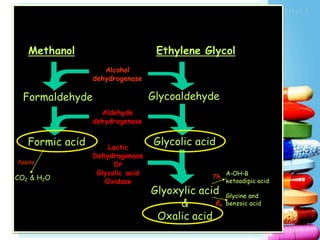
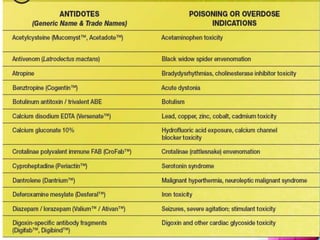
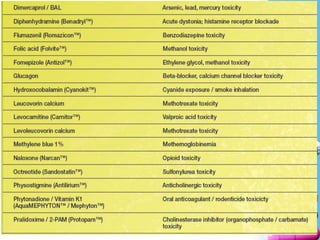
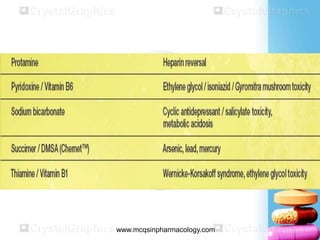
The document discusses antidotes for poisoning treatment. It defines an antidote as a therapeutic substance used to counteract the toxic effects of a xenobiotic. Antidotes are classified according to their mode or site of action, and include physical, chemical, and pharmacological antidotes. Physical antidotes like activated charcoal work by adsorption. Chemical antidotes form non-toxic complexes with toxins or accelerate detoxification. Pharmacological antidotes counteract toxins by antagonism at receptor sites, blocking toxic effects, or aiding normal function restoration. The proper use of antidotes combined with supportive care can significantly reduce morbidity and mortality from poisonings.