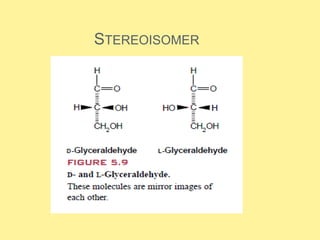
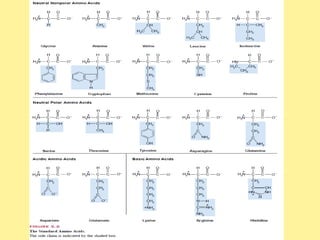
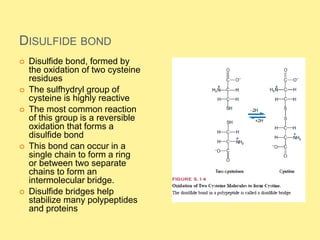
There are 20 standard amino acids that are the building blocks of proteins. They contain a central carbon atom bonded to an amino group, carboxyl group, hydrogen, and side chain. Proline differs in that its amino group forms a ring with its side chain. The amino acids can form peptides through condensation reactions between amino and carboxyl groups. Cysteine residues can form disulfide bridges through oxidation reactions. In addition to forming proteins, some amino acids act as neurotransmitters, hormones, or are precursors to other important biological molecules.