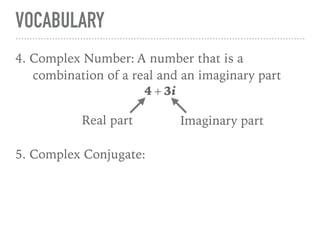
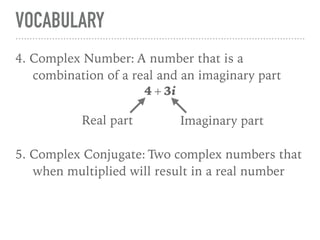
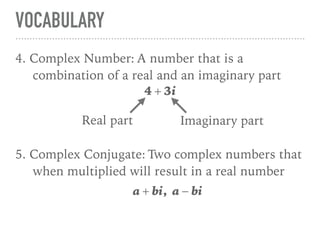
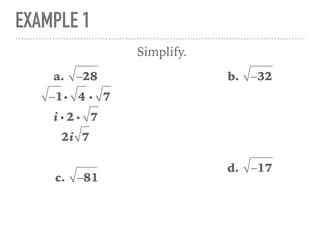
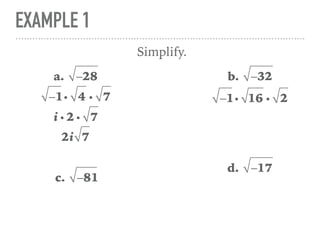
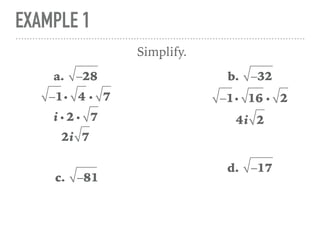
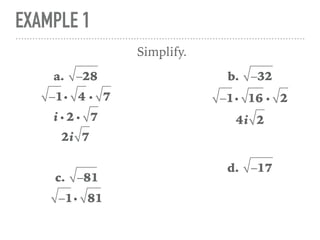
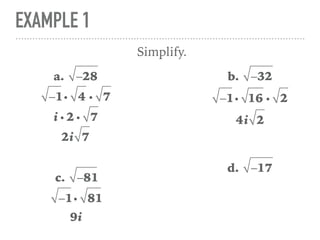
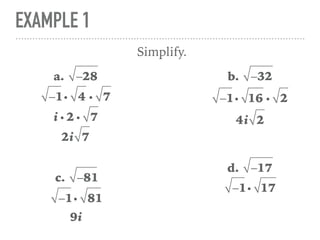
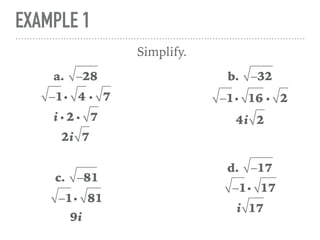
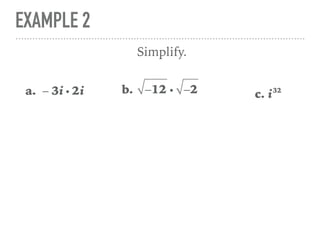
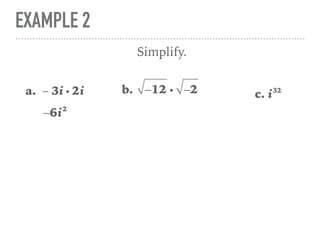
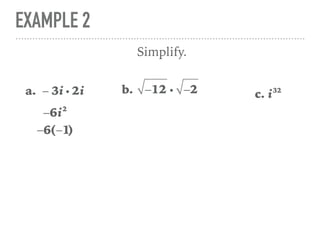
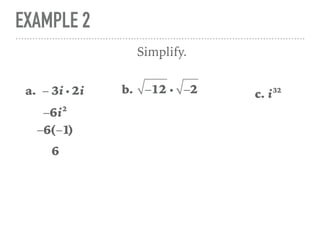
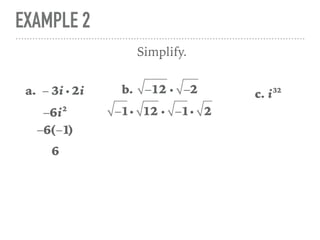
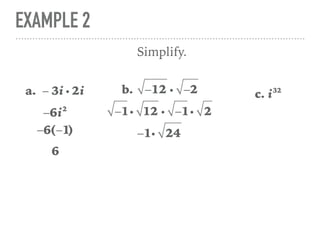
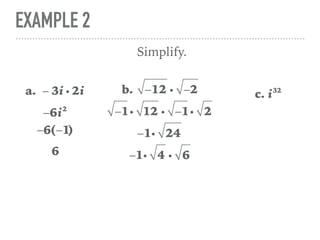
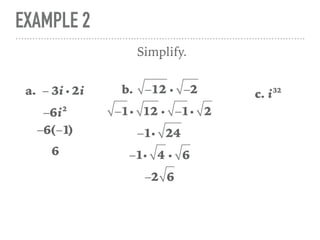
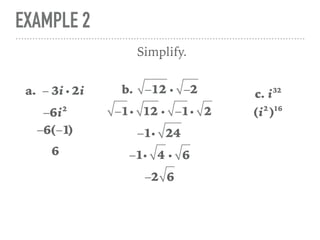
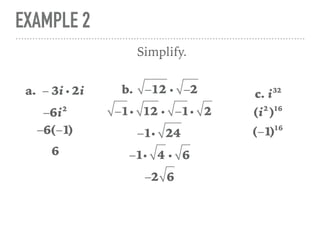
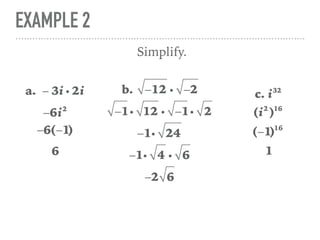
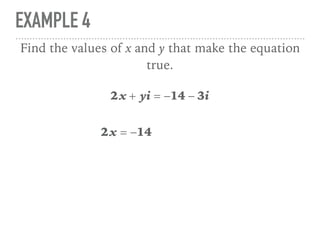
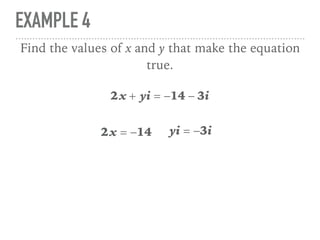
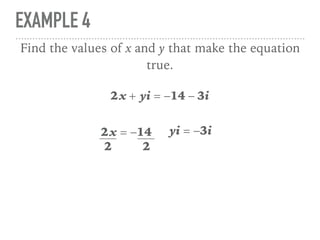
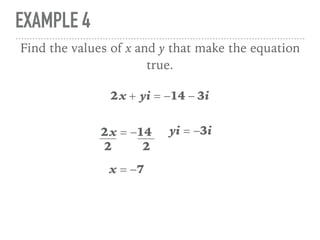
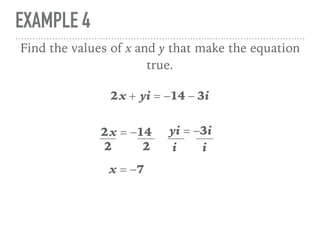
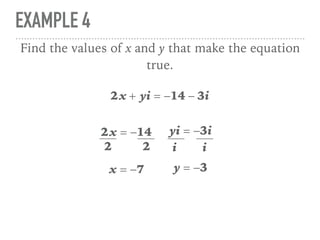
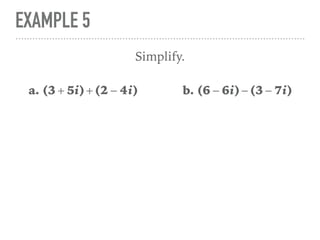
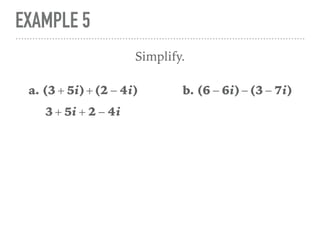
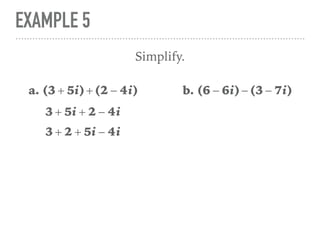
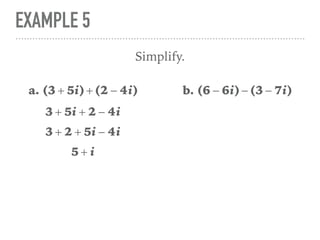
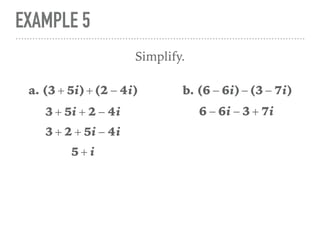
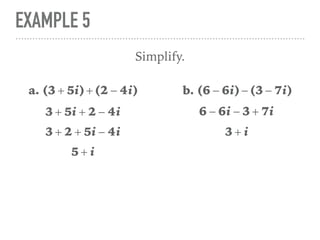
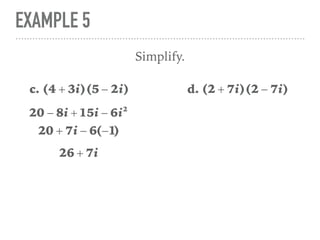
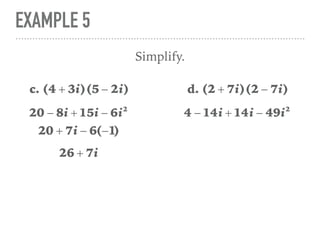
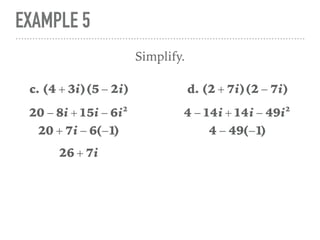
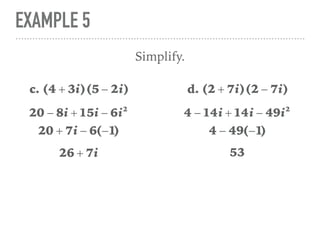
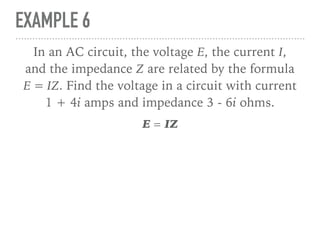
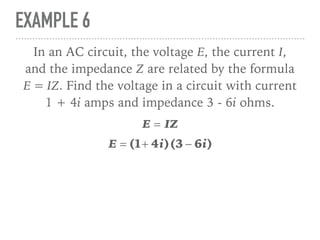
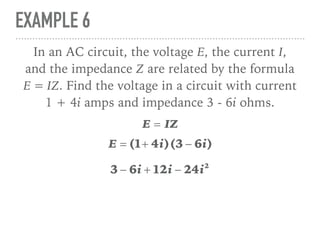
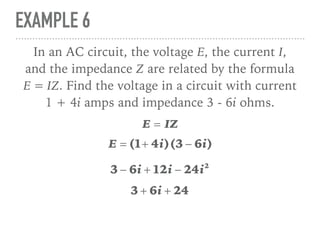
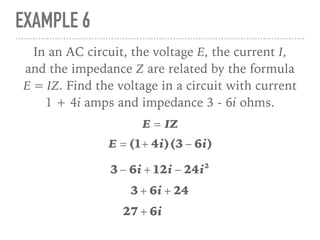
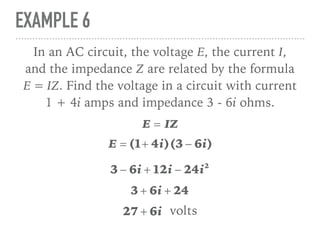
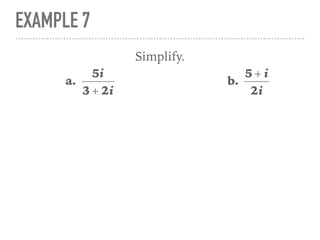
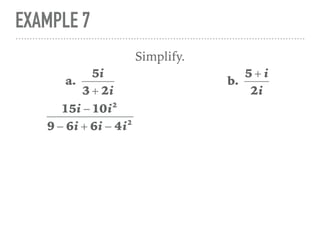
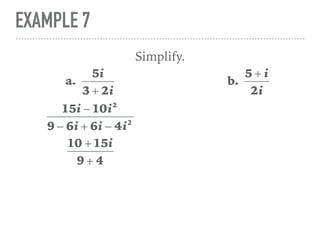
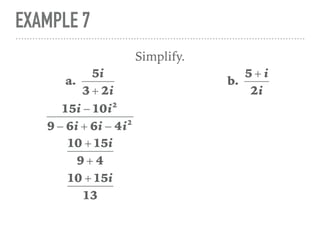
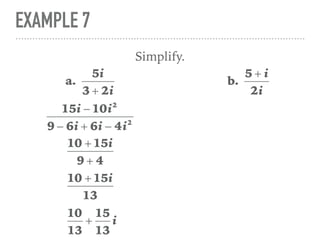
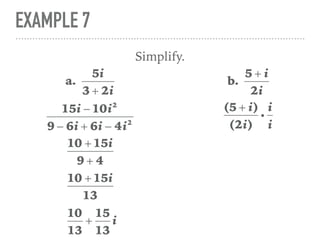
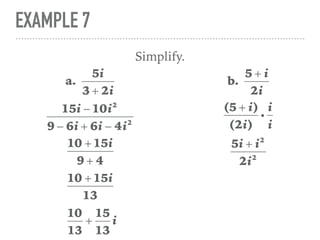
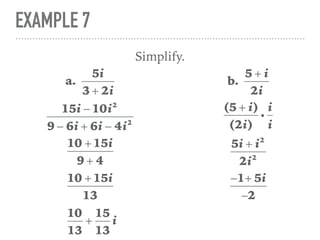
The document defines and provides examples of complex numbers and operations involving imaginary and complex numbers. It begins by defining imaginary and pure imaginary numbers. It then defines complex numbers as combinations of real and imaginary parts and introduces the concept of complex conjugates. The remainder of the document provides examples of simplifying expressions and solving equations involving complex numbers.