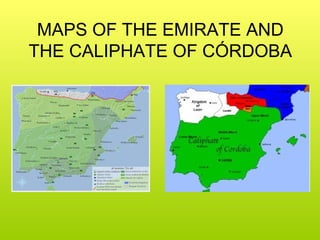
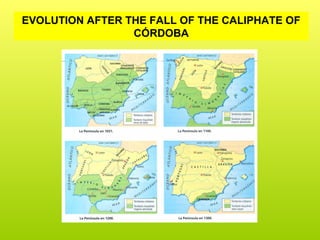
The political situation in the Iberian Peninsula in the early 8th century was unstable, with a civil war occurring between King Rodrigo and the family of the previous king, Witiza. When the Witiza family hired Muslim mercenaries from North Africa to fight for them, the Muslim army led by Musa and Tariq defeated Rodrigo's forces and went on to conquer most of the peninsula over the next few years due to the weakness of the Visigothic nobles. Al-Andalus began as an emirate dependent on the Umayyad Caliphate in Damascus, but it became independent under Emir Abd al-Rahman in 756 and later a caliphate under