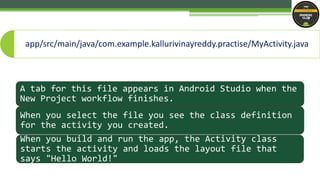
This document provides an introduction to the basic files and structure of an Android project created with Android Studio. It explains the purpose and location of key files like the activity layout (activity_main.xml), activity class (MyActivity.java), manifest (AndroidManifest.xml), Gradle build files, and resource directories for drawables, layouts, menus and strings. The document is serving as a lesson plan to familiarize new Android developers with the basic project organization.