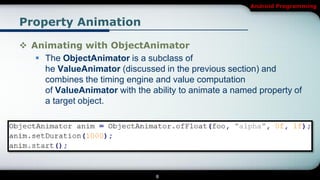
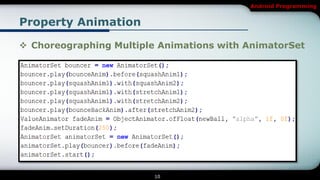
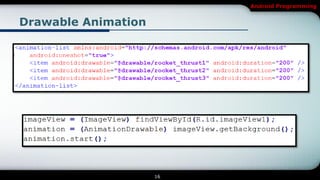
The document discusses different types of animations in Android programming, specifically focusing on property animation, drawable animation, and view animation. It covers the use of ValueAnimator and ObjectAnimator for animating values and properties, and explains how to choreograph multiple animations using AnimatorSet. Additionally, it details drawable animations created with AnimationDrawable and view animations, including tween and frame animations, specifying proper XML structuring for each type.