The document defines and provides examples of different types of tensors including:
1) Contravariant vectors which transform according to the Jacobian of the coordinate transformation.
2) Covariant vectors which transform according to the inverse Jacobian.
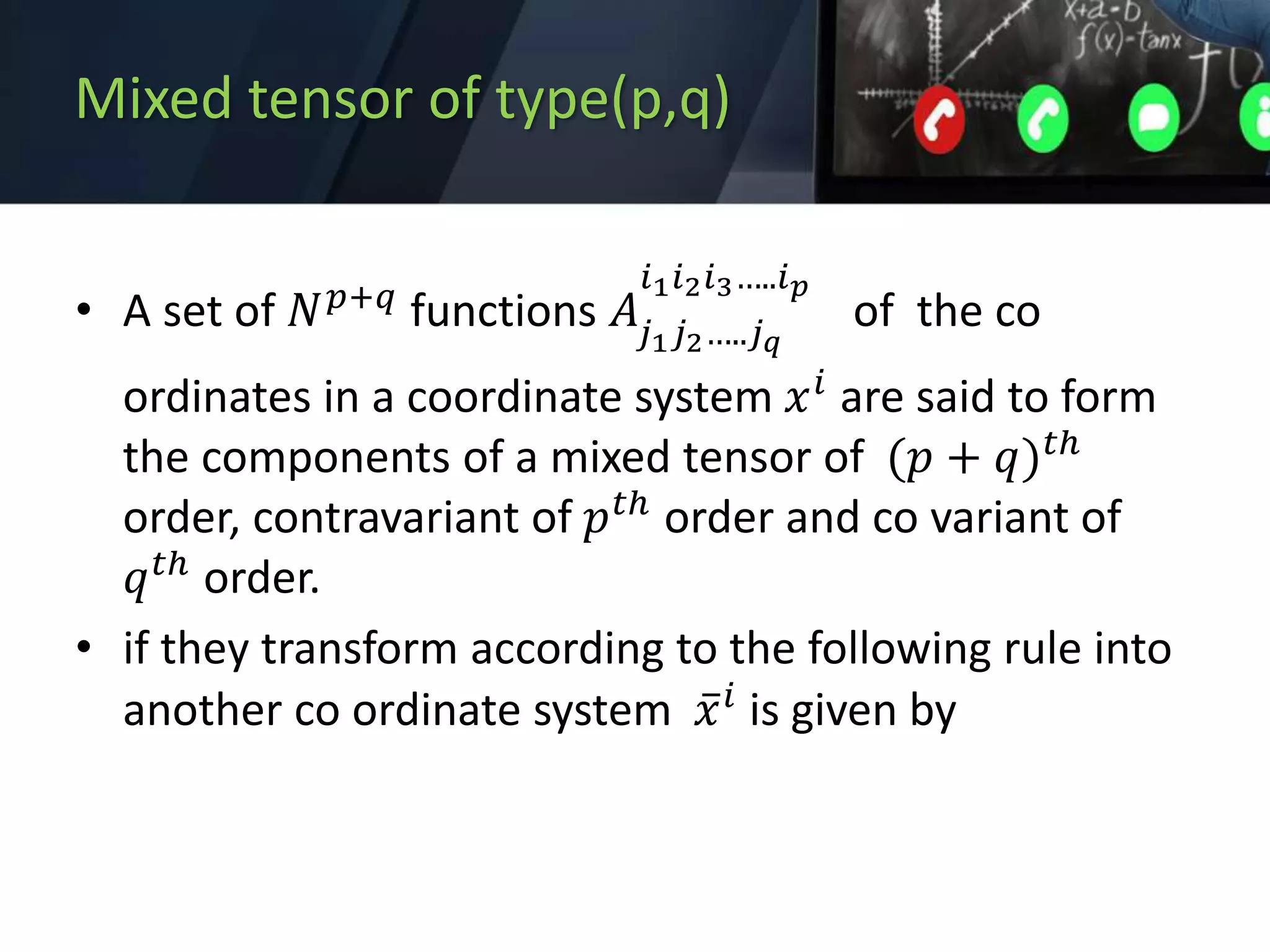
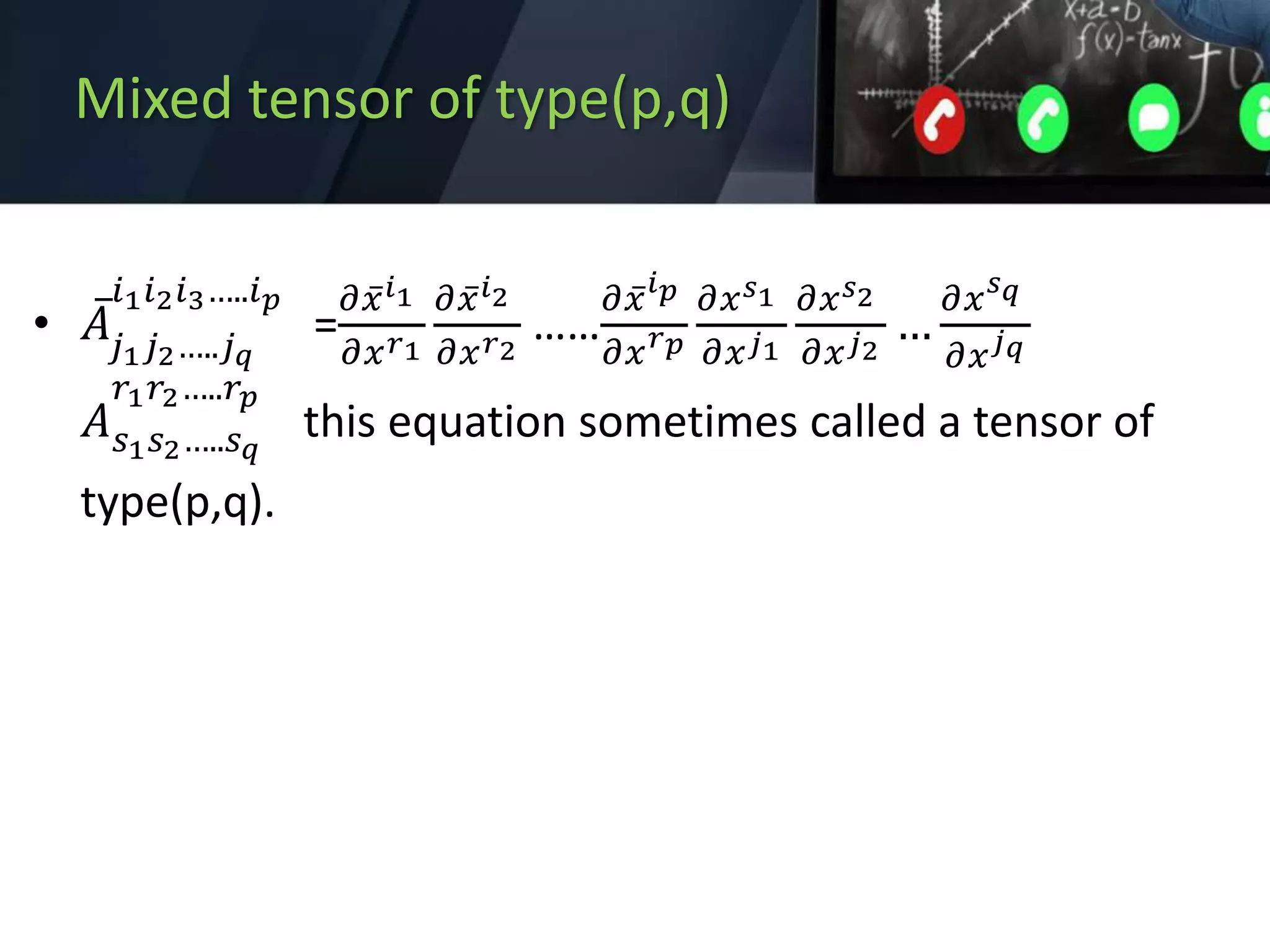
3) Mixed tensors which transform according to the Jacobian and inverse Jacobian.
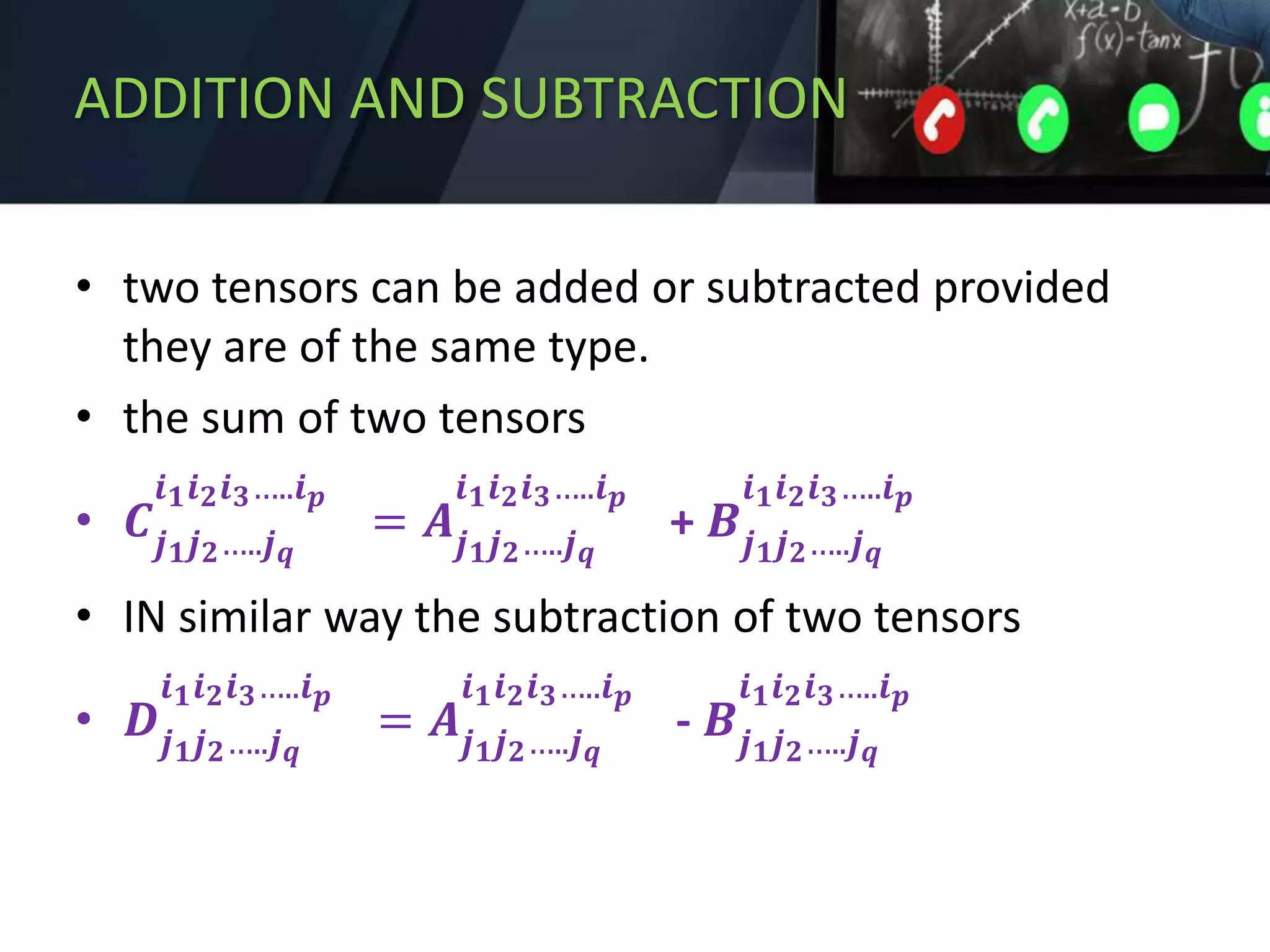
4) Operations on tensors such as addition, subtraction, outer products, and contraction where one index is set equal to another.
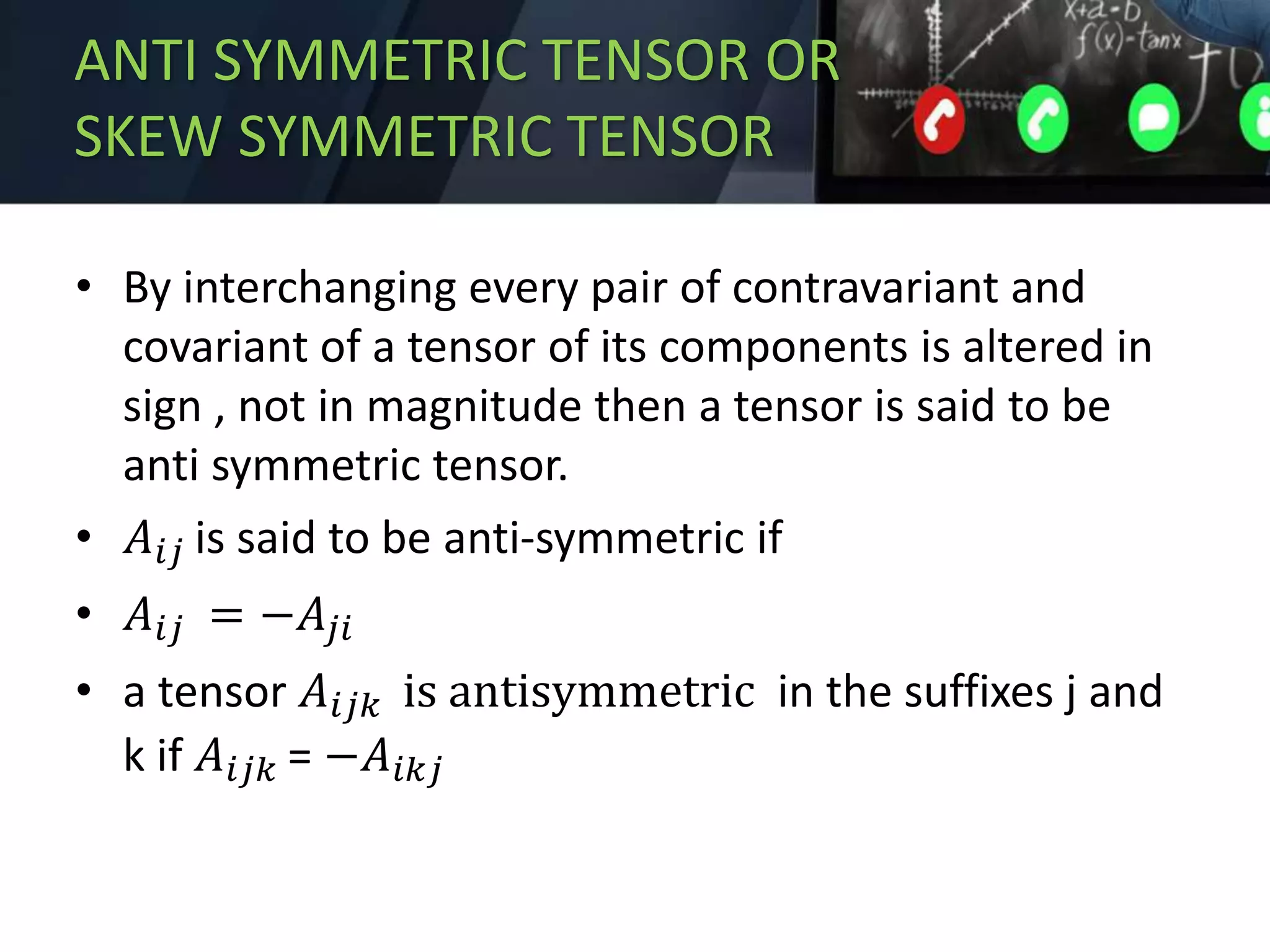
5) Symmetric tensors where interchange of indices does not change the tensor and antisymmetric tensors where interchange changes the sign but not magnitude.