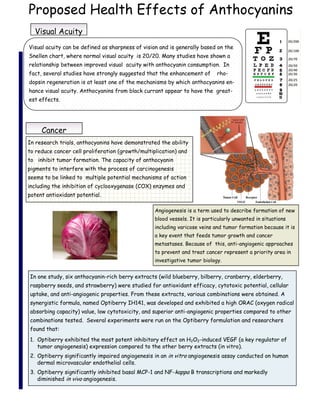
The document discusses anthocyanins, a group of flavonoid phytochemicals found predominantly in berries and red wine, noted for their health benefits. It highlights their roles in enhancing visual acuity, reducing cancer cell proliferation, and providing cardiovascular protection, supported by both anecdotal and empirical evidence. Additionally, challenges in studying their mechanisms of action and bioavailability are mentioned, as well as the Pennington Biomedical Research Center's efforts in nutrition education and research.