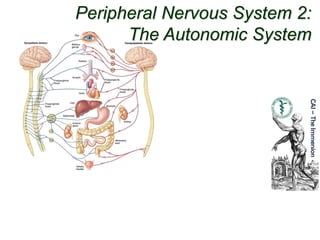
The autonomic nervous system consists of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. The sympathetic division is responsible for the "fight or flight" response and uses norepinephrine as its neurotransmitter. Its preganglionic neurons originate in the spinal cord and project to peripheral ganglia. The parasympathetic division is responsible for "rest and digest" functions and uses acetylcholine as its neurotransmitter. Its preganglionic neurons originate in the brainstem and sacral spinal cord and project to ganglia near target organs. Both divisions regulate involuntary functions like heart rate and gland secretion.