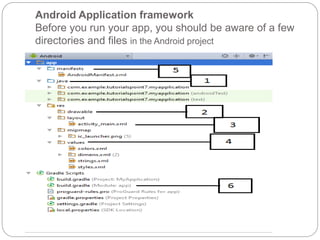
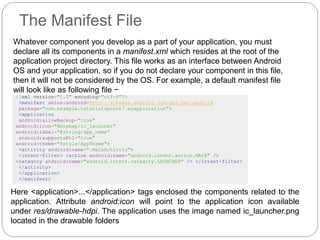
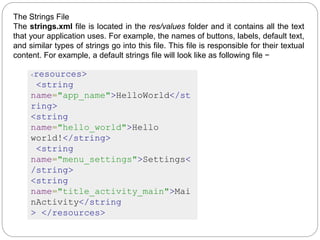
The document discusses the key files and folders in an Android project. It includes the Java folder containing Java source files, res folders for images, layouts and strings, the AndroidManifest file declaring app components, and the Build.gradle file containing project configuration. It then focuses on the MainActivity Java file, the AndroidManifest XML file and its structure, and the strings.xml file for storing text.