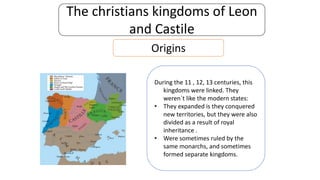
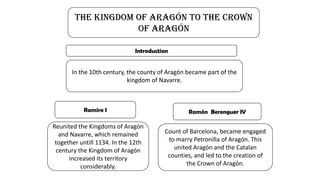
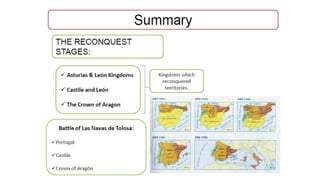
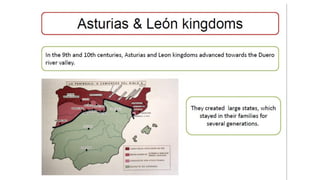
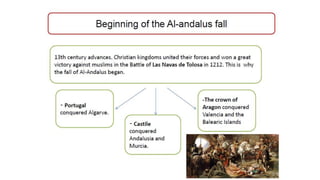
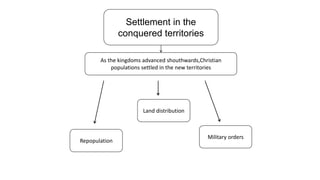
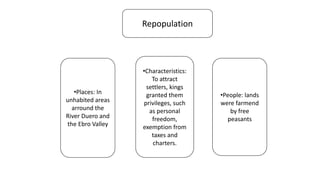
The early history of Al-Andalus
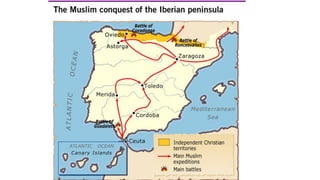
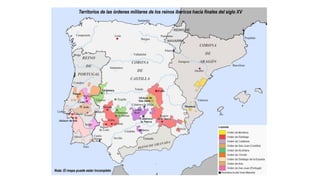
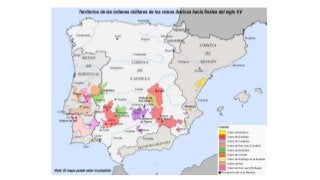
By the 8th century, Muslims had expanded beyond Arabia and controlled North Africa. In 711, they crossed into the Iberian Peninsula, defeating the Visigoth King Roderic. They occupied most of the peninsula but not the mountainous regions. The Muslims called their new territory Al-Andalus, with its capital at Córdoba, dependent on the Umayyad caliphate. Over time Al-Andalus fragmented into taifa states and the Christian kingdoms grew in strength, gradually reconquering Muslim lands.