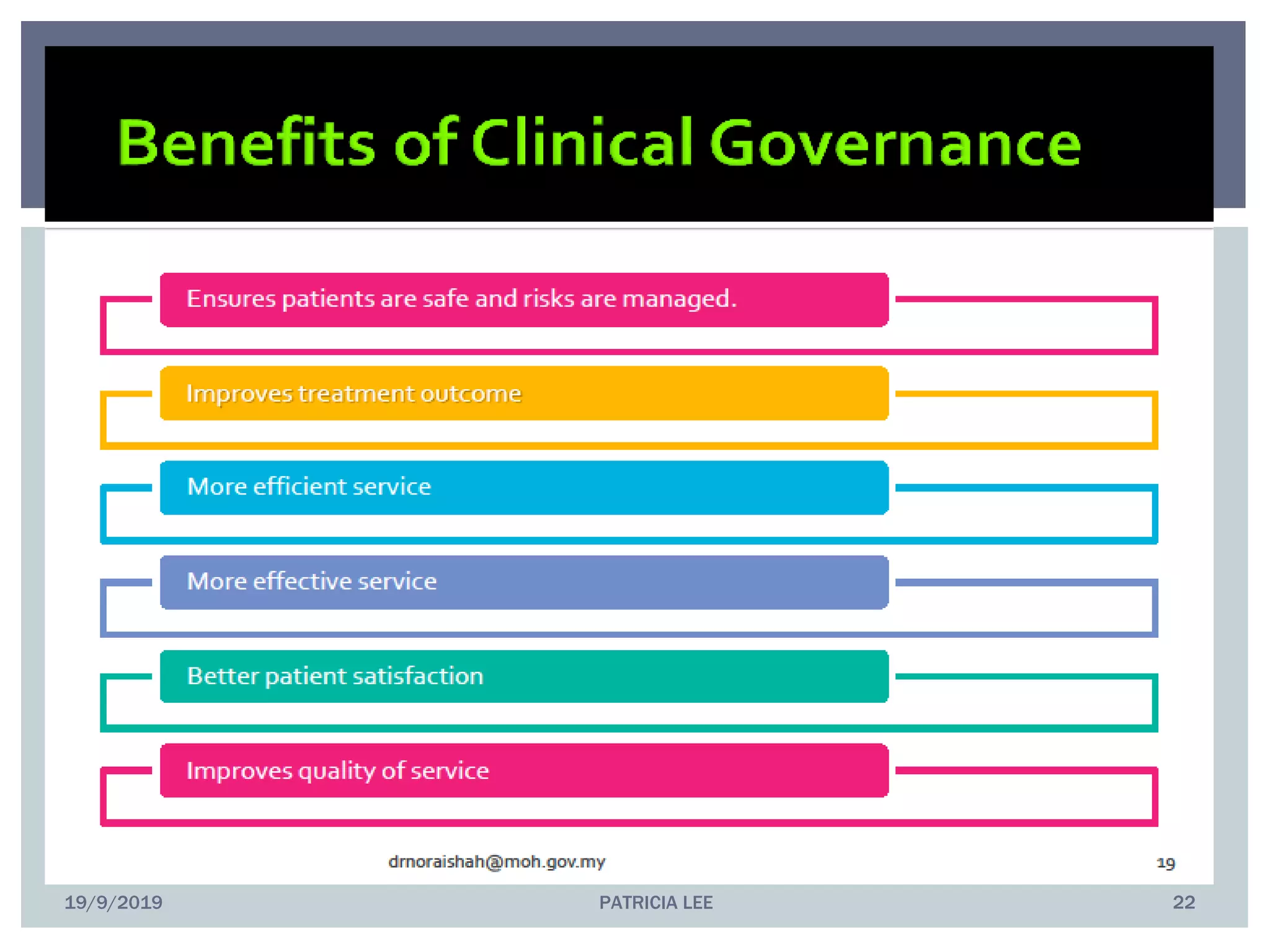
This document discusses clinical governance, which refers to the system by which healthcare organizations share responsibility for quality of care. It identifies seven pillars of clinical governance: patient and public involvement, complaints management, risk management, staff management, education and training, clinical effectiveness and research, and clinical information and IT usage. The document provides examples of implementing each pillar, such as establishing processes for recognizing, reporting, analyzing, and learning from patient complaints and incidents. The conclusion emphasizes that effective governance requires a positive culture of continuous improvement, well-designed care systems with performance monitoring, and ensuring staff have necessary skills and supports.