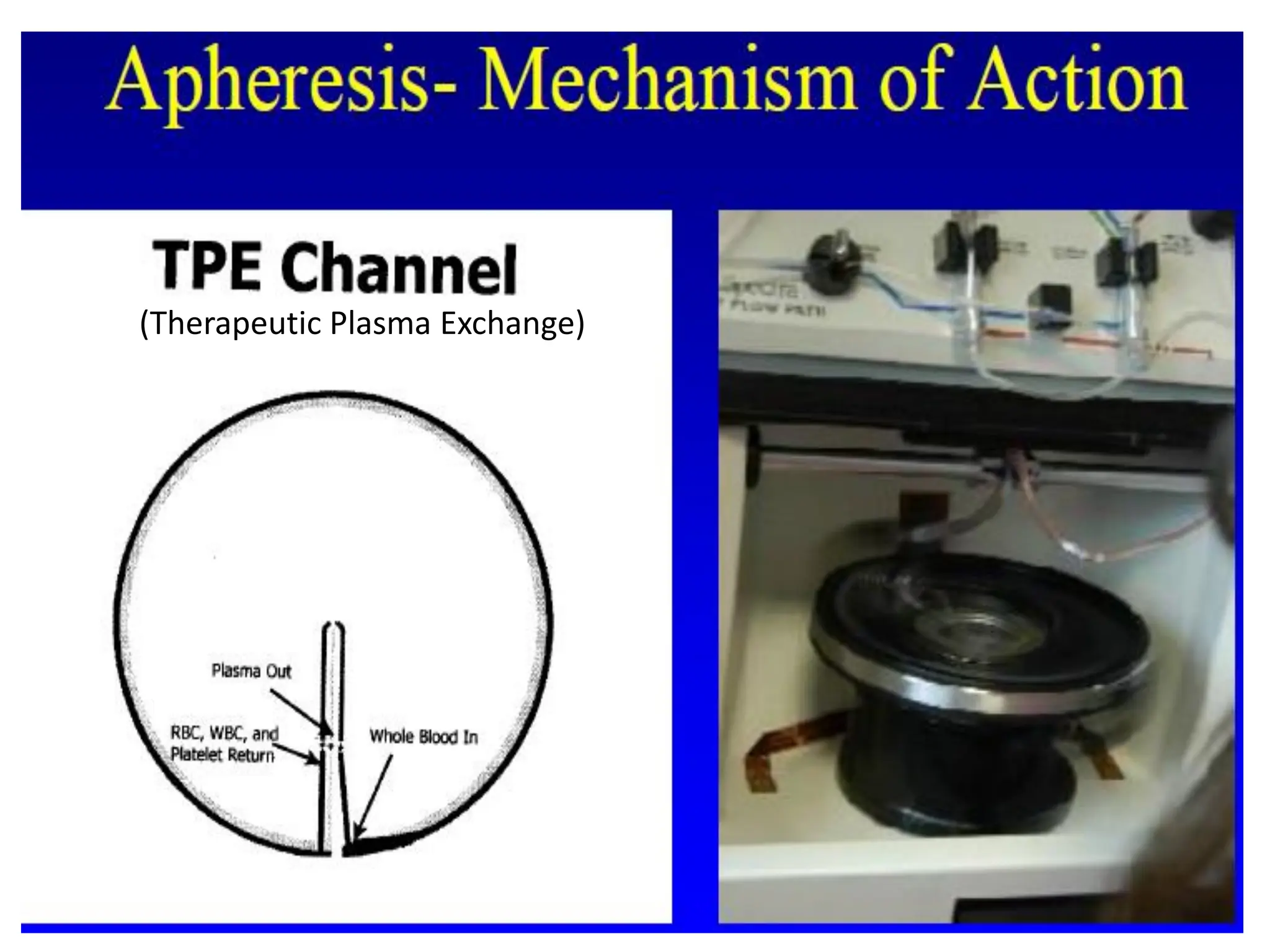
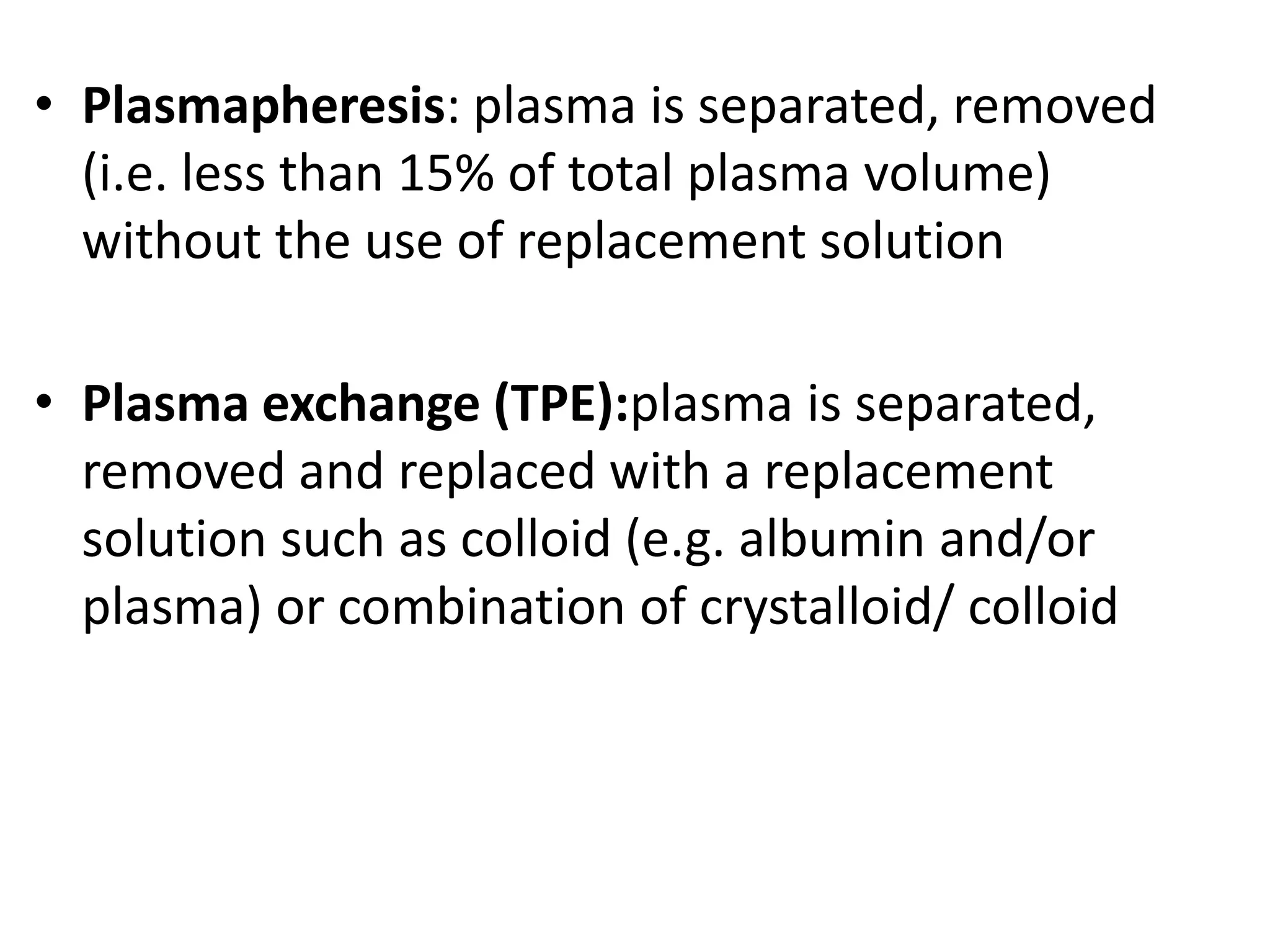
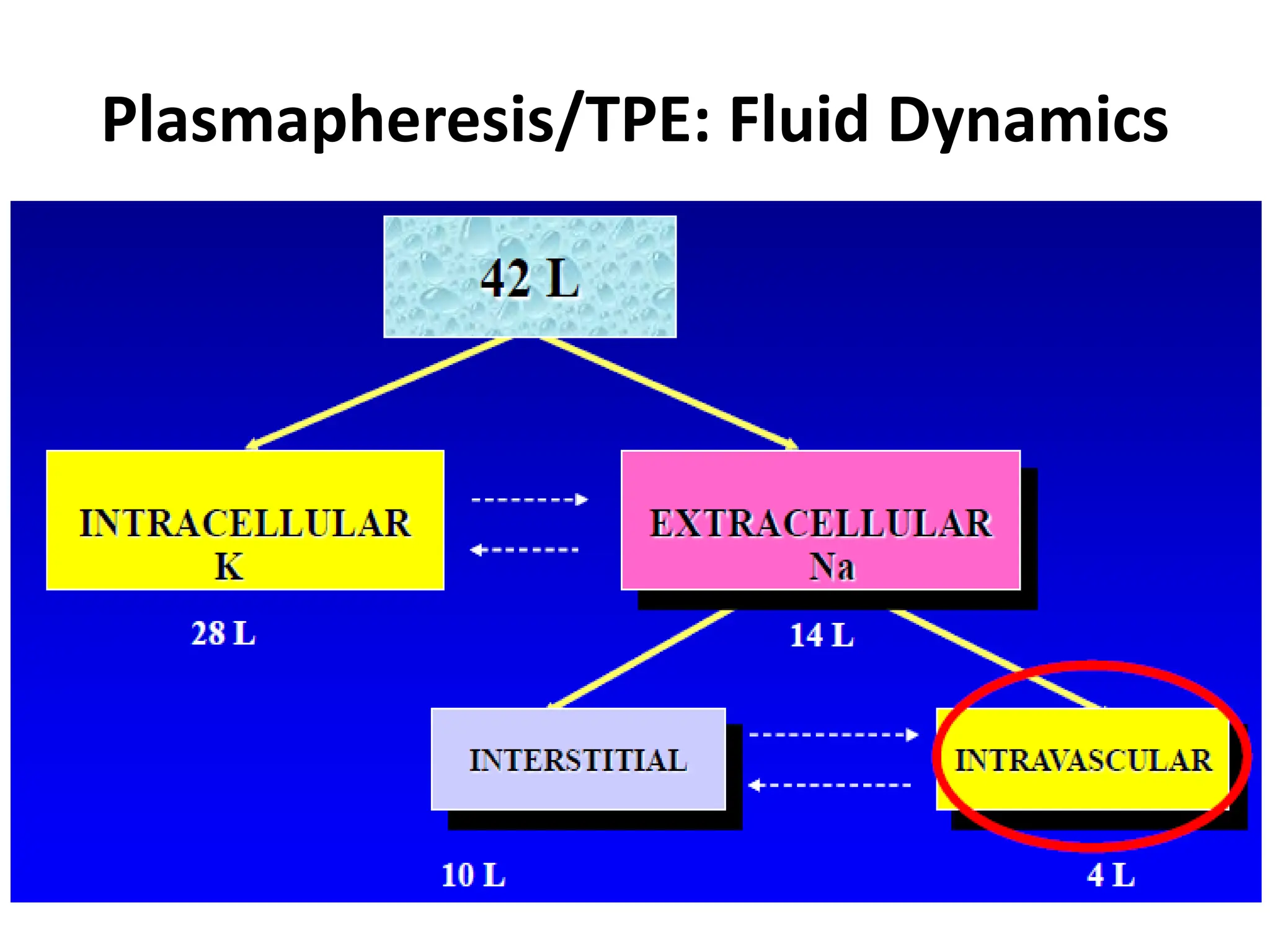
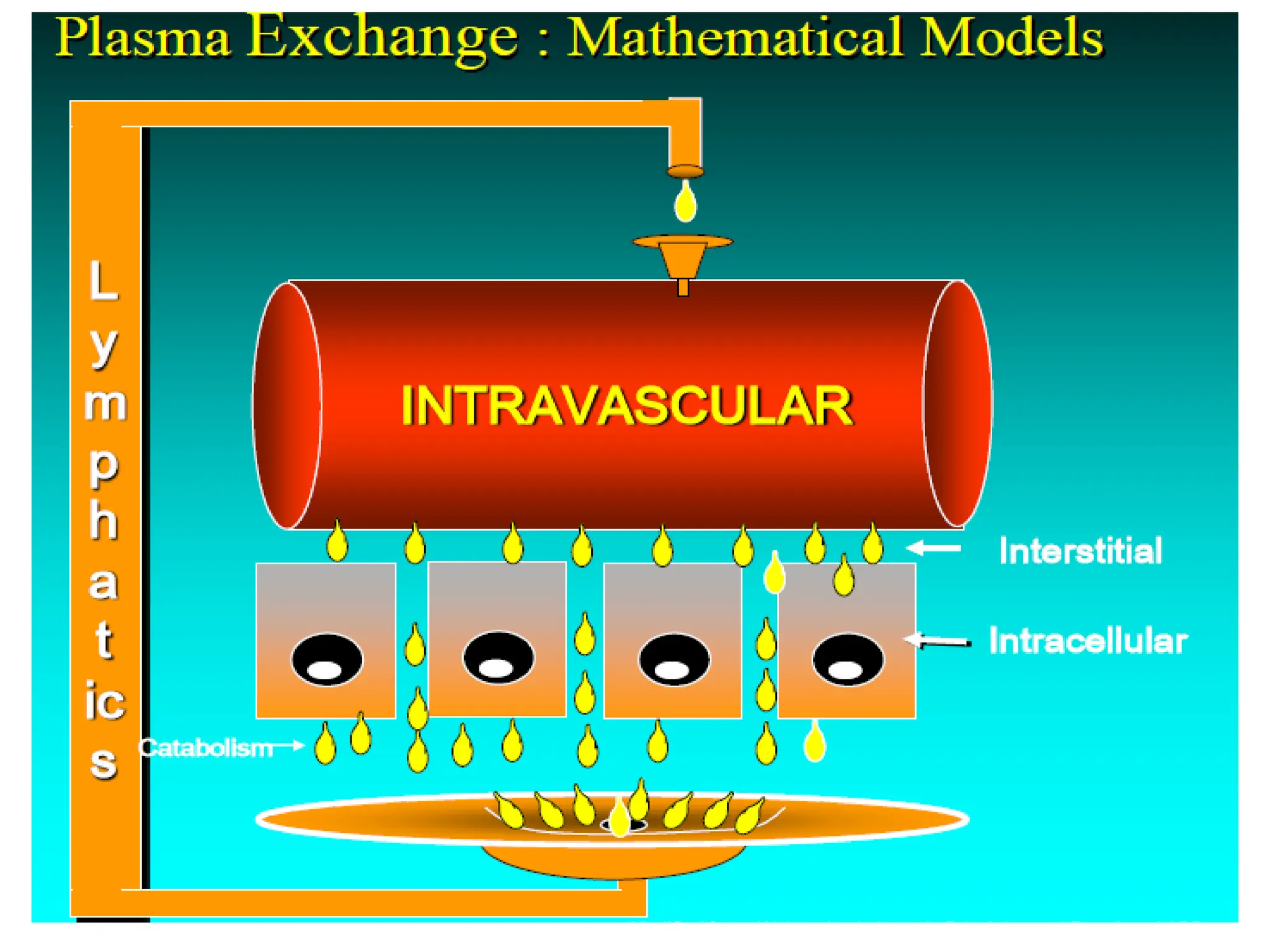
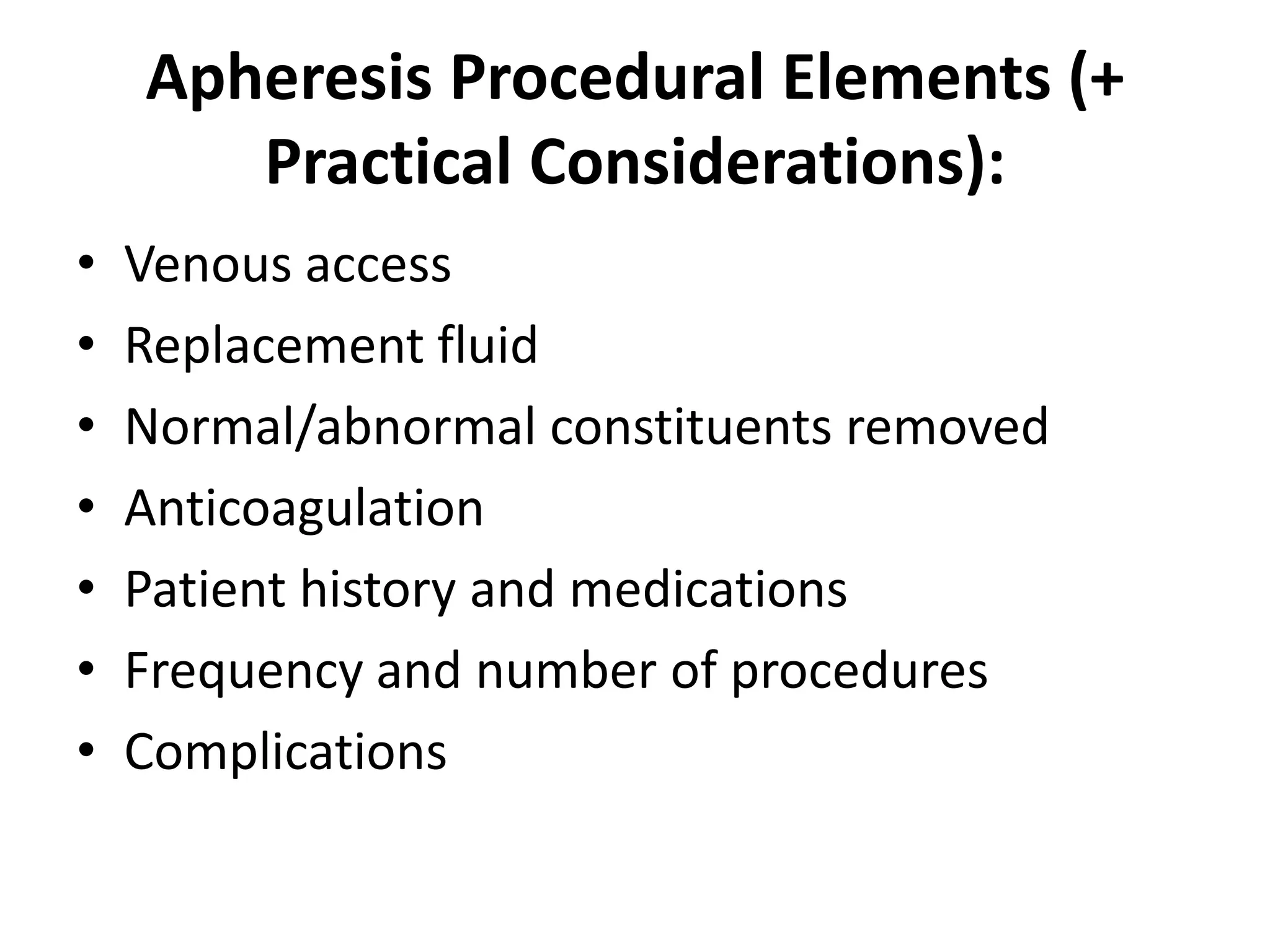
Apheresis is a medical procedure that separates desired components from whole blood using a centrifuge, allowing for therapies such as plasmapheresis and therapeutic apheresis to remove abnormal substances like autoantibodies and toxins. Key aspects include patient history, venous access, anticoagulation, and selection of replacement fluids, which can be either crystalloids or colloids. Effective management of fluid balance and monitoring of coagulation factors post-procedure are essential for patient safety and treatment efficacy.









![Replacement Fluid
• Fluid Must be FDA approved to use w/blood
products [ get mixed w/rbc before the return
phase]
• Replacement solutions:
– *Crystalloids–normal saline 0.9%
– *Colloids–5% albumin; plasma
*The primary function of the replacement fluid is to
maintain intravascular volume
**additional features:-Restoration of important plasma
proteins-Maintenance of colloid osmotic pressure-
Maintenance of electrolyte balance](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/11-240520161435-7483d11e/75/11-Lecture-Apheresis-by-Riaz-pdf-what-is-apheresis-written-precisely-19-2048.jpg)