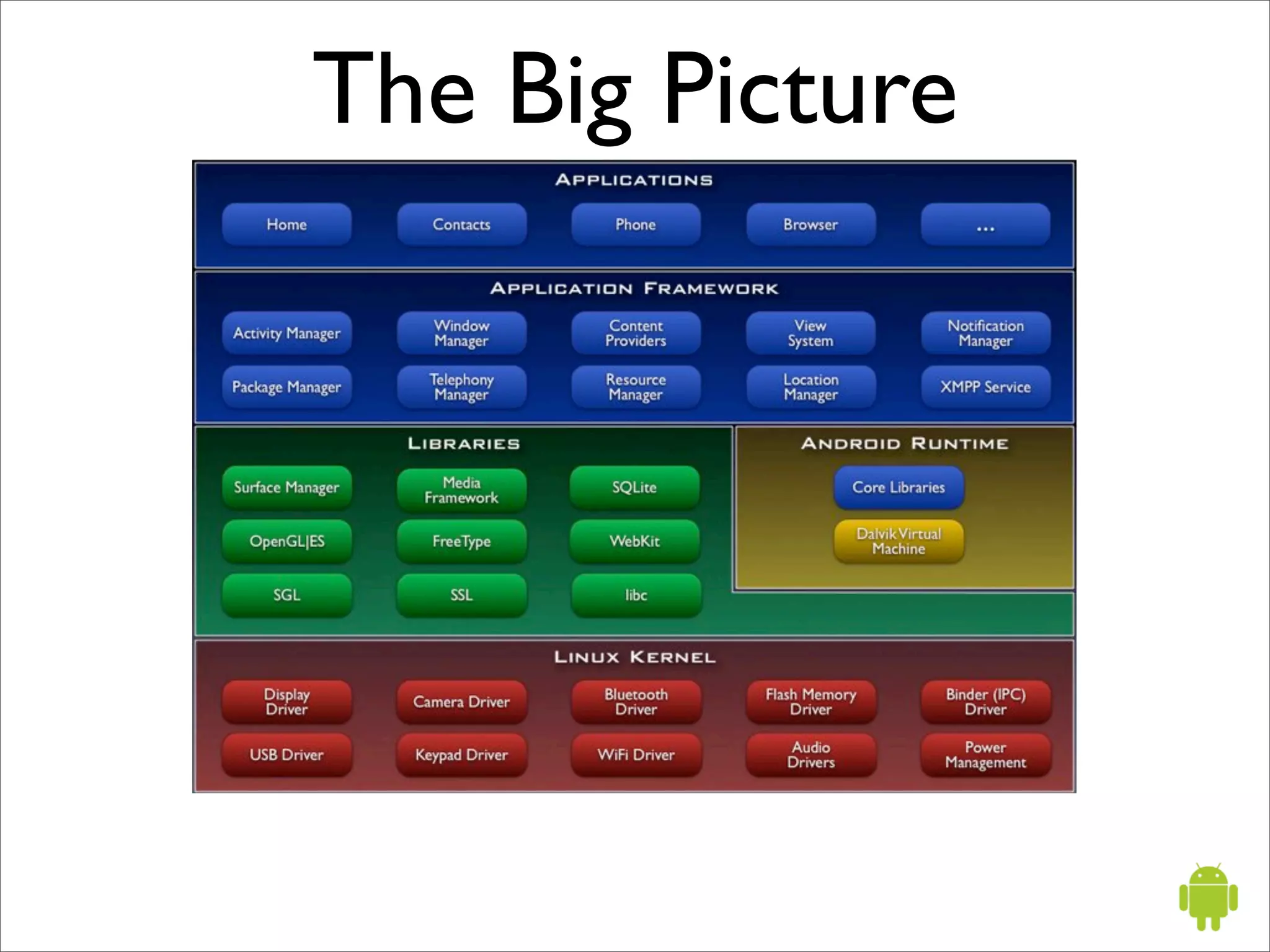
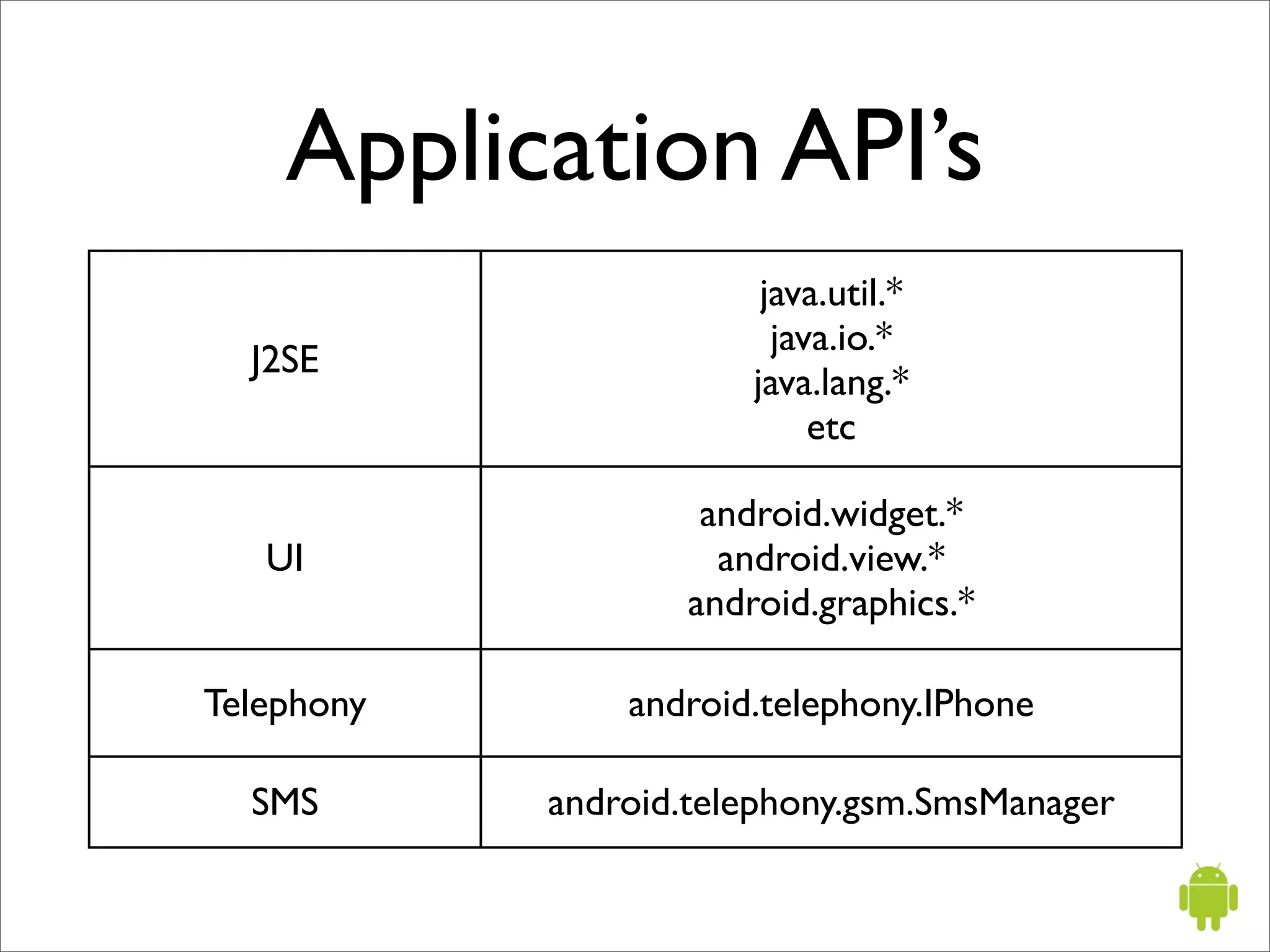
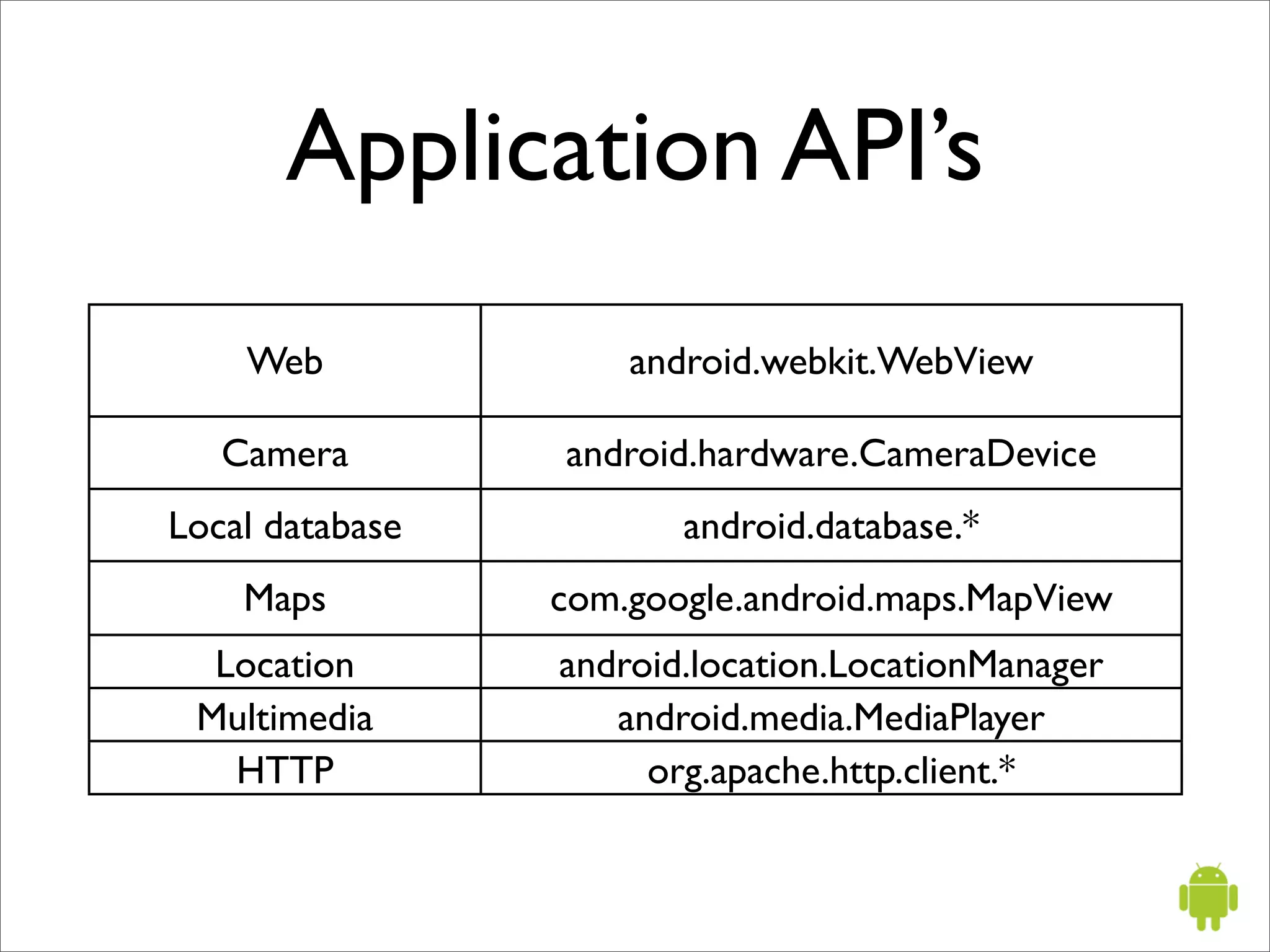
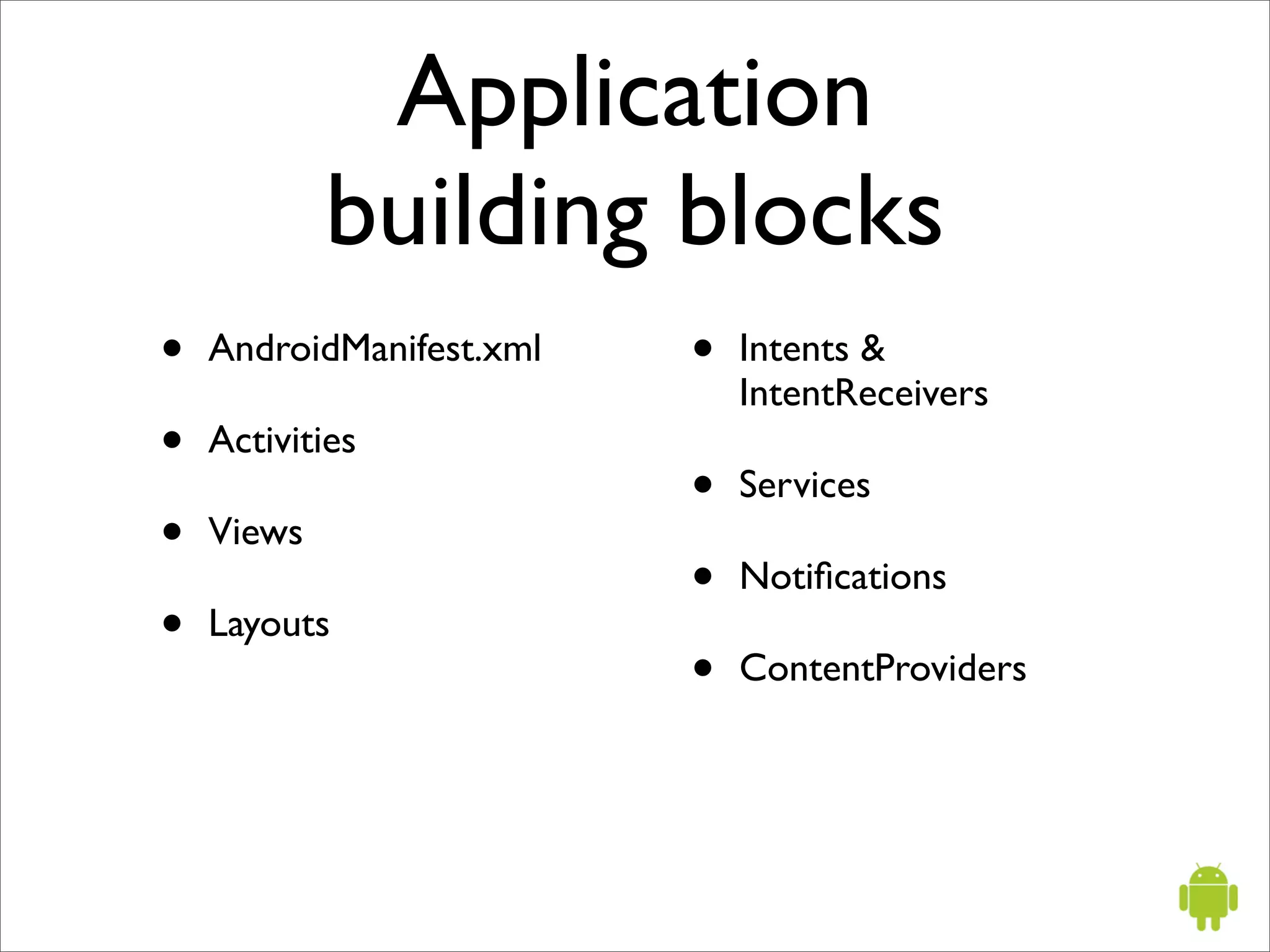
The document provides an overview of Google Android, including that it is an open source software stack for mobile devices consisting of an operating system, middleware, and key applications. It describes Android application development using the Java programming language, the Dalvik virtual machine, and Android SDK tools like Eclipse. It also summarizes some important Android application programming interfaces and concepts like activities, intents, and the Android manifest file.