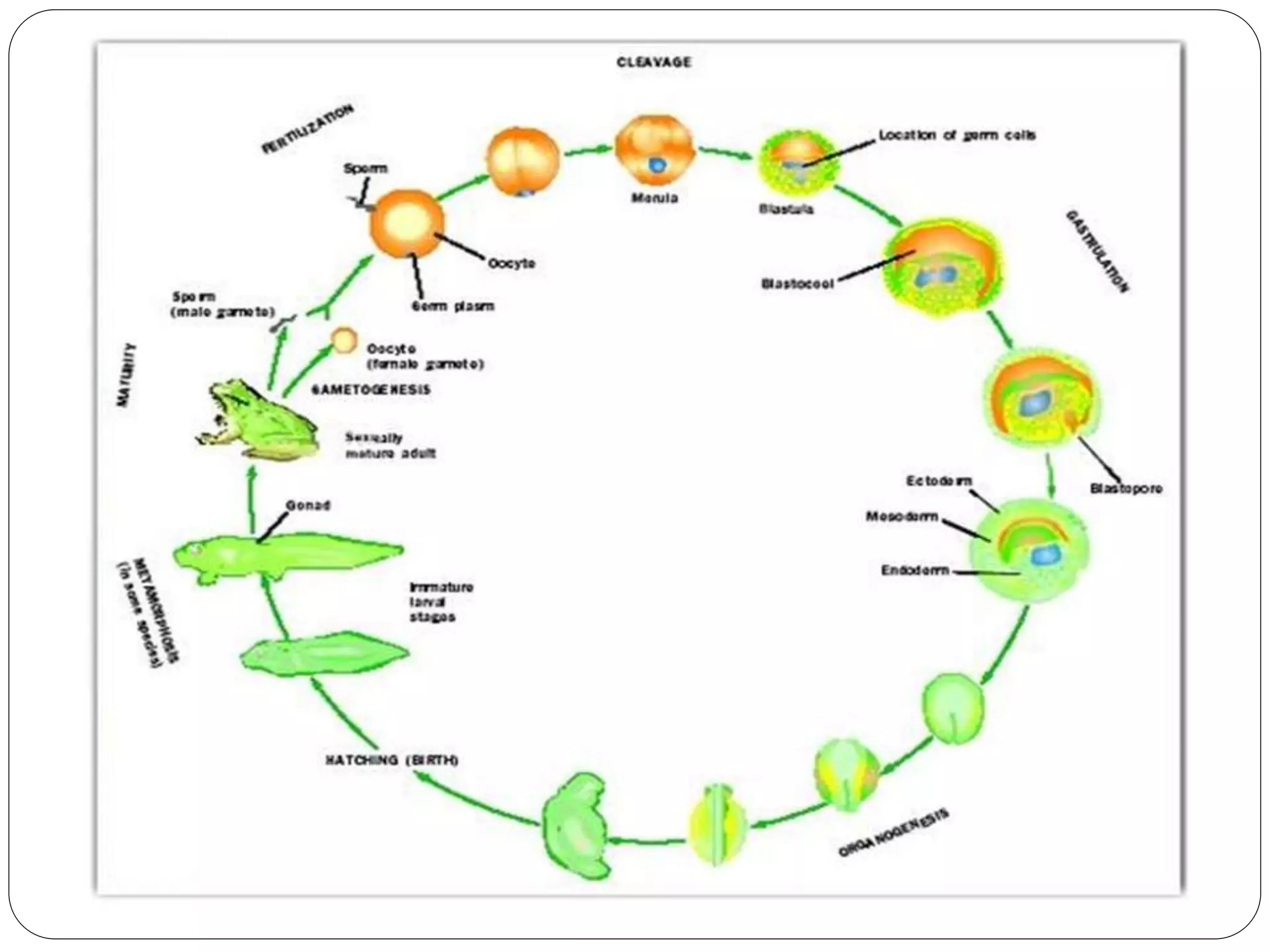
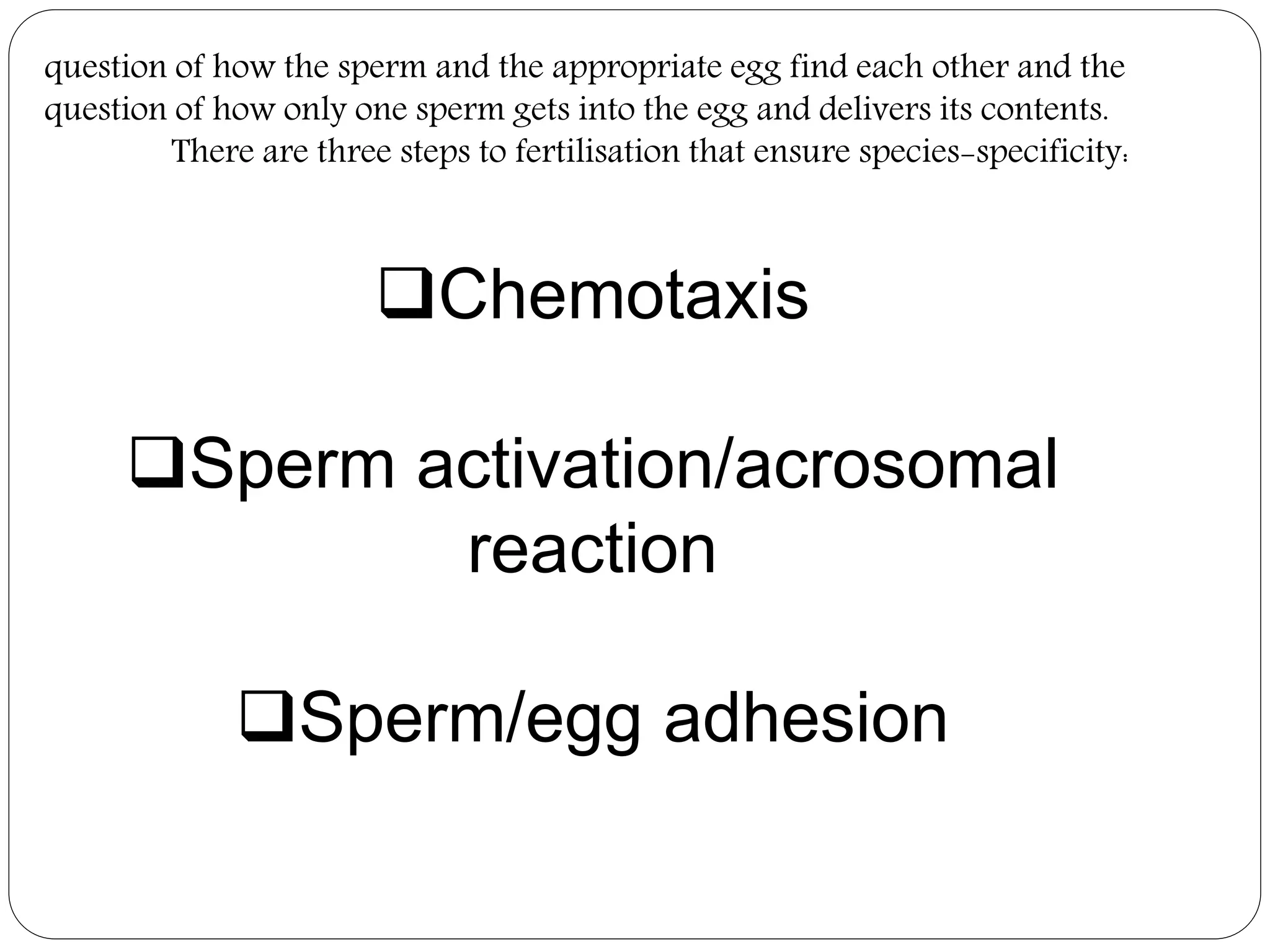
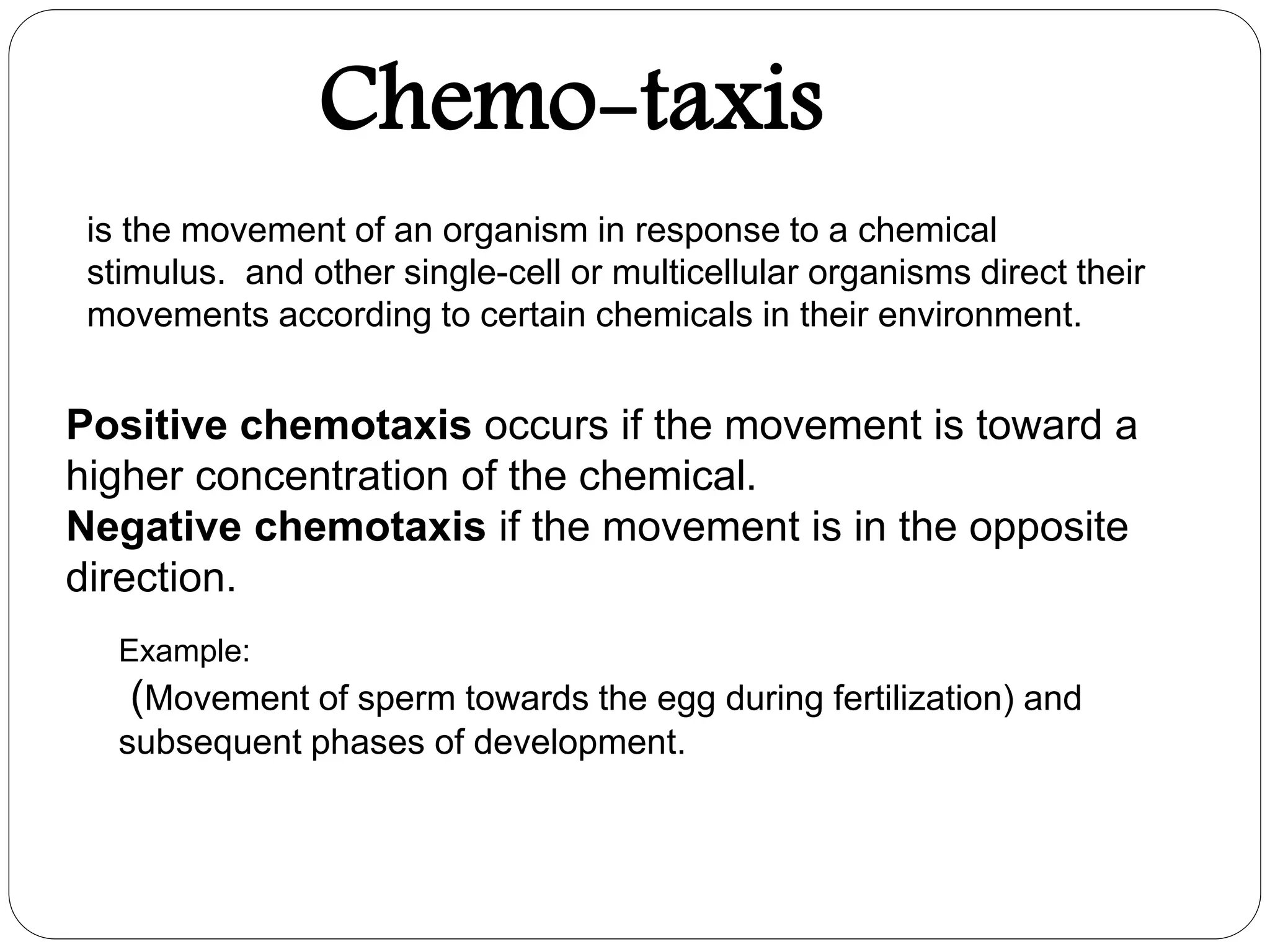
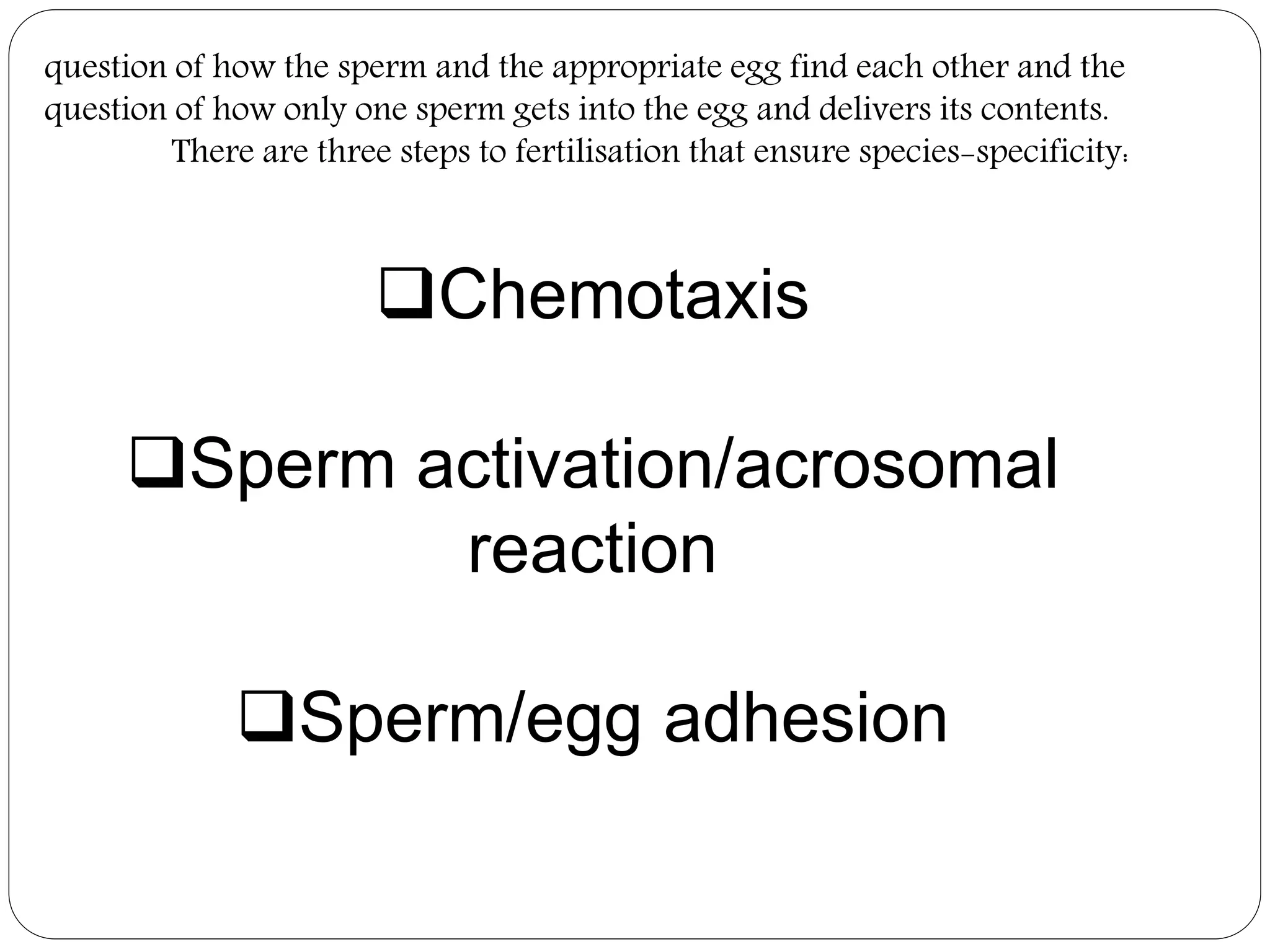
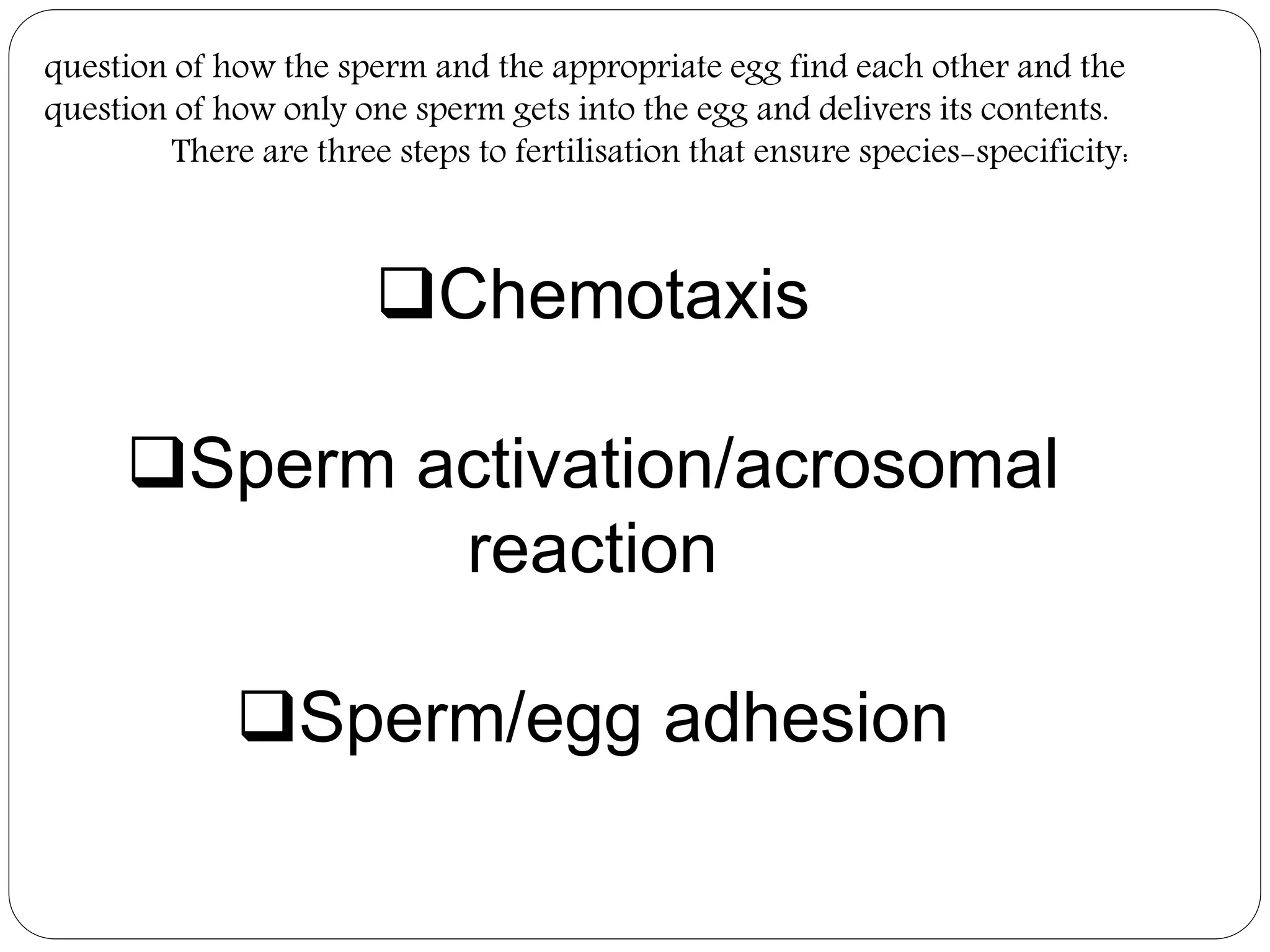
Fertilization in animals involves the fusion of an egg and sperm to form a zygote and initiate embryo development. It can occur internally, within the female's body, or externally in aquatic environments. There are three key steps to ensure species-specific fertilization: chemotaxis, where sperm are attracted to the egg via chemicals; the acrosome reaction, where the sperm undergoes changes to penetrate the egg; and sperm-egg adhesion, where attachments form between the gametes. Internal fertilization protects developing embryos and results in higher offspring survival for land animals.