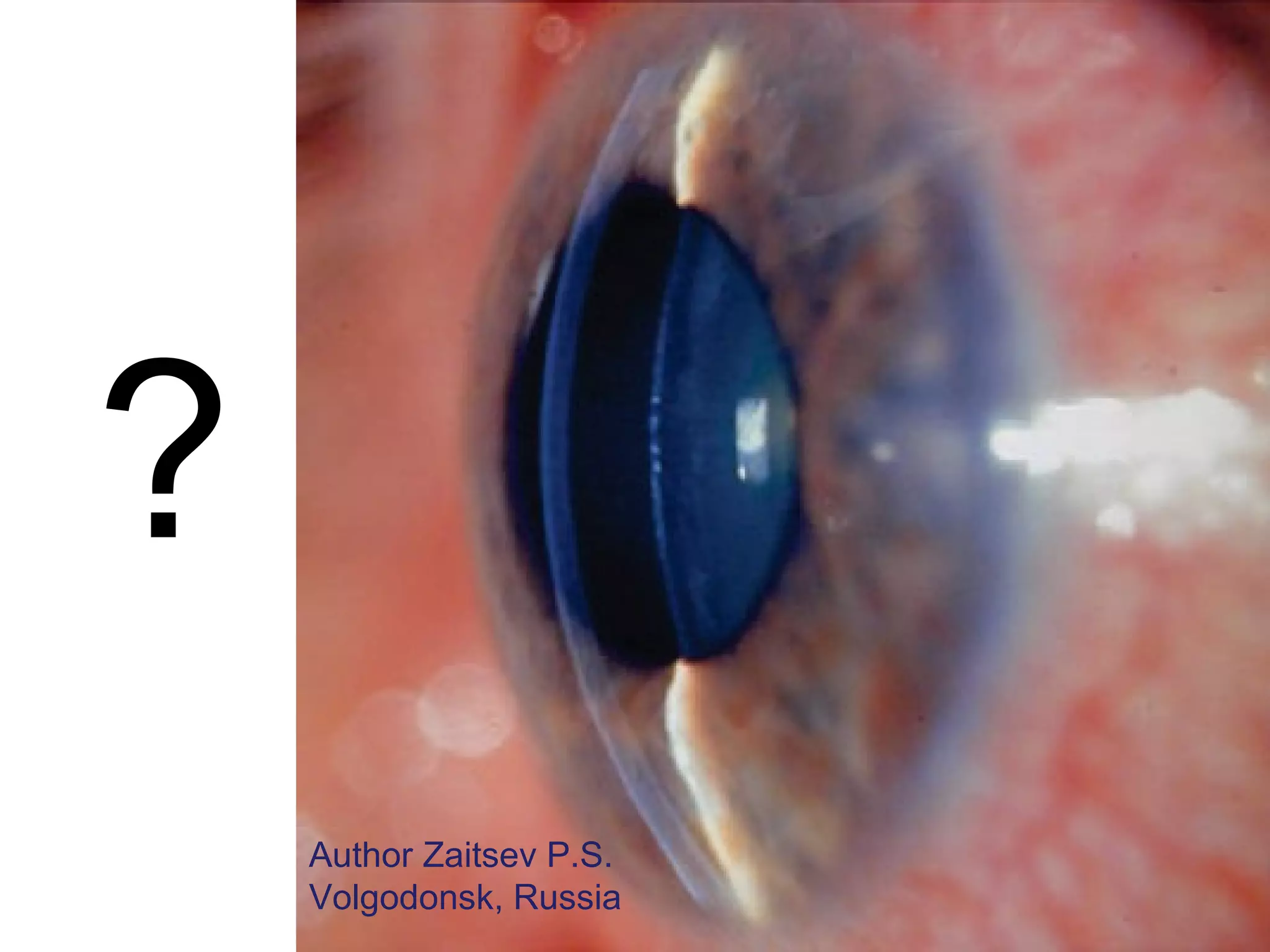
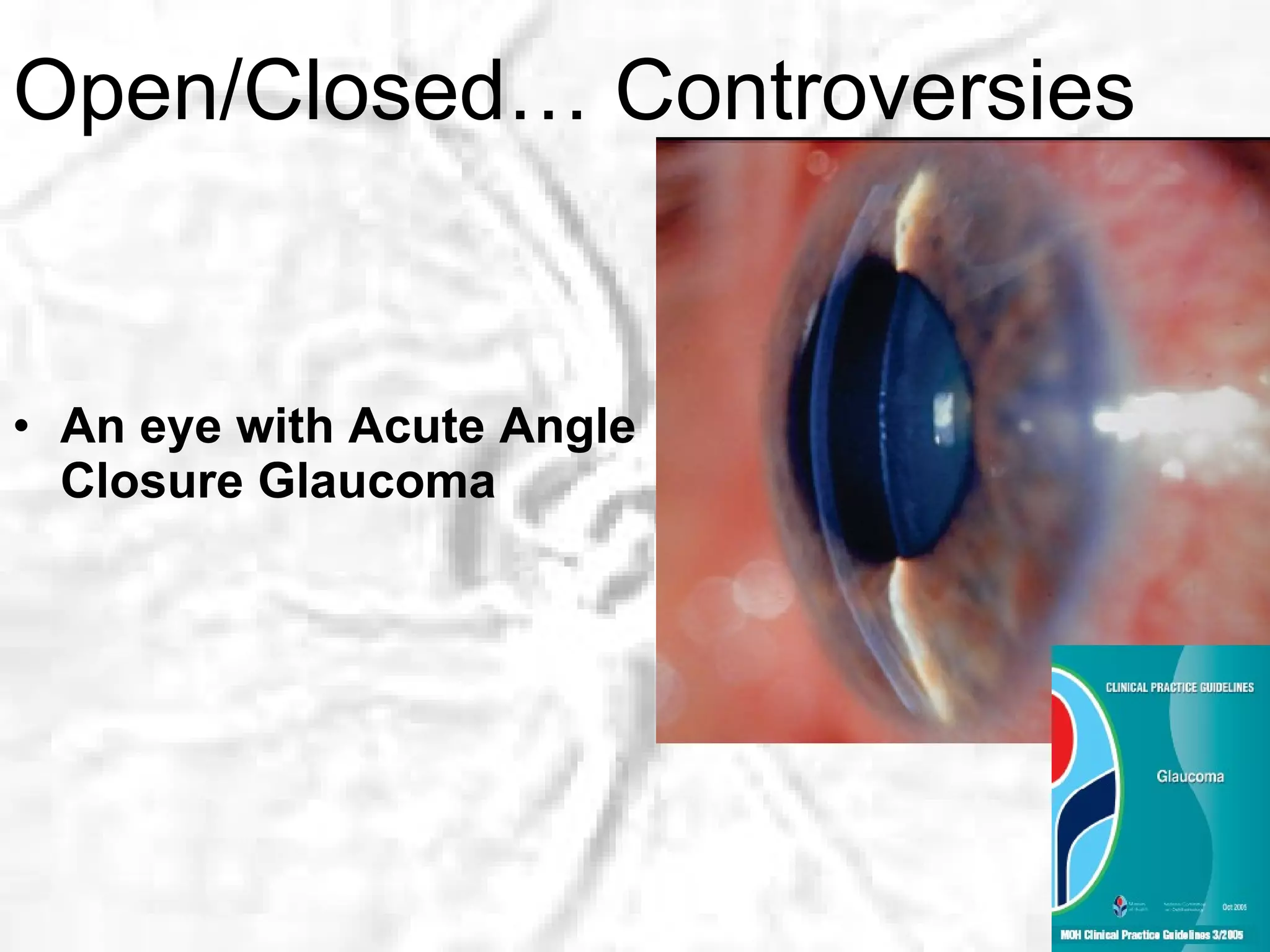
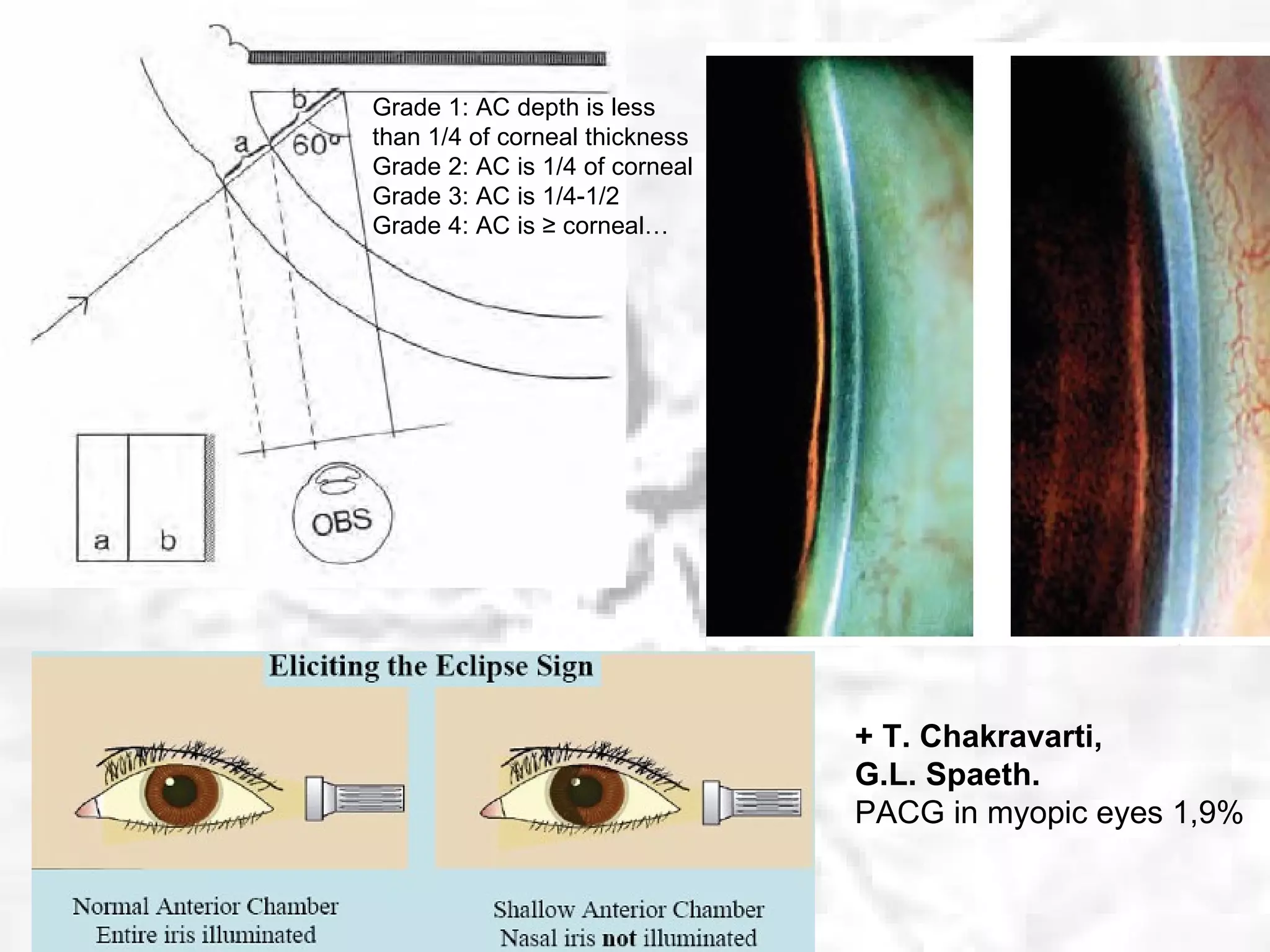
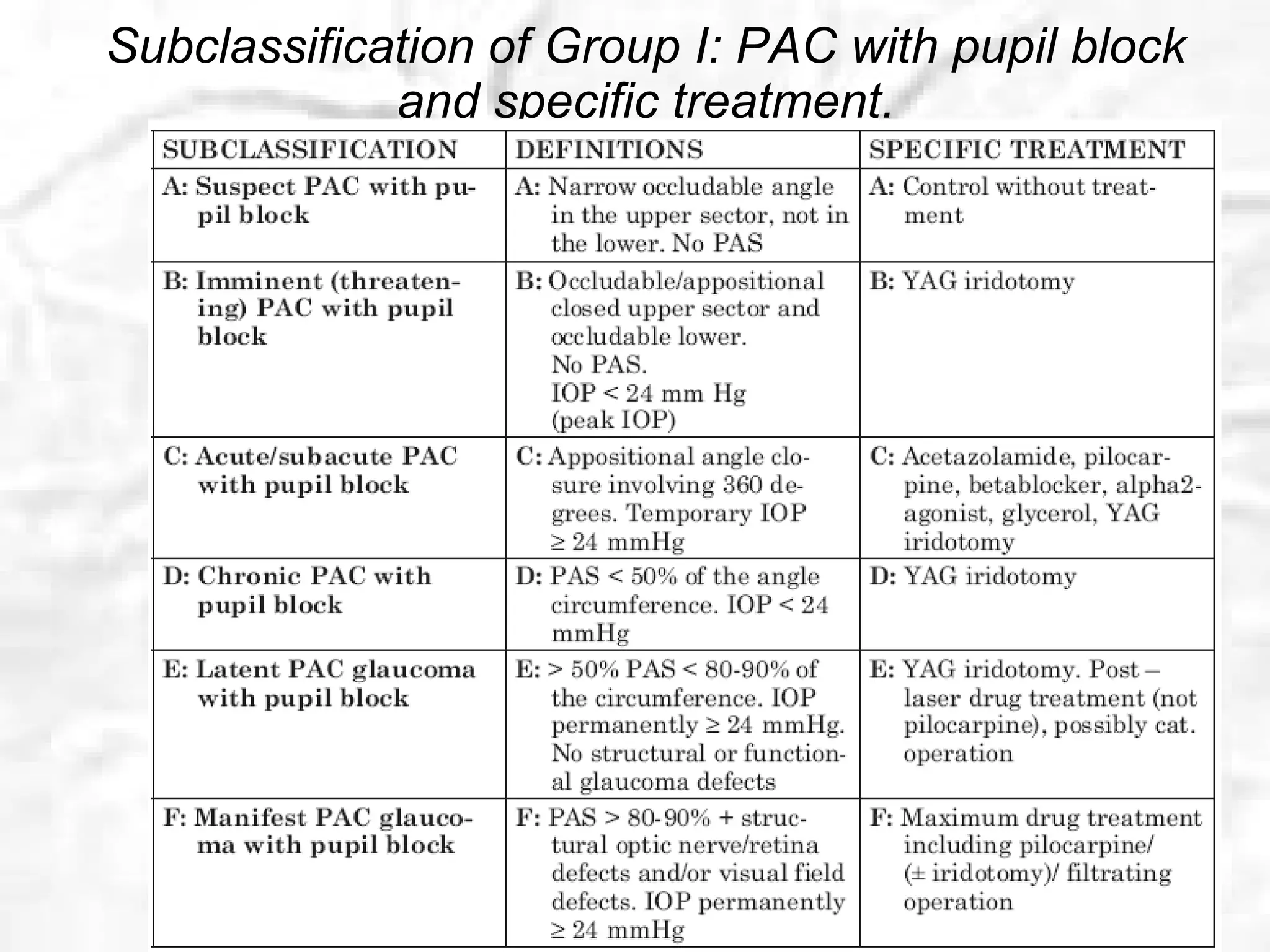
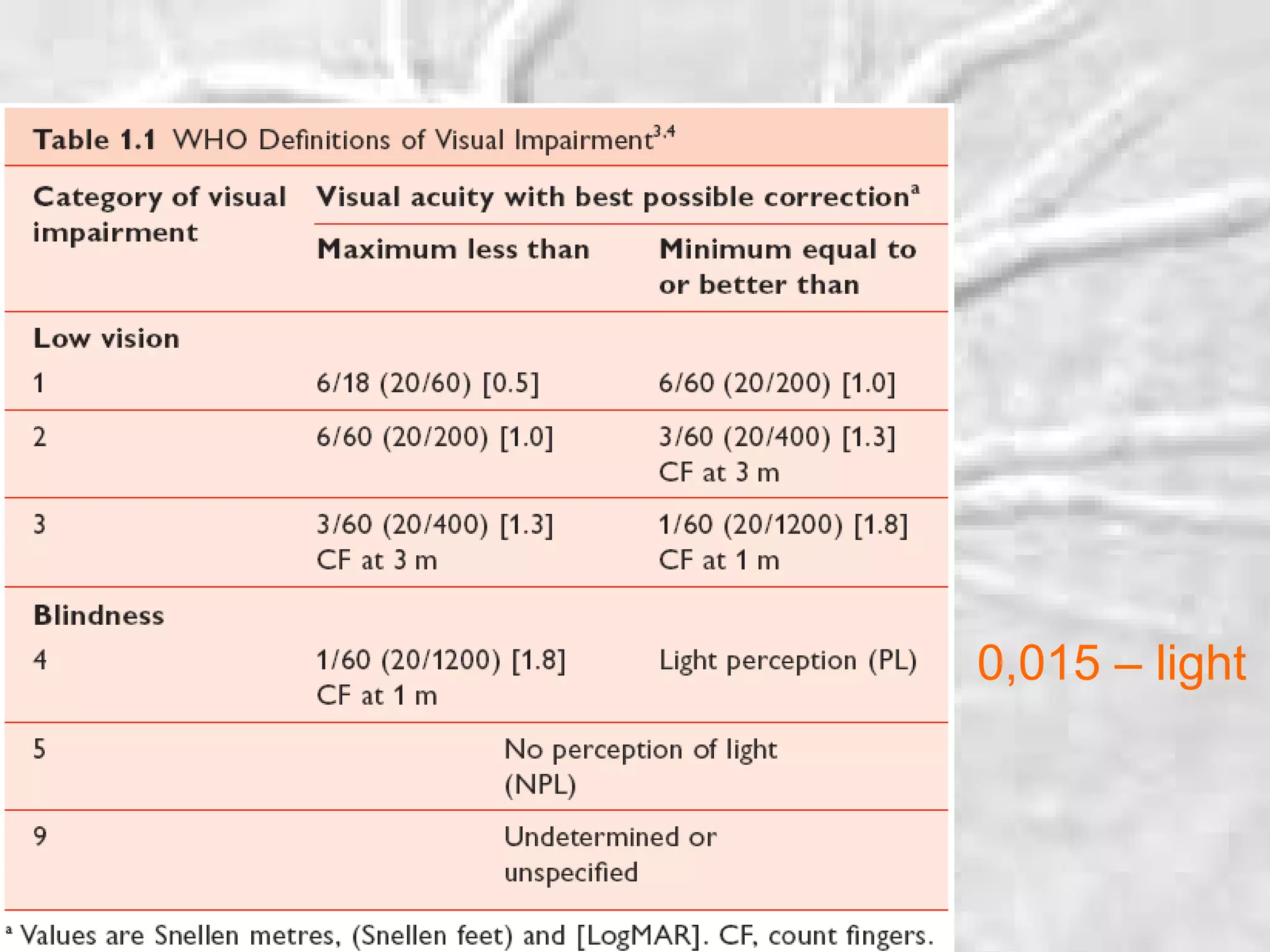
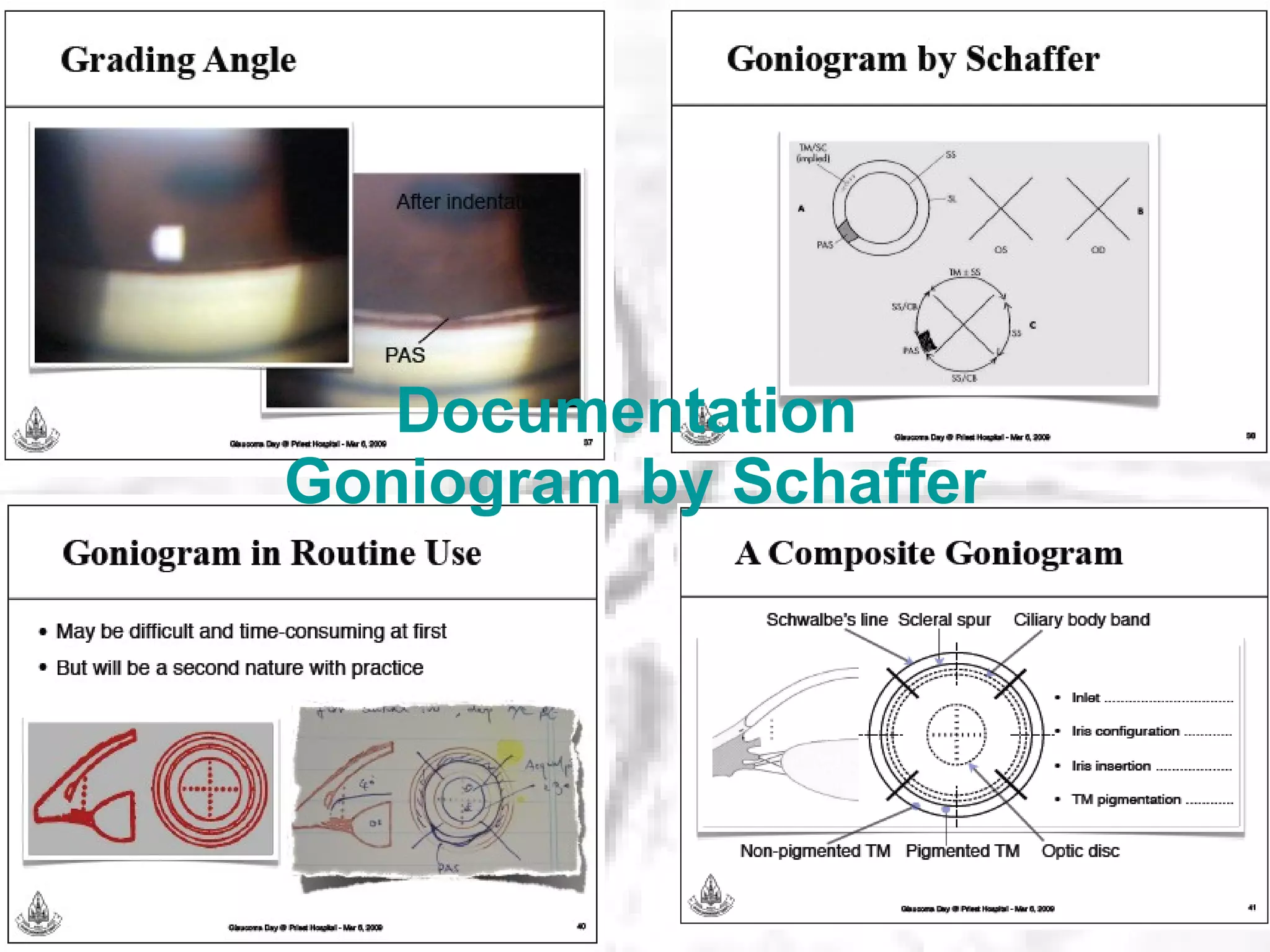
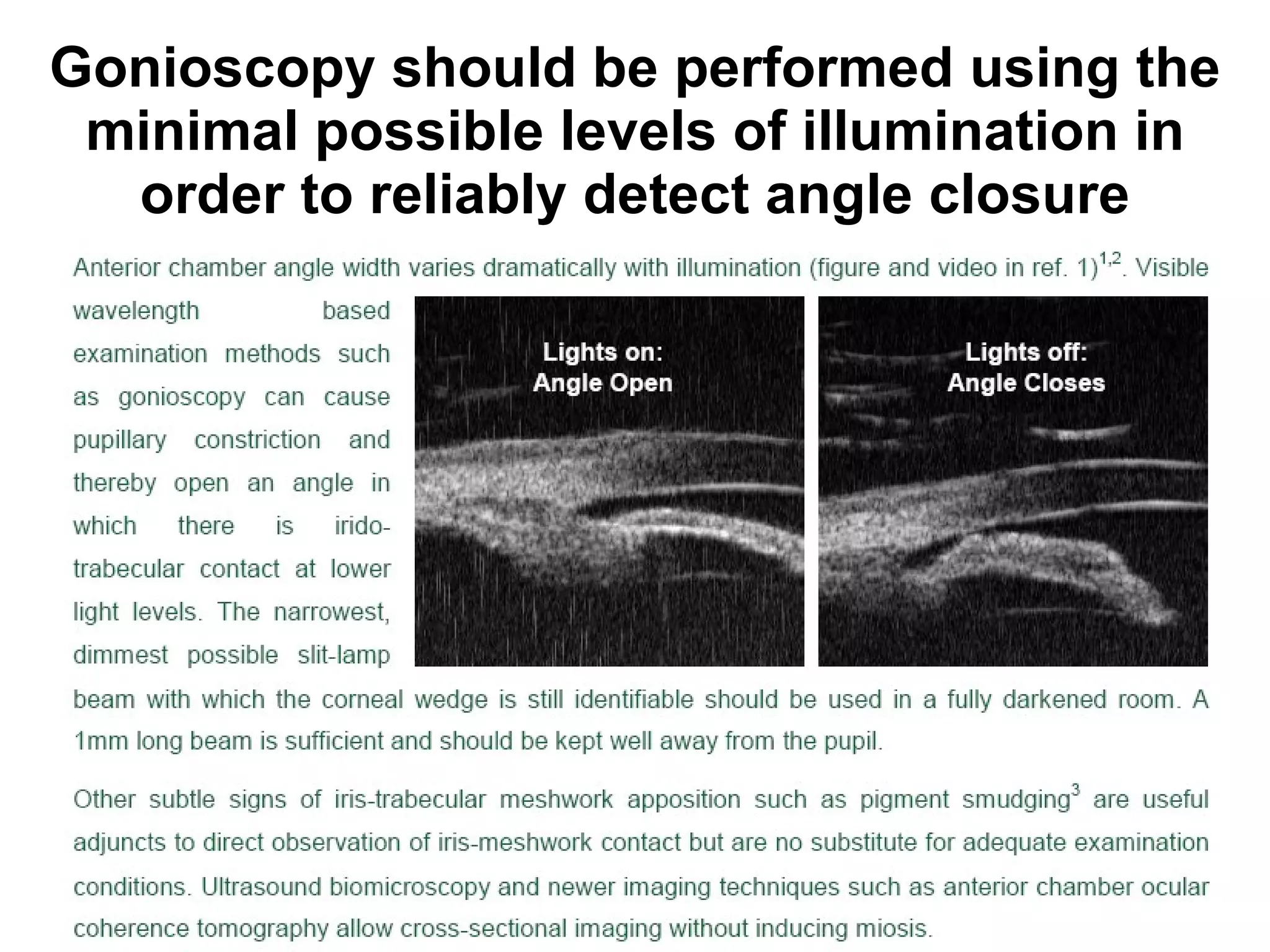
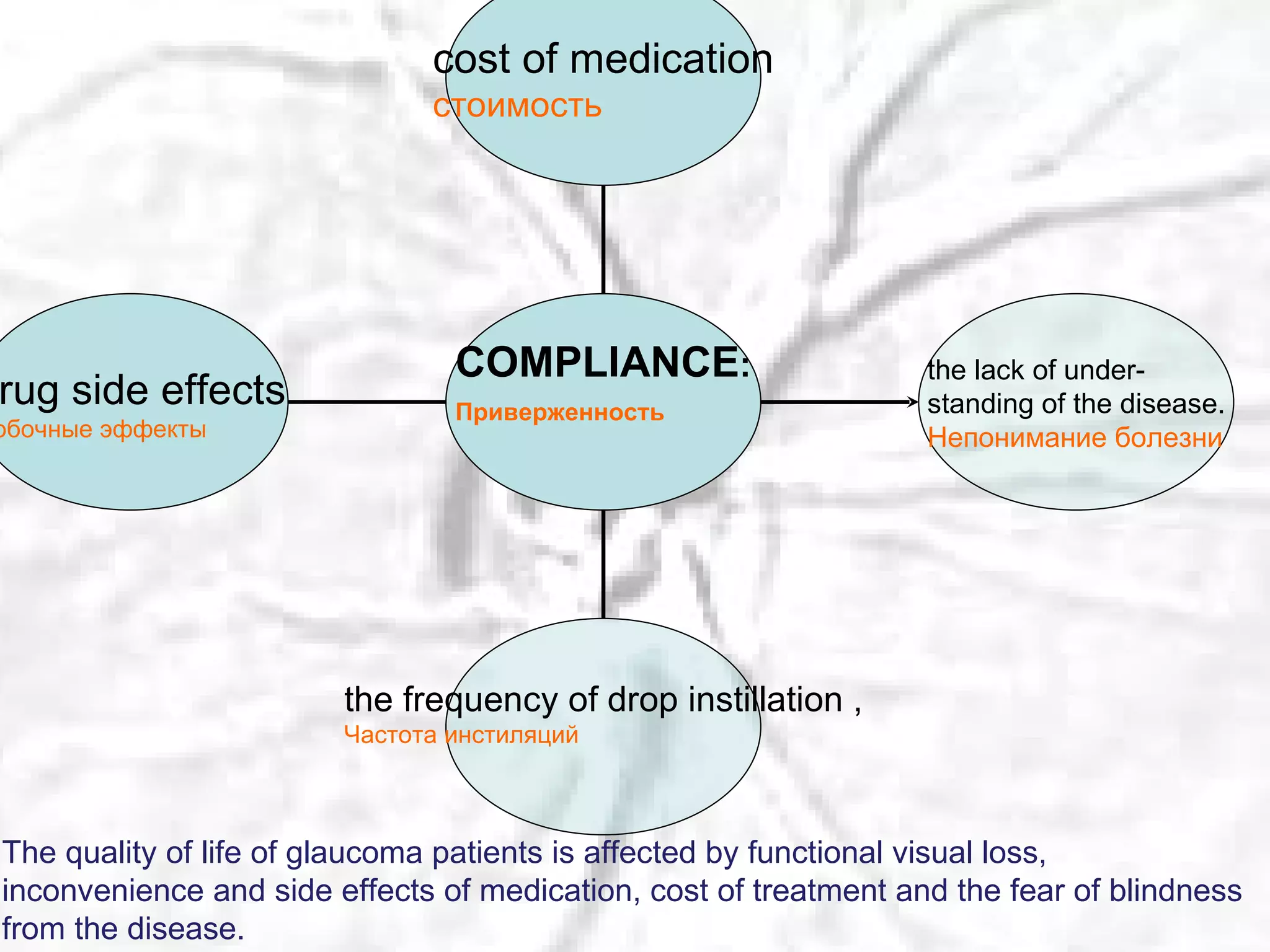
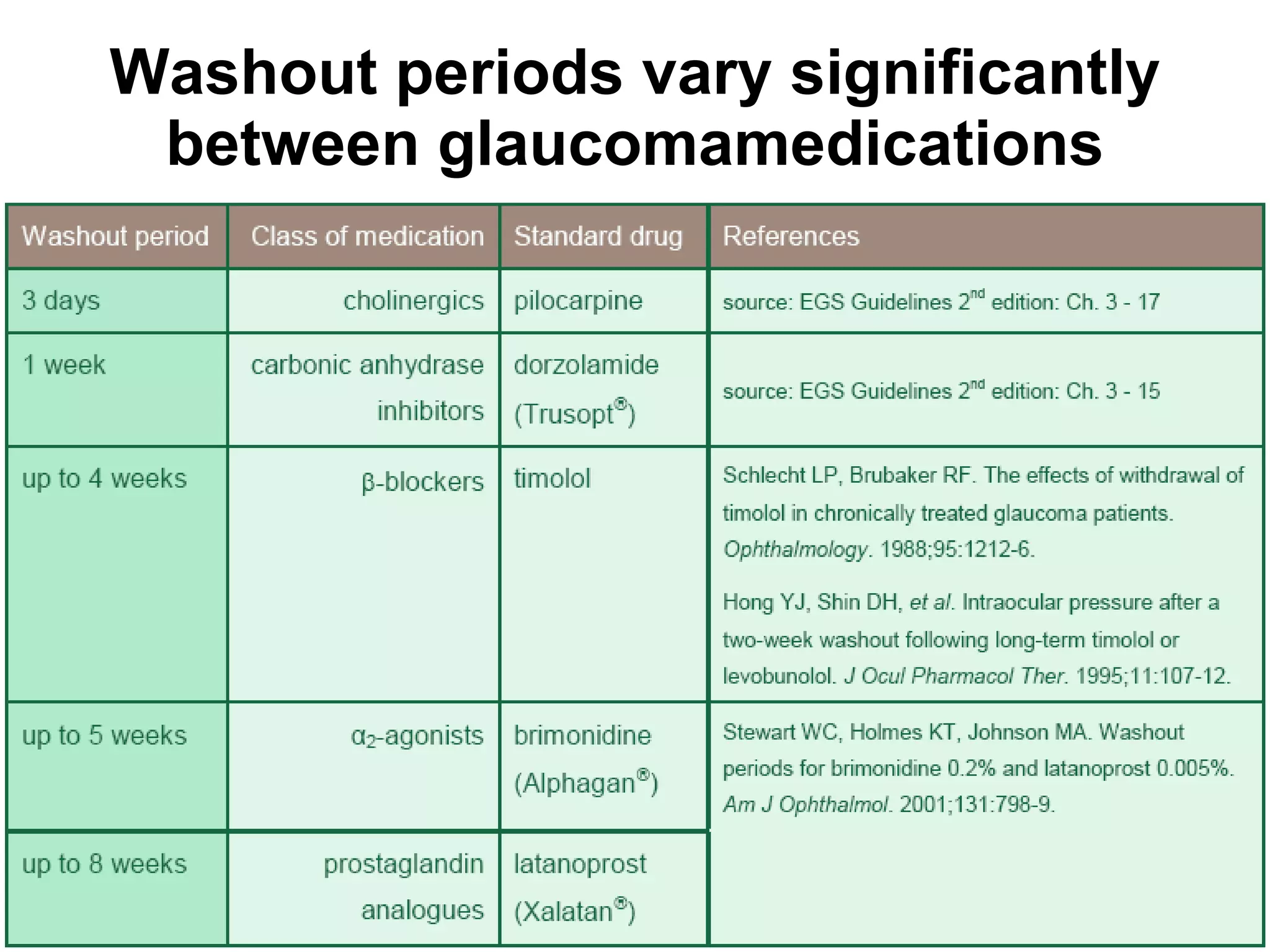
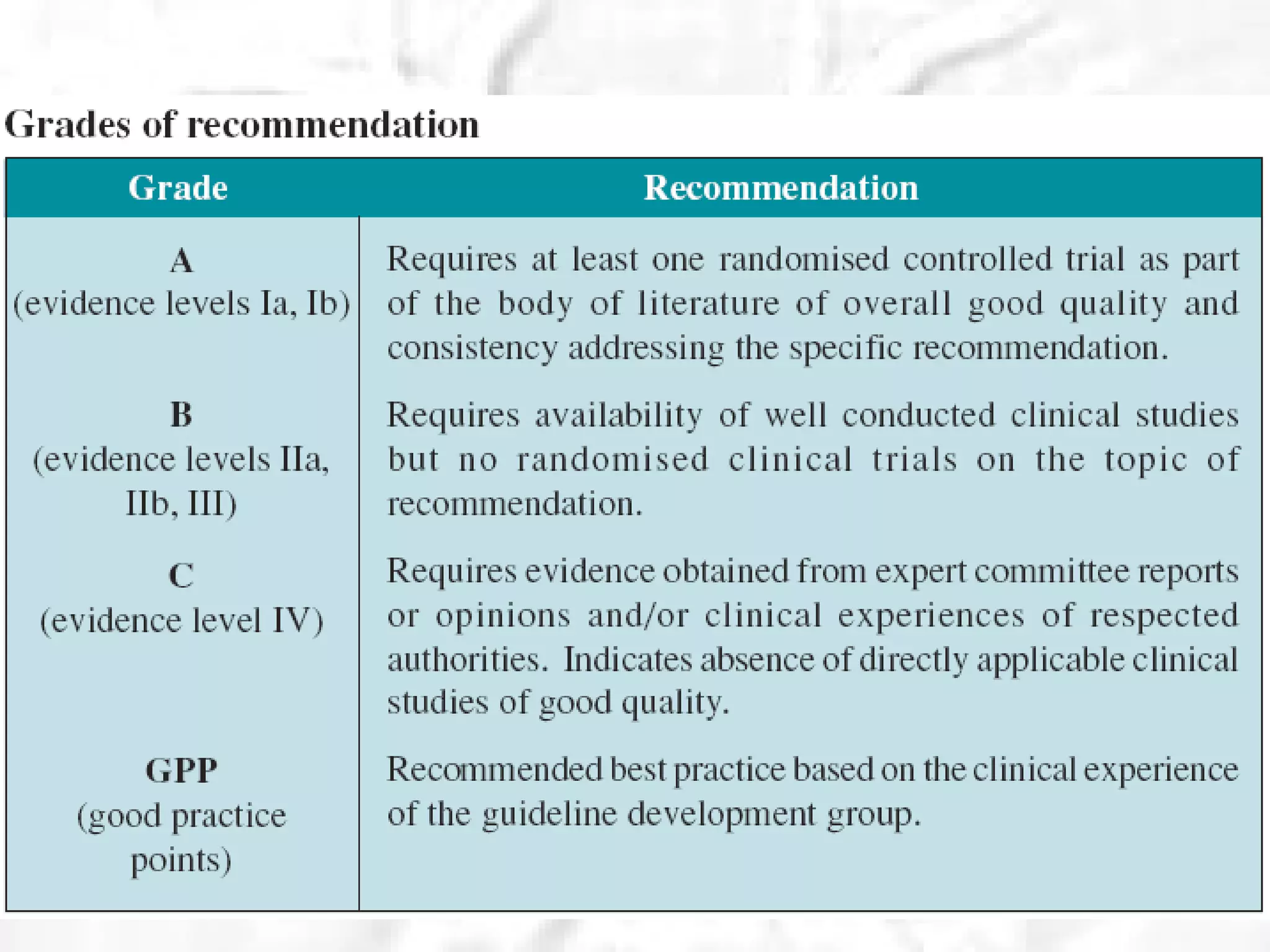
This document summarizes information about angle closure glaucoma, including risk factors, treatment strategies, and complications. It discusses populations that are particularly at risk of angle closure glaucoma like Asians. It also mentions treatment options for angle closure glaucoma such as laser iridotomy and supplemental medical therapy.