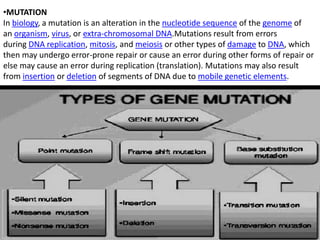
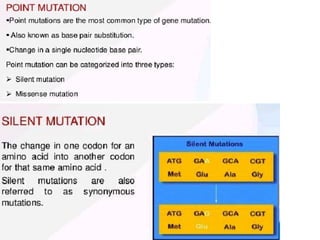
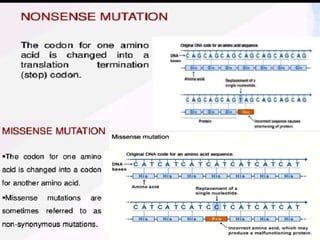
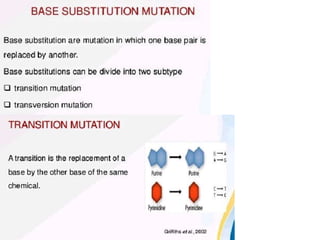
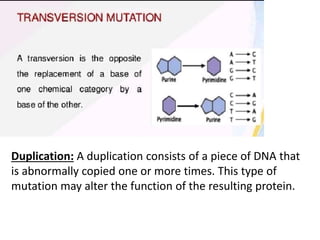
Mutations can occur through various mechanisms that alter the DNA sequence, including substitutions, insertions, deletions, duplications, frameshifts, and loss of heterozygosity. These mutations can change amino acid sequences and cause proteins to malfunction or not function at all. Specific types of mutations include substitutions, in which a single nucleotide is exchanged; deletions, in which a DNA segment is removed; duplications, where a DNA segment is copied multiple times; and translocations, where a DNA segment is moved to a new location. These genetic alterations can contribute to diseases if they impact important genes.