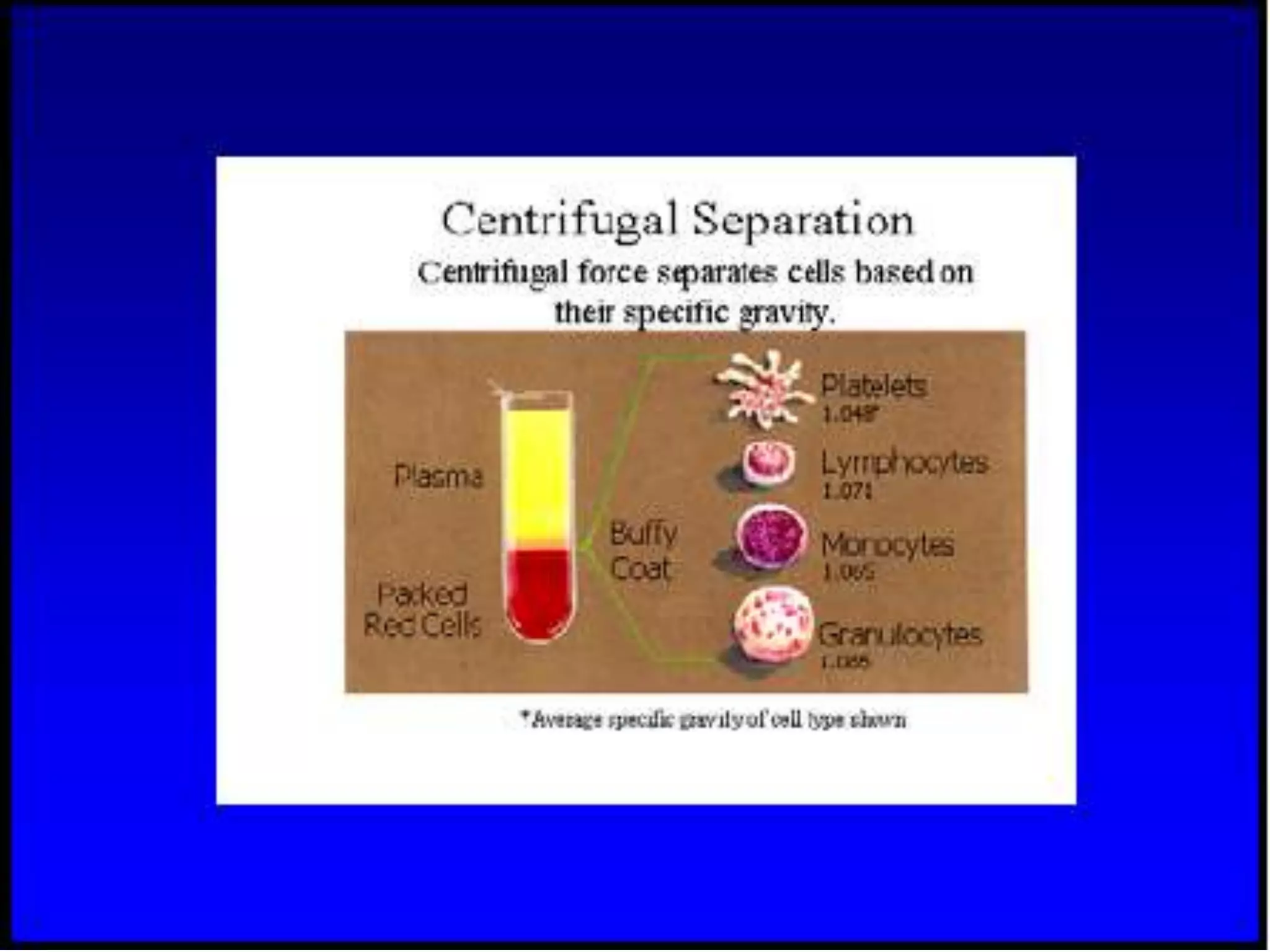
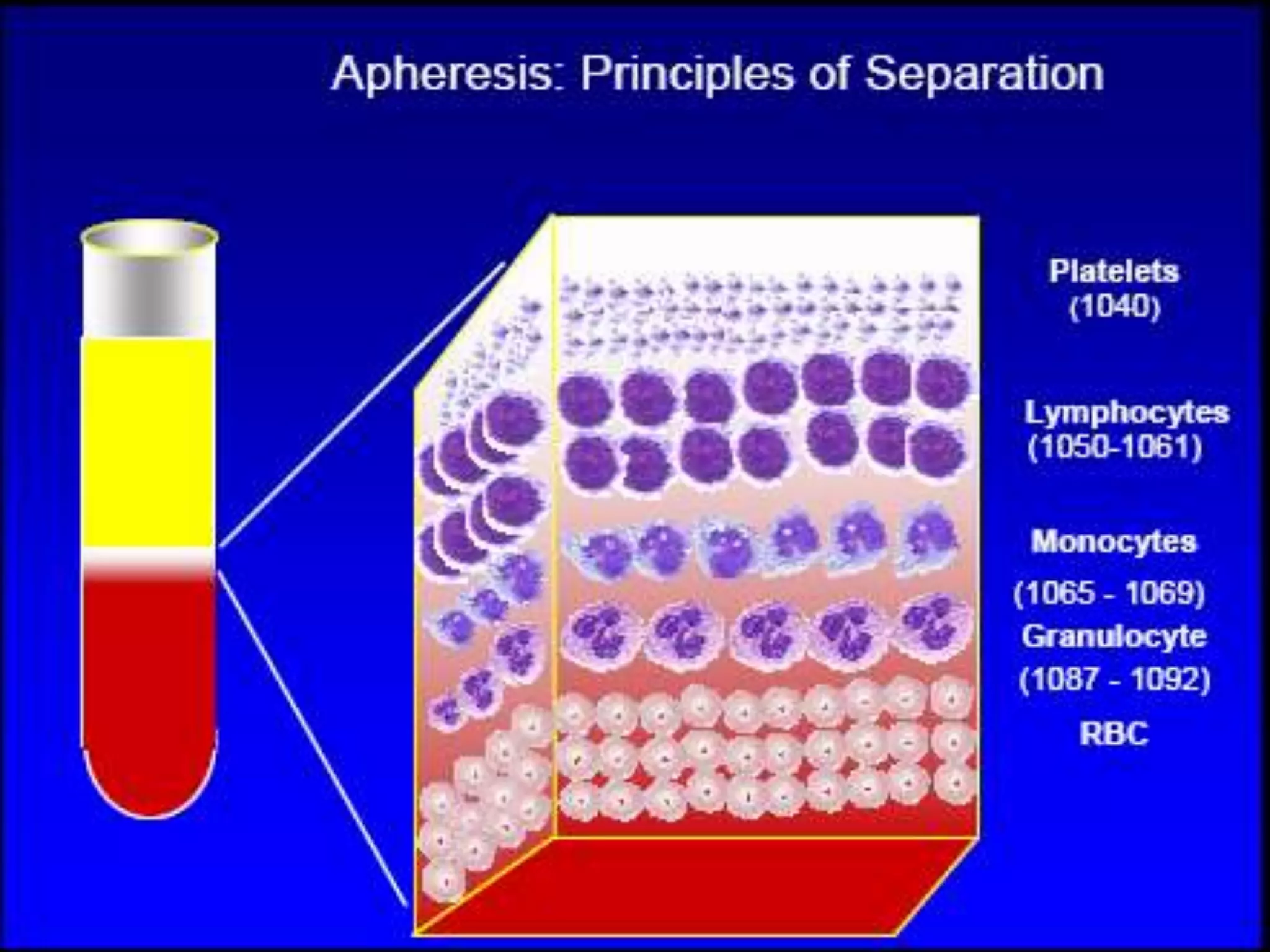
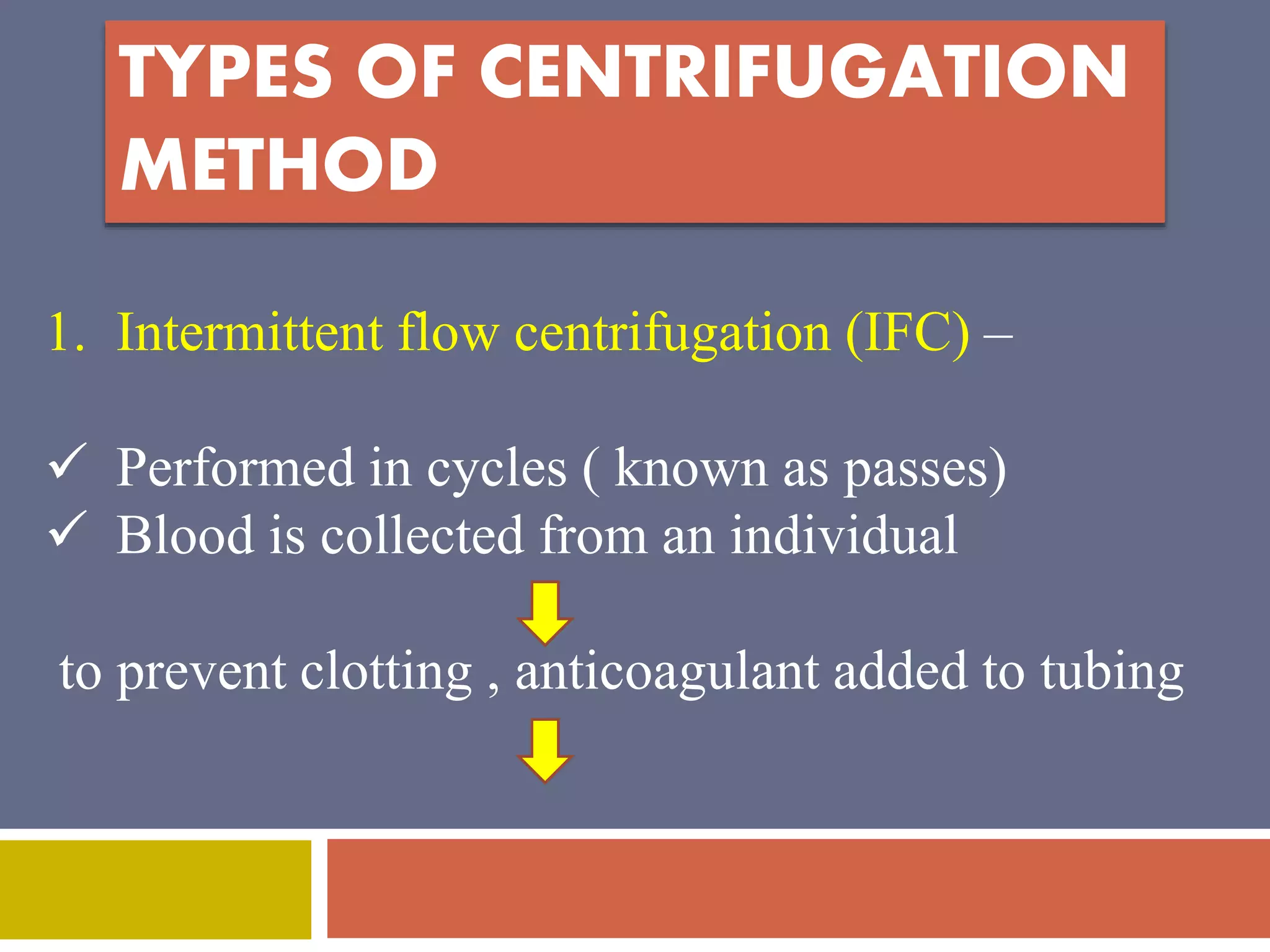
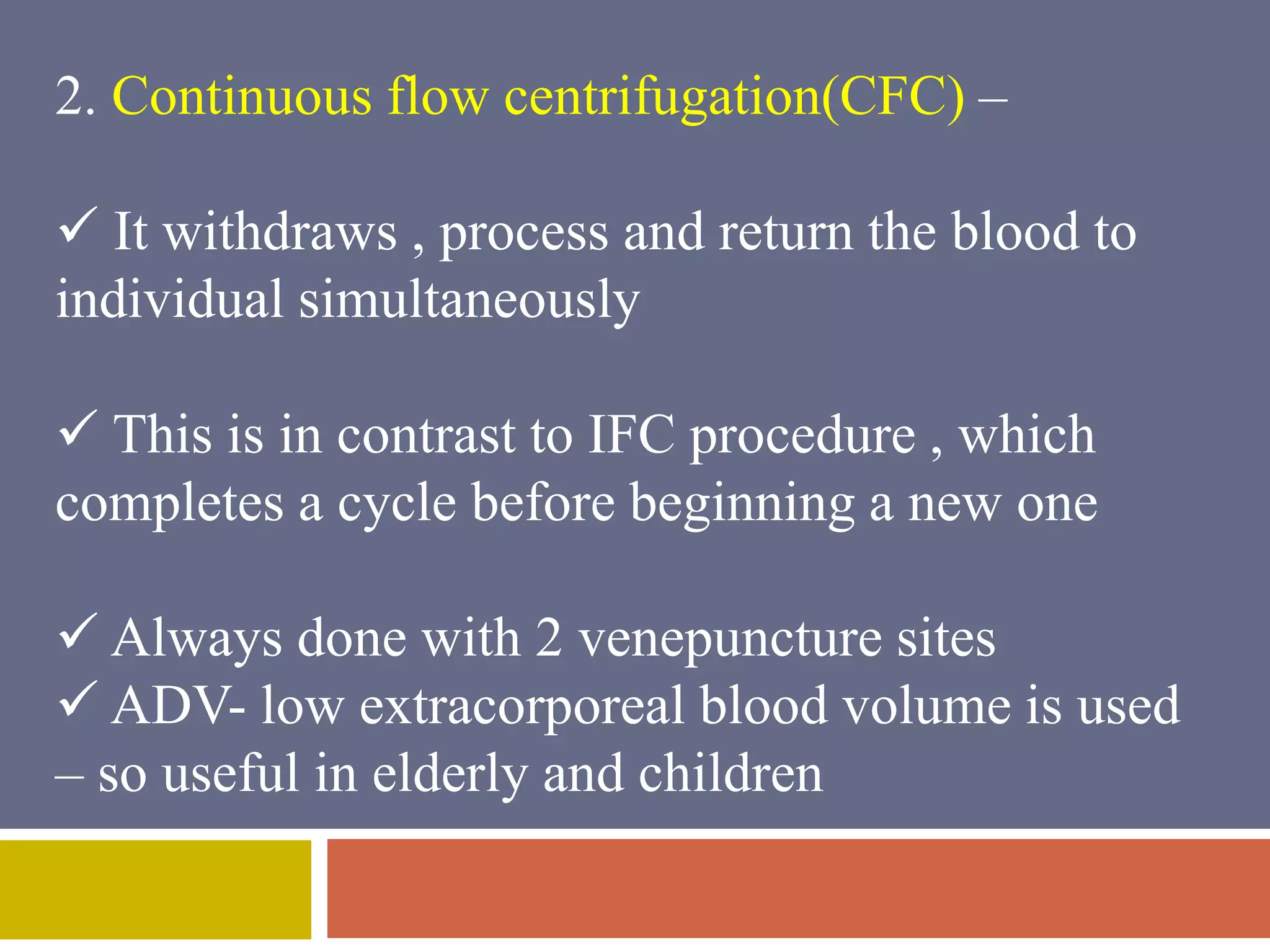
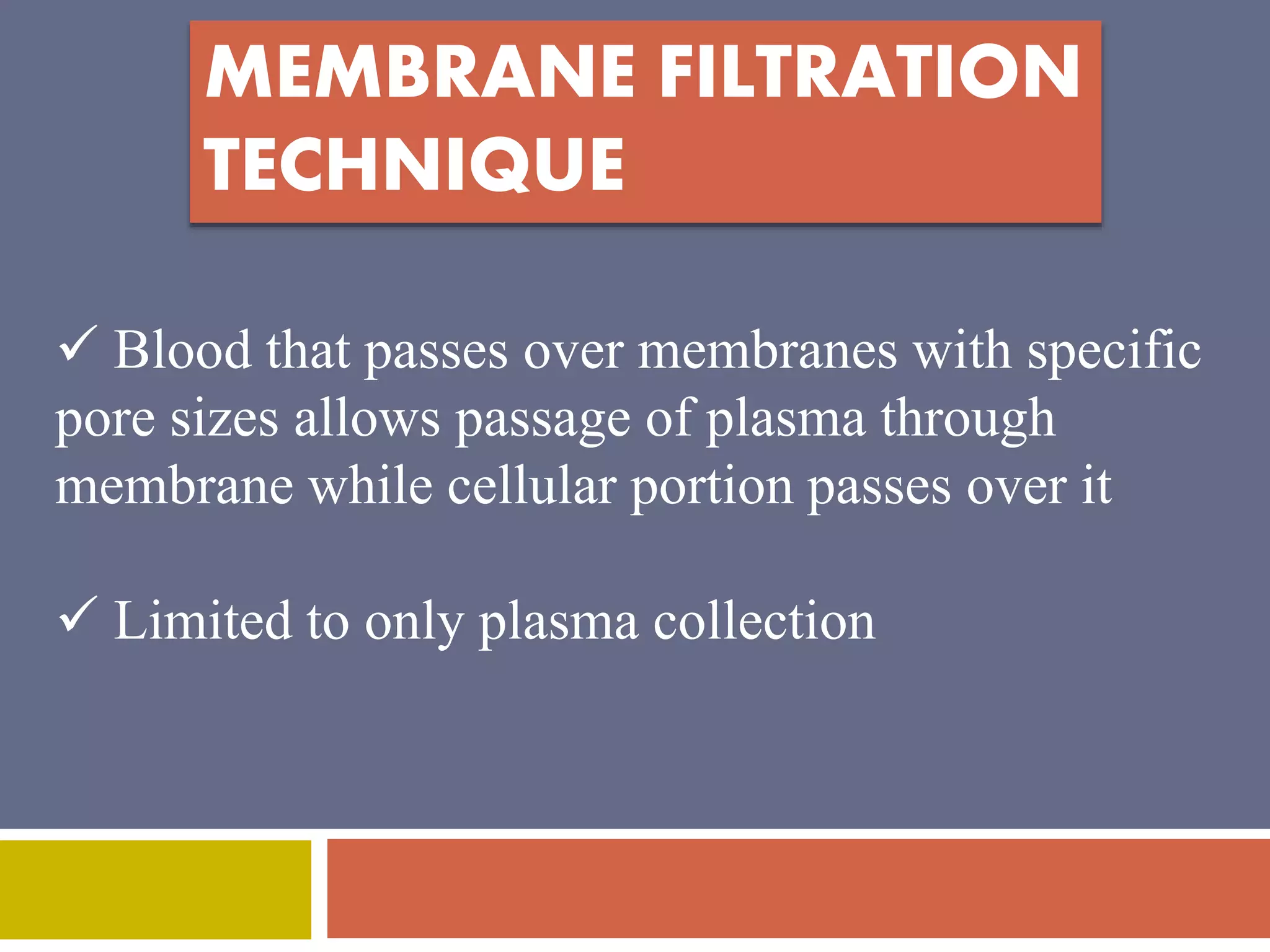
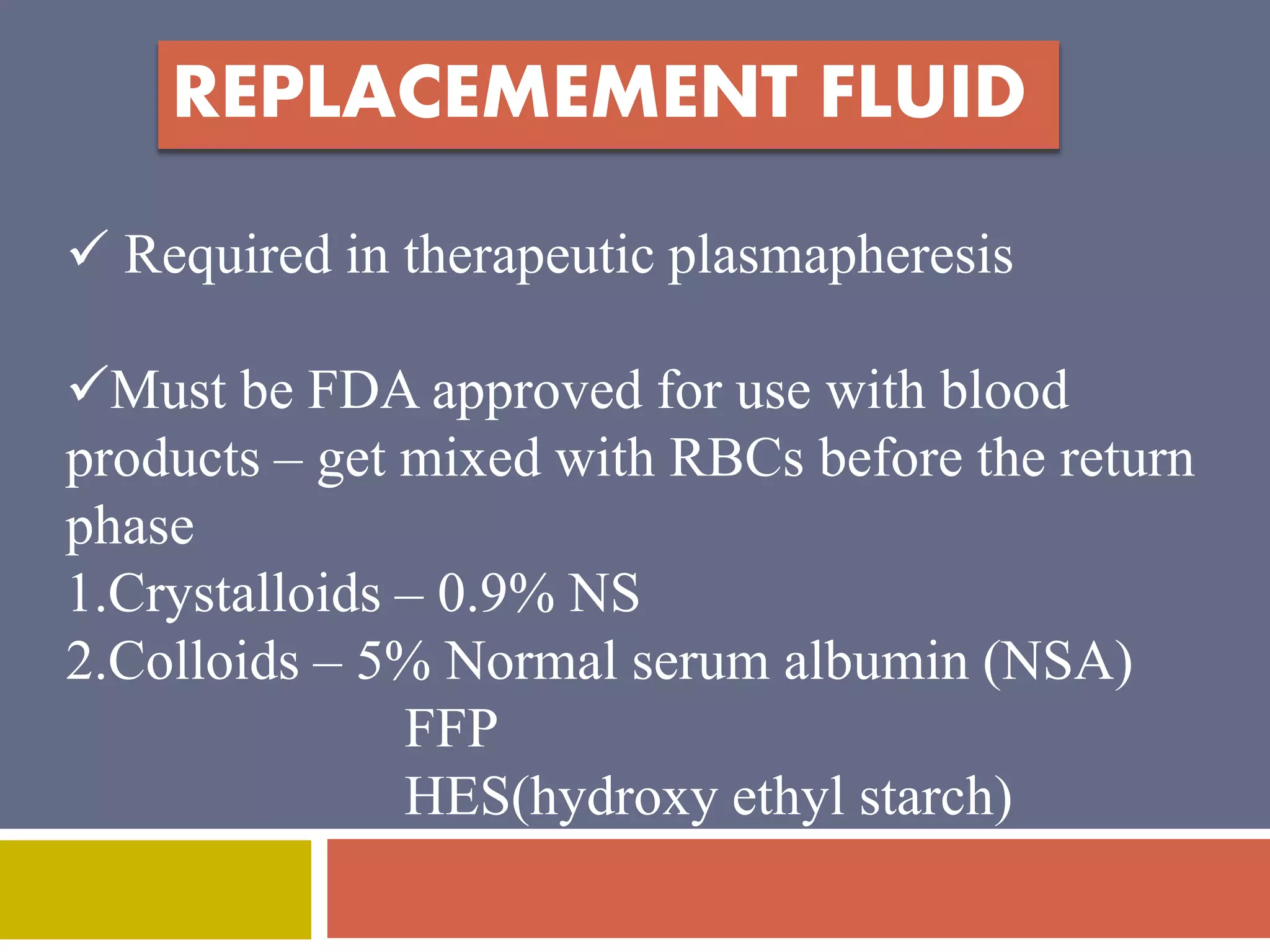
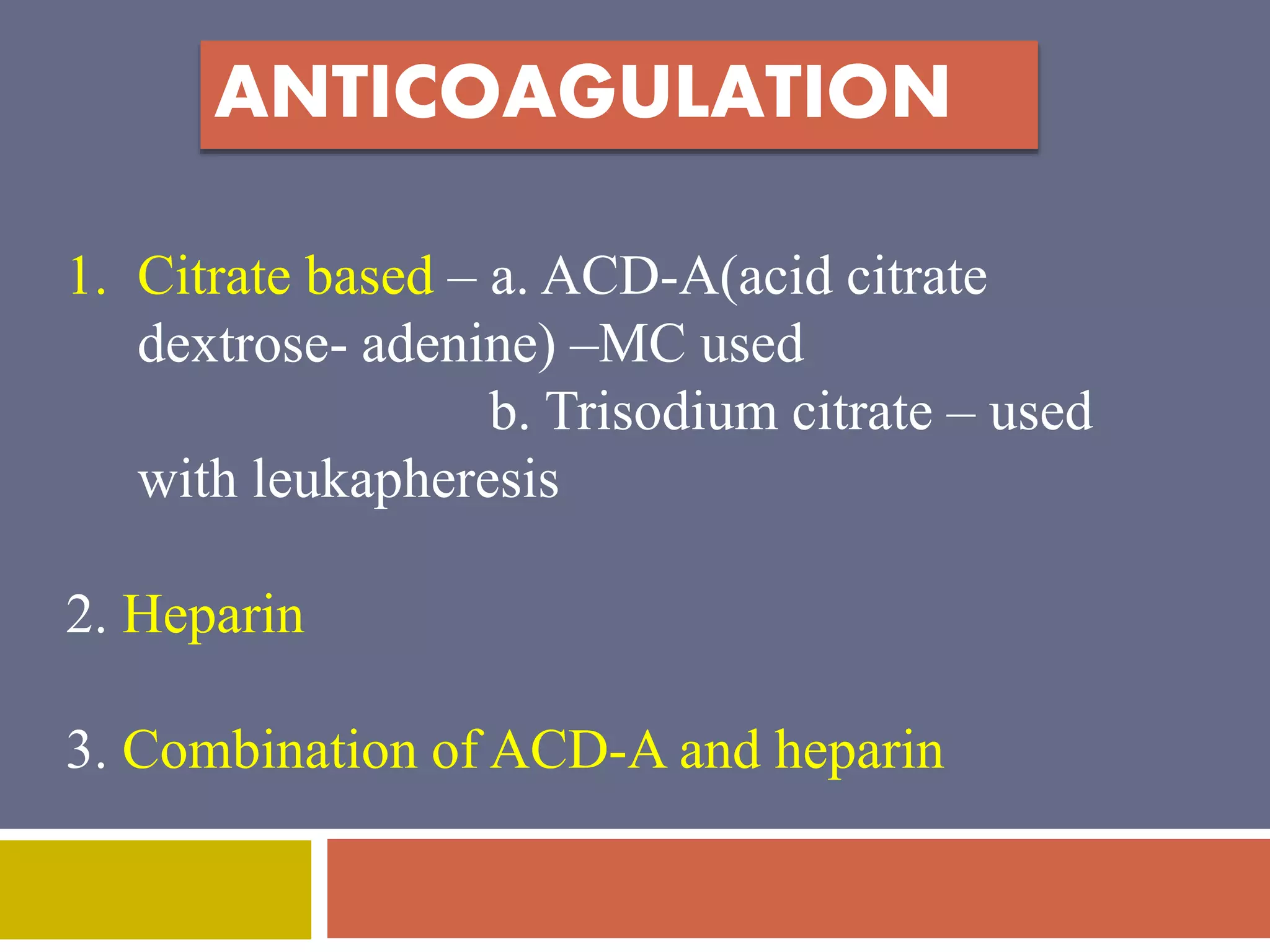
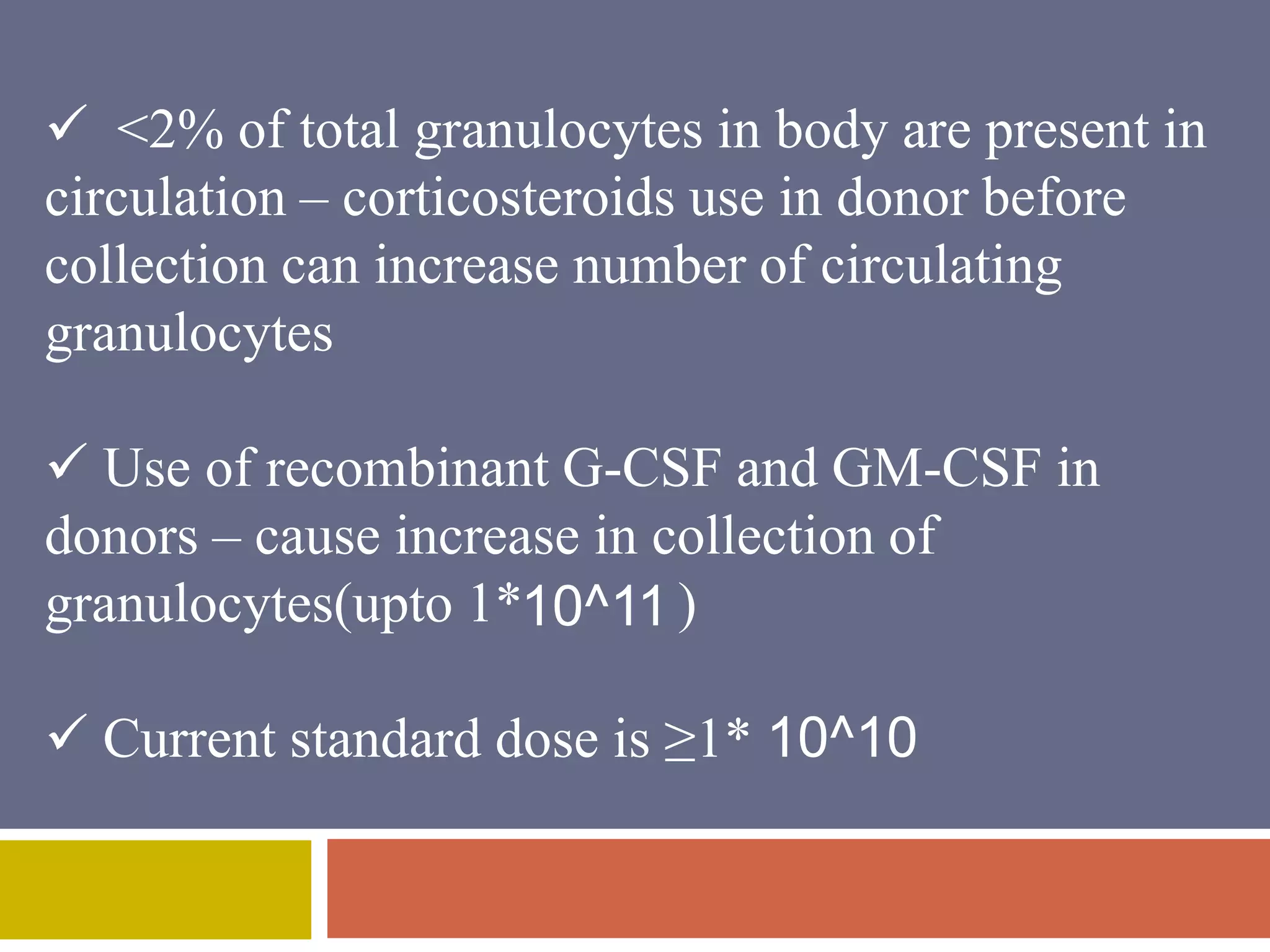
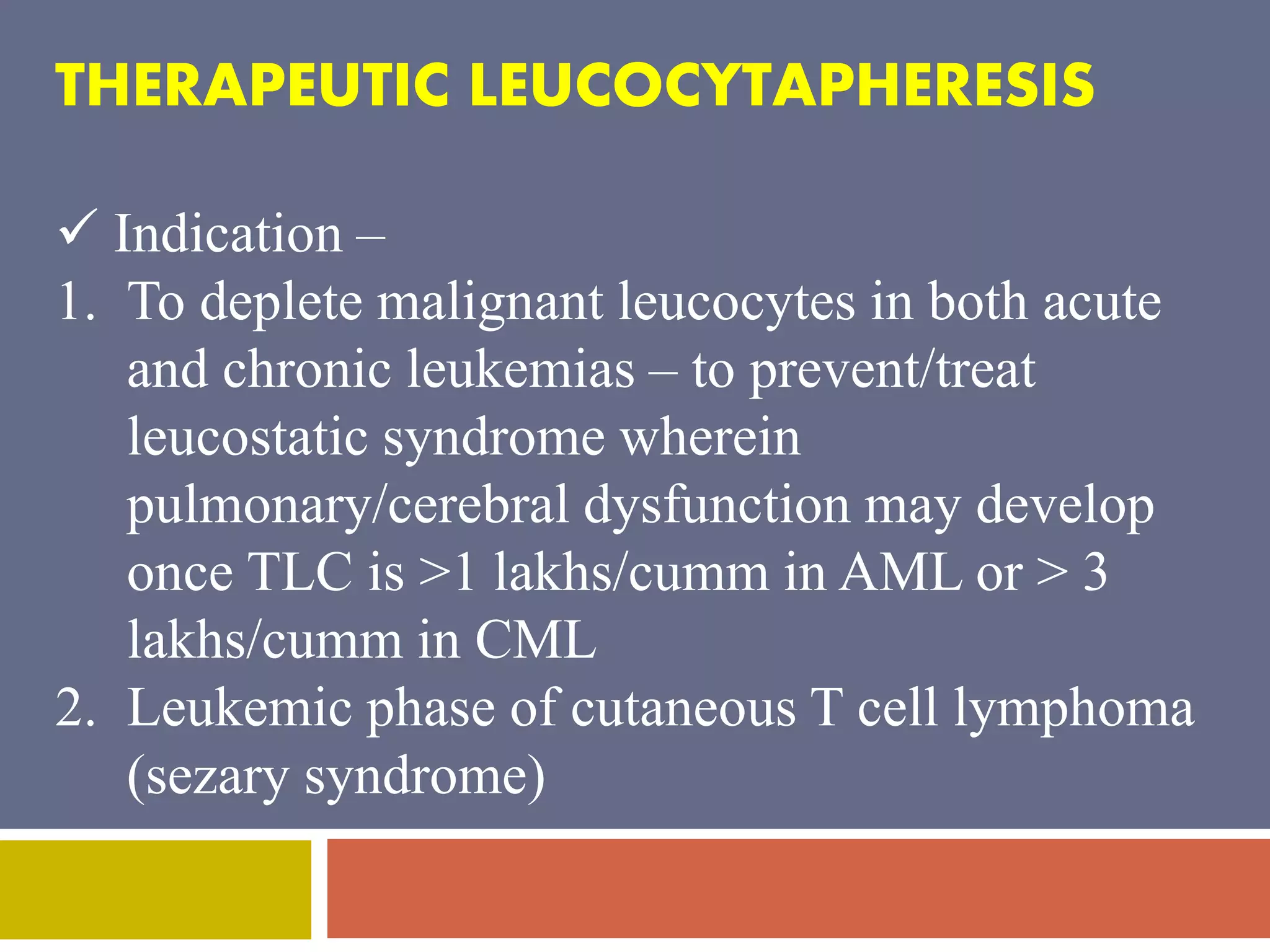
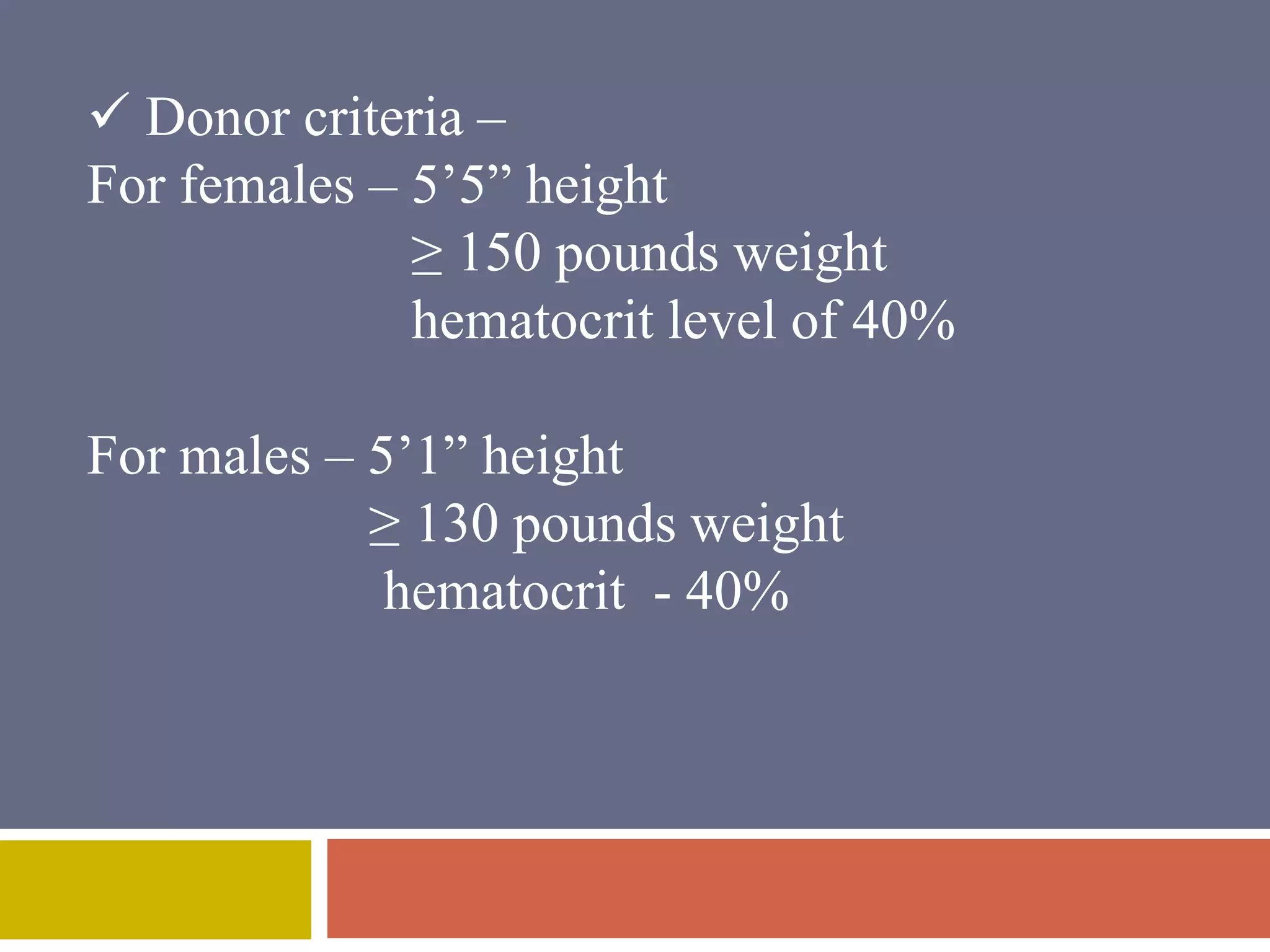
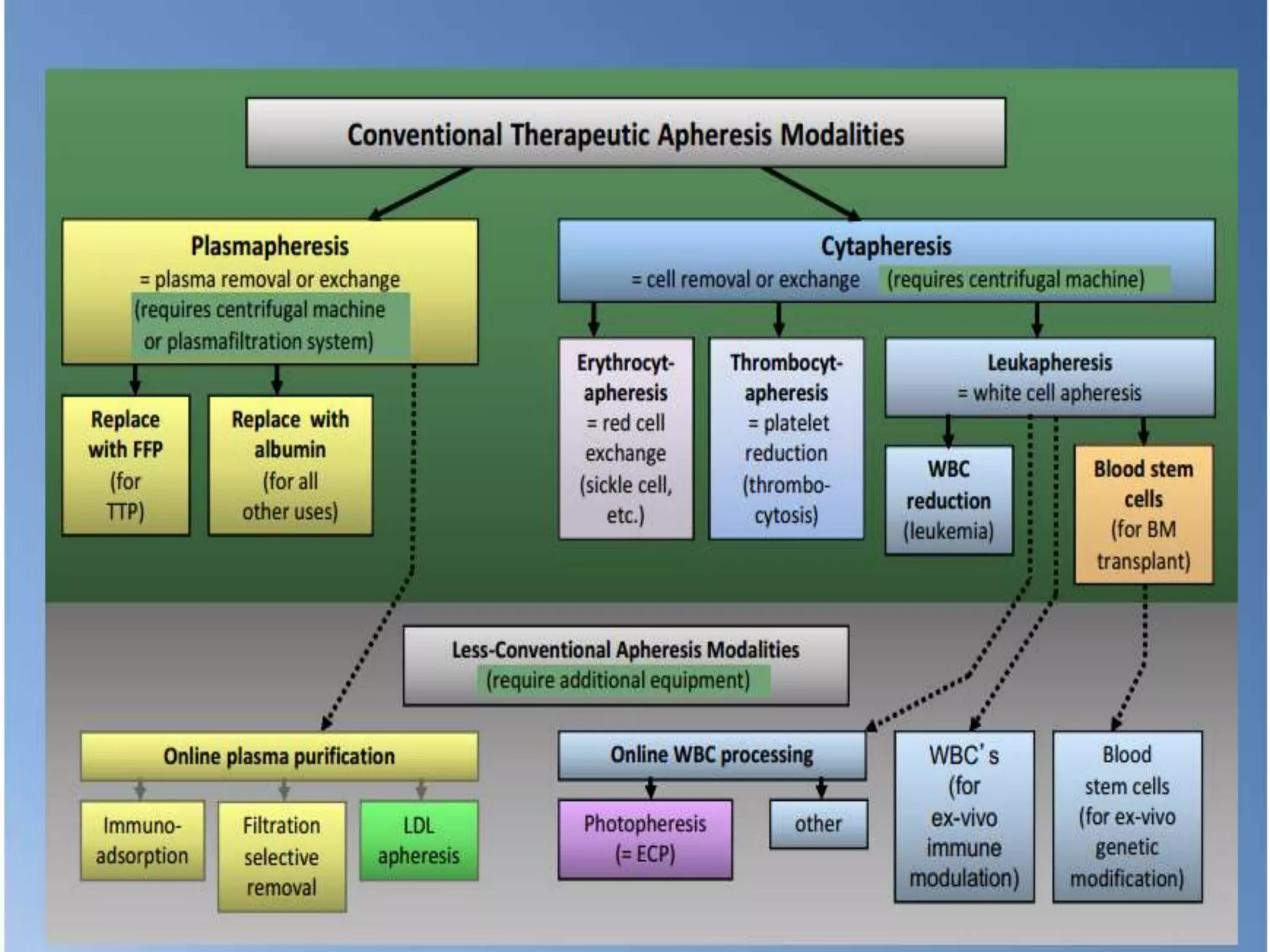
Apheresis is a technique where whole blood is collected from a donor or patient and separated into its components. The desired component is retained while the rest are returned. It is commonly used to collect platelets, leukocytes, erythrocytes, and plasma through centrifugation or membrane filtration methods. Therapeutic apheresis uses this technique to remove pathogenic substances from the blood to treat various conditions like thrombocythemia or autoimmune diseases. Procedural elements include venous access, anticoagulation, replacement fluids, and monitoring for complications.