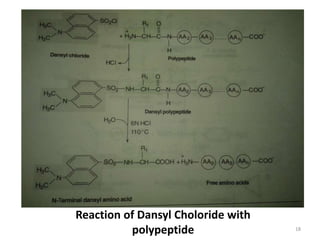
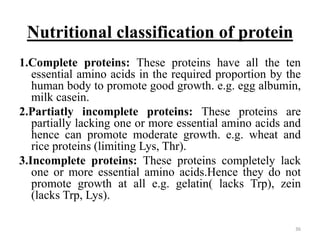
This document provides information about proteins. It begins with an introduction stating that proteins are abundant organic molecules that are found in all parts of cells and make up about 50% of cellular dry weight. It then discusses the origin of the word "protein" and the elemental composition of proteins. The document outlines the bonds responsible for protein structure, including peptide bonds, disulfide bonds, and non-covalent bonds. It describes the four levels of protein structure - primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. Key properties of proteins and methods of determining protein structure are summarized. The document concludes by discussing clinical aspects of proteins, including prion diseases and Alzheimer's disease.