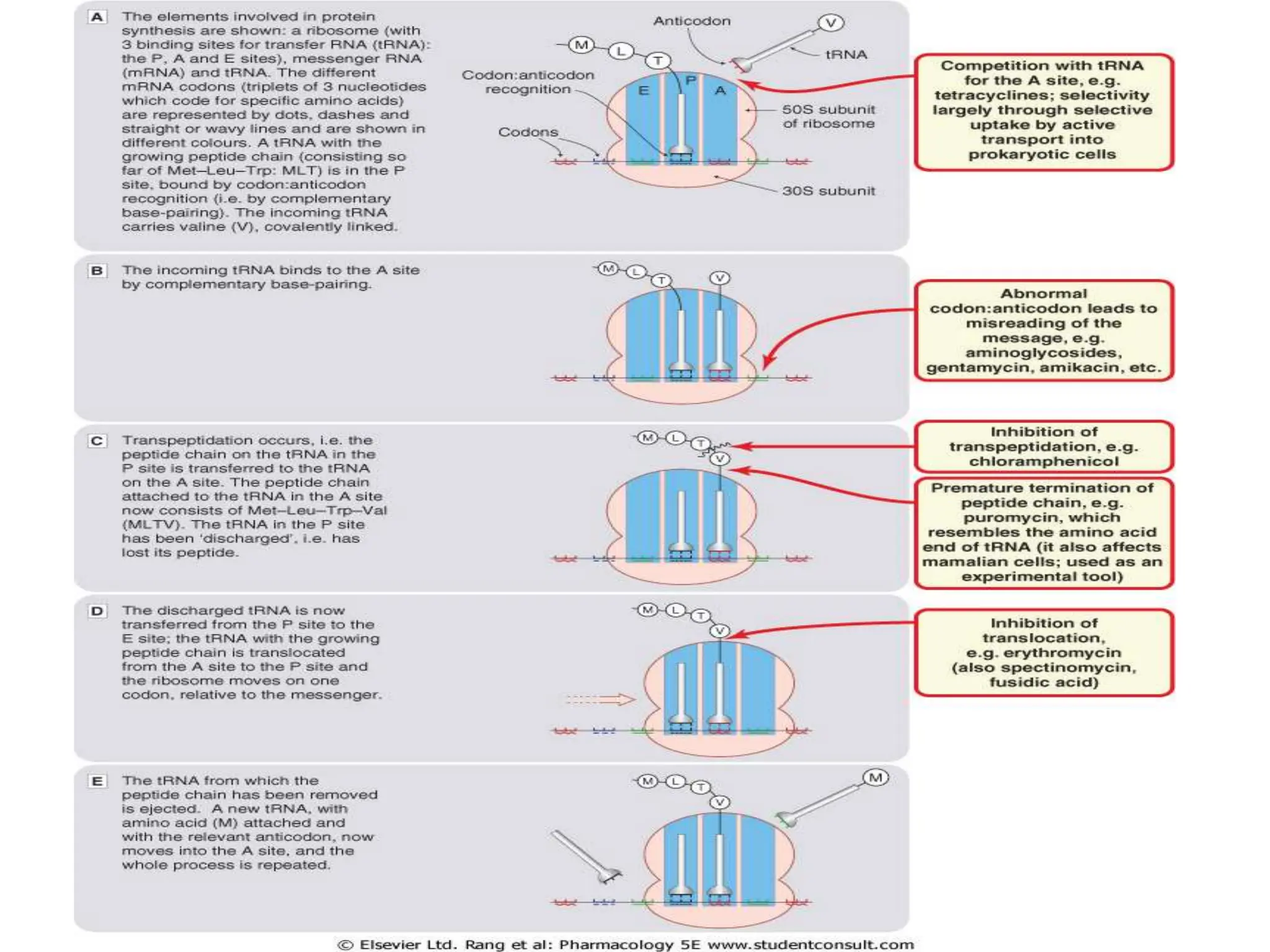
This document discusses aminoglycoside antibiotics, including their mechanism of action, spectrum of activity, pharmacokinetics, therapeutic uses, and adverse effects. Aminoglycosides inhibit bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit and are effective against many gram-negative and some gram-positive bacteria. They have concentration-dependent bactericidal activity but can cause ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity. Common aminoglycosides include gentamicin, tobramycin, and amikacin, which are used to treat serious infections like sepsis, pneumonia, and endocarditis.