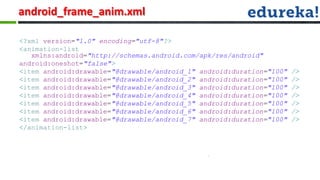
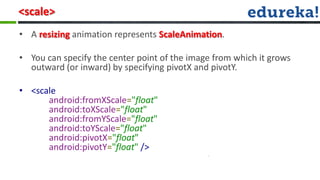
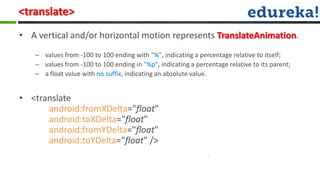
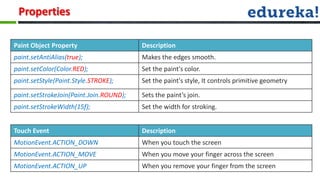
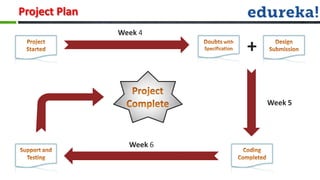
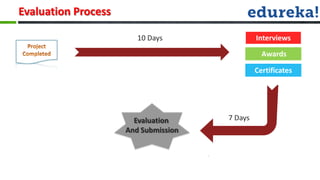
The document provides information about various Android concepts like storing files, animations, AsyncTasks, Canvas, and Paint. It discusses storing files internally or externally on a device and how to access them. It describes two types of animations - frame animations using AnimationDrawable and tween animations using XML attributes like alpha, scale, translate, and rotate. AsyncTask is explained as a way to run background tasks and update UI asynchronously. Canvas and Paint are discussed as components for drawing, with Paint representing the drawing brush and its various properties. The document concludes with an overview of the process for submitting and evaluating student projects.