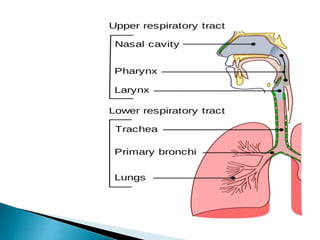
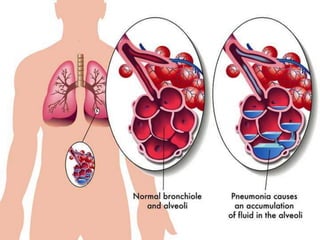
The document discusses airborne diseases affecting the respiratory system, focusing on upper respiratory tract infections, pneumonia, and tuberculosis. It outlines the causes, symptoms, diagnostic tests, treatments, and preventive measures for these infections, emphasizing the importance of proper hygiene and vaccination. Upper respiratory infections are primarily viral, while pneumonia can be caused by bacteria or viruses, and treatment often includes symptomatic care and antibiotics depending on the causative agent.