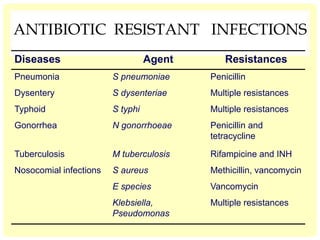
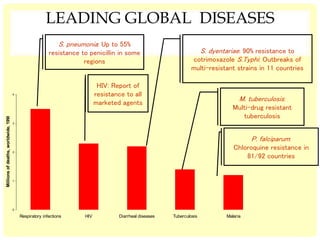
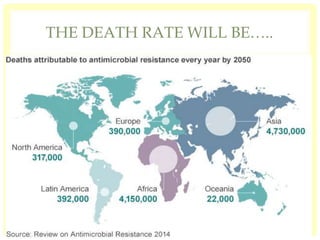
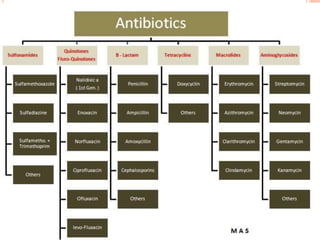
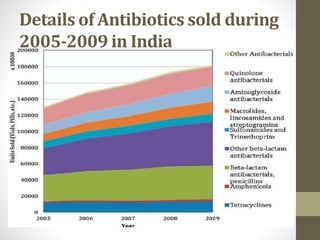
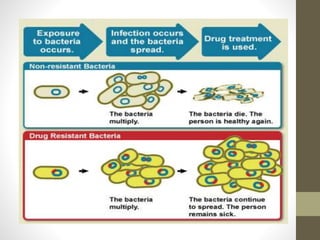
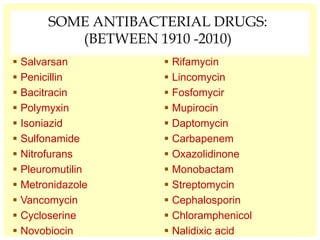
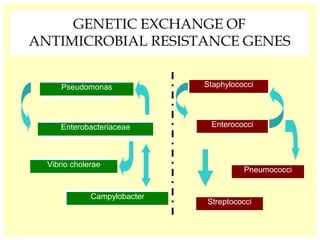
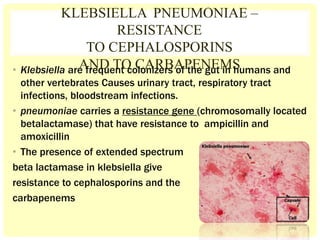
This document discusses the emerging issue of antimicrobial resistance in microorganisms. It provides an overview of antibiotics and multi-drug resistance. Common multi-drug resistant organisms include MRSA, ESBL-producing bacteria, and carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. The mechanisms of antibiotic resistance include reduced permeability, enzymatic inactivation, efflux pumps, and target modification. Inappropriate antibiotic usage accelerates the development of resistance. If not addressed, antimicrobial resistance could lead to untreatable infections and increased mortality.















![DRUG RESISTANCE
IN MALARIA:
• Malaria is caused by the protozoan parasite
Plasmodium which is transmitted via the bite of
female Anopheles mosquitoes.
• Among the five species of Plasmodium parasites [P.
falciparum, P. vivax, P. ovale,P. malariae and P.
knowlesi] that infect humans are P. falciparum and P.
vivax
• Malaria has slow resistant to chloroquine,
mefloquine or piperaquine
• P. falciparum to amodiaquine and sulfadoxine-
pyrimethamine](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drugresistanceppt-170913145410/85/Multidrug-resistance-in-Microbes-22-320.jpg)