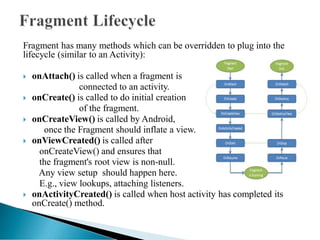
Fragments in Android allow developers to divide an activity's user interface into modular components. Fragments have their own layouts and lifecycle methods similar to activities. Developers can optimize apps for different screen sizes by dynamically adding, removing, or replacing fragments at runtime using the fragment manager. To create a fragment, developers extend the fragment class and override lifecycle methods like onCreateView() to inflate layouts.