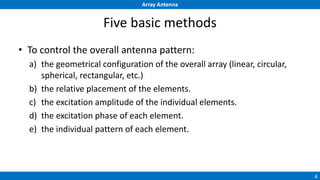
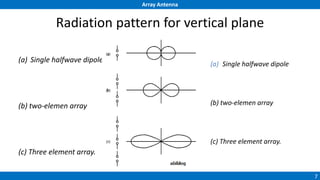
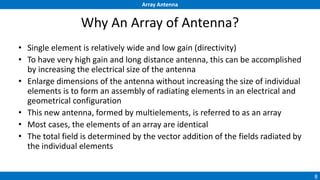
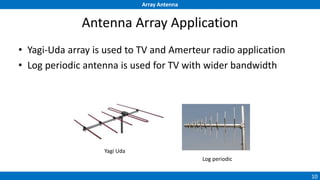
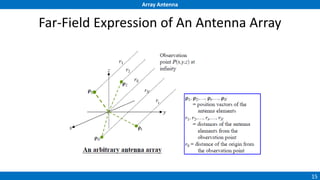
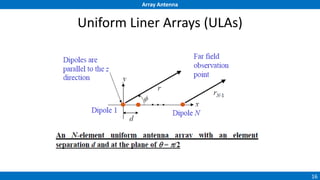
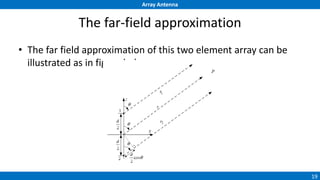
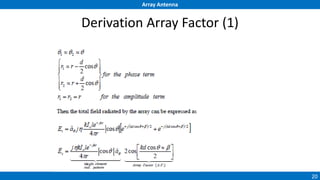
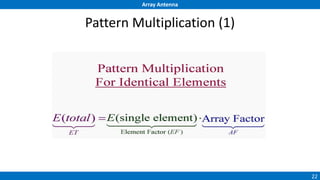
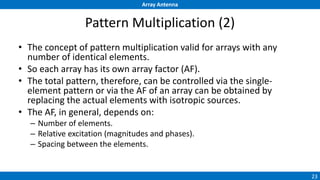
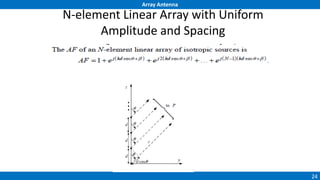
An array antenna uses multiple antenna elements to increase directivity and gain over a single element. It allows controlling the radiation pattern through configuration of elements, their excitation amplitude and phase. A linear array's far-field pattern is determined by its array factor, which is calculated based on number of elements, their spacing and excitation. Common array types include uniform linear arrays and end-fire/broadside arrays. The total pattern is obtained by multiplying the array factor and single element pattern. Arrays find applications in mobile communication base stations, TV reception and more.