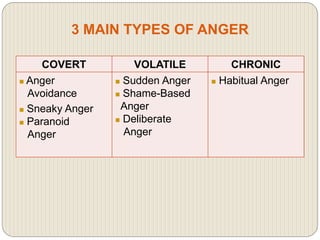
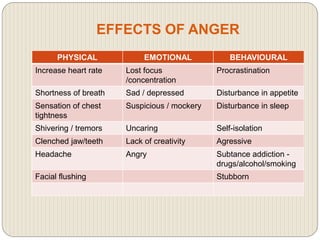
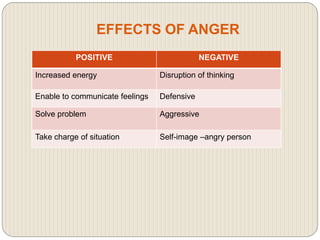
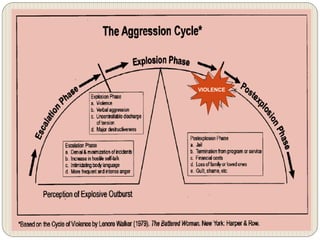
This document discusses anger management and provides information on types and effects of anger. It describes anger as a basic human emotion triggered by hurt that feels unpleasant. Aggression results from angry and frustrated states. Anger is commonly caused by frustration over unmet goals, misunderstandings, poor communication, or feeling disrespected or treated unfairly. The main types of anger discussed are covert, volatile, and chronic anger. The document also outlines effects of anger on physical, emotional, and behavioral health and provides anger management strategies.