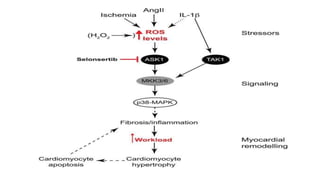
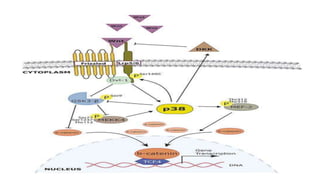
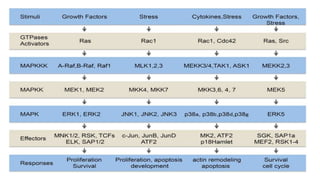
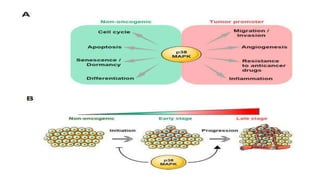
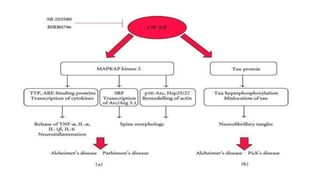
The document summarizes the MAPK-P38 pathway, also known as the death pathway. It discusses that p38 was discovered in cells treated with inflammatory cytokines and as the target of an anti-inflammatory drug. It describes the four p38 subfamily members identified through cloning strategies and notes they all contain the TGY sequence in their activation loops. The document also outlines that p38 isoforms are differentially sensitive to inhibitors and can be activated by various stresses and stimuli. It discusses a splice variant of p38 called Mxi that has unique properties compared to p38a in terms of activation and insensitivity to inhibitors. In closing, it mentions the kinases MEK3 and MEK6 that activate p38 family members