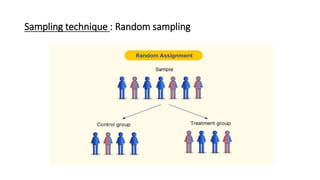
This study aims to evaluate the effect of reduced sodium intake on hypertensive patients through a randomized controlled study. Hypertensive patients will be randomly assigned to an intervention group that receives dietary counseling to reduce sodium intake to less than 2g per day or a control group. The blood pressure of both groups will be monitored and compared over 3 months. The primary objective is to assess the impact of reduced sodium intake on blood pressure. Secondary objectives include evaluating how patients replace salt and any benefits or adverse effects. Results will compare the blood pressure effects of reduced versus normal sodium intake. The study concludes reduced sodium intake can help control blood pressure and raises awareness of limiting salt consumption.


![INTRODUCTION
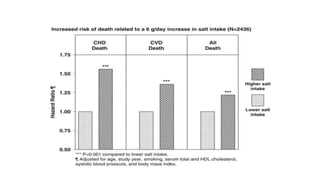
• The close relationship between hypertension and dietary sodium
intake is widely recognized and supported by several studies. [1]
• A reduction in dietary sodium not only decreases the blood
pressure and the incidence of hypertension, but is also associated
with a reduction in morbidity and mortality from cardiovascular
diseases. [1]
• Excessive sodium consumption (defined by the World Health
Organization as >5 g sodium per day) has been shown to produce
a significant increase in BP and has been linked with onset of
hypertension and its cardiovascular complications. [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectfinal-240229035024-b1770757/85/project-final-pptx-ffdfdgfhghjfghghghghghgh-3-320.jpg)
![• Most guidelines suggest a low salt intake, defined as <2-2.3 g
of sodium (equivalent to <5-5.75 g of sodium chloride) per day
to reduce high blood pressure and to improve cardiovascular
outcomes [3,4].
• Globally, the usual sodium intake is between 3.5–5.5 g per day
(equivalent to 9 - 12 g of daily salt). [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectfinal-240229035024-b1770757/85/project-final-pptx-ffdfdgfhghjfghghghghghgh-4-320.jpg)
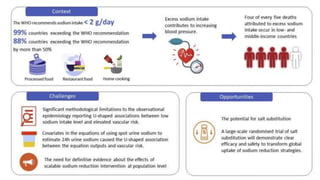
![Current recommendations
• The 2020 International Society of Hypertension Global
Hypertension Practice Guidelines recommend reducing the
quantity of salt added when cooking and at the table, and to
avoid or limit the consumption of high salt containing foods,
such as fast foods, soy sauce and processed food (including
breads and cereals). They also recommend population-based
efforts to reduce salt intake and encourage consumption of
fresh vegetables and fruits [6].
• The 2018 European Society of Cardiology Hypertension
Guidelines [3] and the WHO 2020 statement [4] recommend
that sodium intake should be limited to <2 g per day (equivalent
to <5 g salt per day) in the general population as well as in](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectfinal-240229035024-b1770757/85/project-final-pptx-ffdfdgfhghjfghghghghghgh-7-320.jpg)
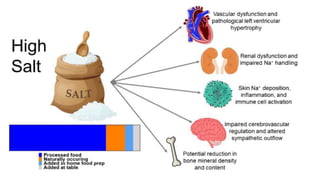
![NEED FOR THE STUDY
• Hypertension is a major public health problem due to its high
prevalence all around the globe [1–4]. Around 7.5 million deaths
or 12.8% of the total of all annual deaths worldwide occur due to
high blood pressure [5]. It is predicted to be increased to 1.56
billion adults with hypertension in 2025.
• Hypertensive patients are unaware of the Non pharmacological
approaches to manage Hypertension so the study helps in
providing evidence for the reduction in blood pressure by reduced
intake of sodium to <2g/day.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectfinal-240229035024-b1770757/85/project-final-pptx-ffdfdgfhghjfghghghghghgh-8-320.jpg)