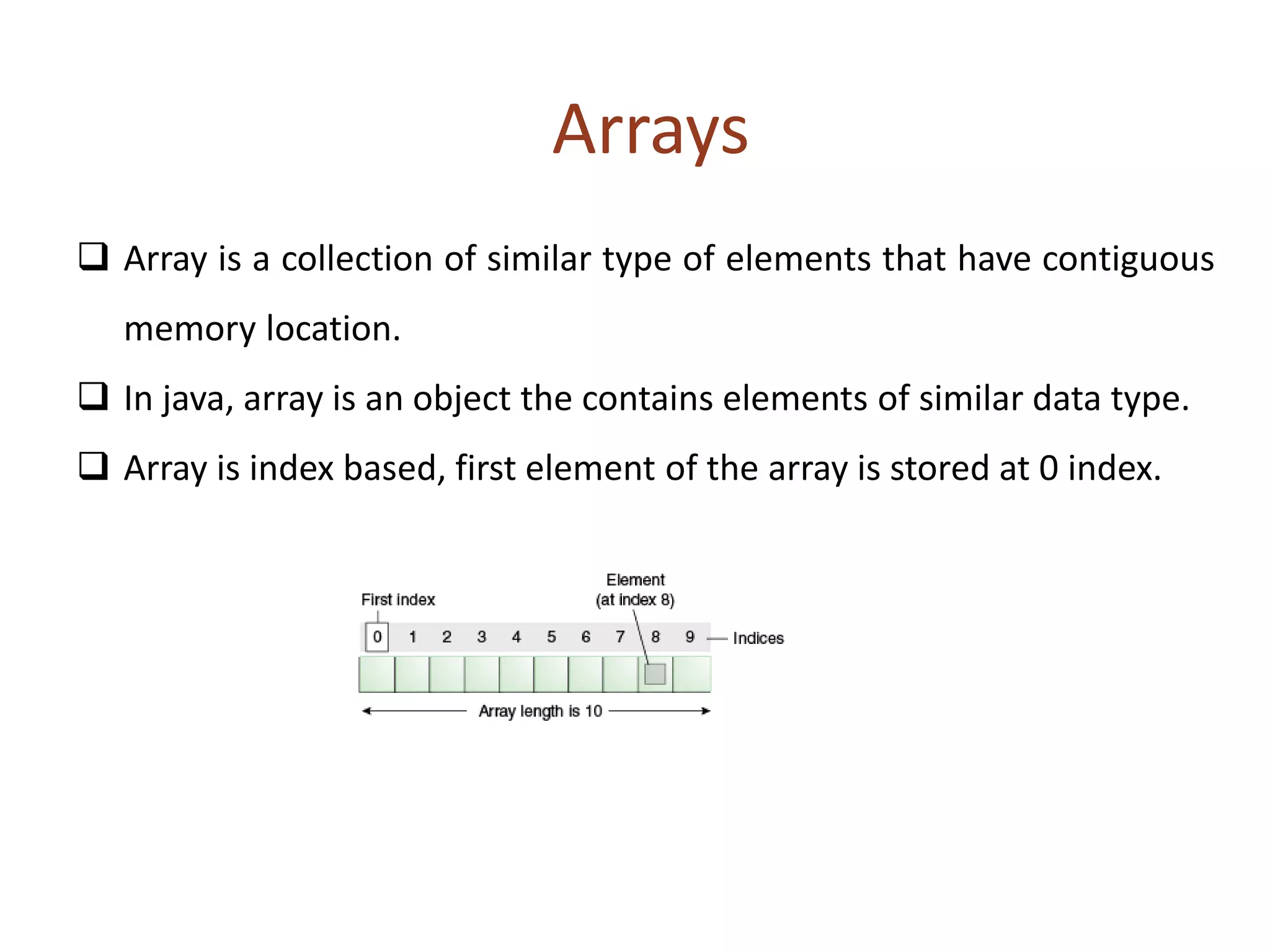
Arrays allow for the storage of multiple values of the same data type in contiguous memory locations that can be accessed via indexes. In Java, arrays are objects that hold a collection of similar type elements. Arrays are declared with a type followed by empty brackets, and initialized using the new keyword along with the size of the array. Multidimensional arrays are arrays of arrays, allowing the use of multiple subscript operators to access elements.
![ Types of Array
Single Dimensional Array
Multidimensional Array
Declaration of Arrays – 3 steps
Declare the array
Create storage area in primary memory.
Put values into the array (i.e., Memory location)
Declaration of Arrays: 1 step
Form 1: Type arrayname[]
Form 2: Type [] arrayname;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-150203104426-conversion-gate02/85/Java-arrays-2-320.jpg)
![ Creation of arrays: 2 step
arrayname = new type[size]; // create a memory
Initialization of arrays:
arrayname [index/subscript] = value; or {list of values};
Example:
int [] students = new int[7];
int [] students = {1,2,3,4,5};
Two Dimensional Arrays:
array with two subscript operator – [] []
datatype [] [] array_name=new datatype [row][column];
int [] [] student=new int[2][2];
int tableA[2][3] = {{10, 15, 30}, {14, 30, 33}};
int tableA[][] = {{10, 15, 30}, {14, 30, 33}};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-150203104426-conversion-gate02/85/Java-arrays-3-320.jpg)
![4
Variable Size Arrays
Java treats multidimensional arrays as “arrays of arrays”. It is
possible to declare a 2D arrays as follows:
– int a[][] = new int [3][];
– a[0]= new int [3];
– a[1]= new int [2];
– a[2]= new int [4];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-150203104426-conversion-gate02/85/Java-arrays-4-320.jpg)
![import java.io.*;
class B{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
//int[] a={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
int a[]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};//declaration, instantiation and initialization
//printing array
for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++)//length is the property of array
System.out.println(a[i]);
int b[]=new int[50];
DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the no");
int c=Integer.parseInt(dis.readLine());
for(int j=0;j<c;j++)//length is the property of array
{b[j]=Integer.parseInt(dis.readLine());}
System.out.println("Entered Numbers are:");
for(int j=0;j<c;j++)//length is the property of array
{System.out.println(b[j]);}}
catch(Exception e)
{
}}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-150203104426-conversion-gate02/85/Java-arrays-5-320.jpg)
![import java.io.*;
class B1{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
int arr[][]={{1,2,3},{2,4,5},{4,4,5}}; //declaring and initializing 2D array
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
System.out.print(arr[i][j]+" ");}
System.out.println(); }
int [][] f=new int[10][10];
DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the row and column values");
int c=Integer.parseInt(dis.readLine());
int d=Integer.parseInt(dis.readLine());
for(int i=0;i<c;i++){
for(int j=0;j<d;j++){
f[i][j]=Integer.parseInt(dis.readLine());}}
System.out.println("2D-array");
for(int i=0;i<c;i++){
for(int j=0;j<d;j++){
System.out.print(f[i][j]+ " " );}
System.out.println(); }}
catch(Exception e)
{}}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-150203104426-conversion-gate02/85/Java-arrays-6-320.jpg)