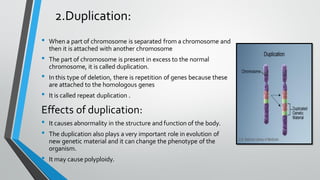
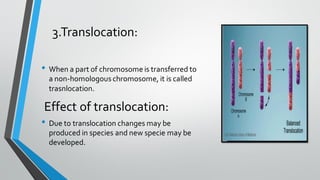
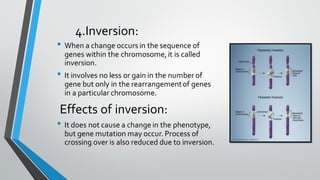
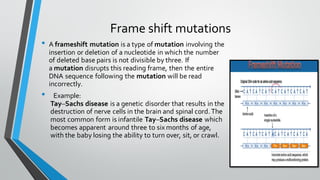
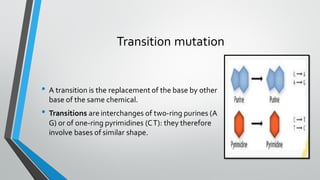
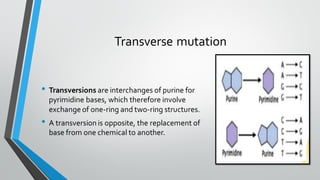
Chromosomal and gene mutations can cause human diseases and defects. Chromosomal mutations include structural changes like deletions, duplications, translocations, and inversions as well as changes in chromosome number like aneuploidy and euploidy. Down syndrome results from trisomy 21 while Turner syndrome is caused by monosomy X. Klinefelter syndrome involves an extra X chromosome. Gene mutations include point mutations, frameshift mutations, and base substitutions. Point mutations can be silent, missense, or nonsense. Frameshift mutations alter the reading frame. Sickle cell anemia is caused by a single base change altering hemoglobin.