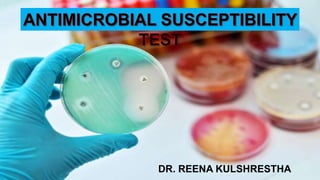
This document discusses antibiotic sensitivity testing (AST), including the Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion method and minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) method. It provides details on selecting media, control strains, preparing antibiotic discs and inoculum, and interpreting zone sizes. AST is useful but has limitations as it only measures in vitro drug activity, not in vivo effects. Proper technique and quality controls are important for accurate results. New automated methods can generate reports faster than traditional AST.